-
离轴三反消像散(Three-Mirror Anastigmatism, TMA)光学系统具有大视场、分辨率高、无中心遮拦、无色差等优点,在遥感相机、激光通讯和环境监测等方面得到了广泛应用[1-5]。随着小像元CCD芯片技术和计算机技术的发展,大大提高了图像的分辨率,使离轴TMA光学系统在亚微米级细胞成像方面的应用成为可能。文中研制的生物成像检测仪创新性地将离轴TMA光学系统应用在循环肿瘤细胞(Circulating Tumor Cell, CTC)检测方面。基本原理是对平铺在载玻片上的7.5 mL染色全血单细胞样品,通过TMA光学系统和计算机图像处理系统实现了超大视场(150 mm×200 mm)荧光细胞清晰成像,在上亿背景细胞中快速(10 min以内)检测出CTC细胞并记录细胞数量,检测准确率和效率高于国内外现有检测设备[6]。
离轴TMA光学系统有主镜、次镜和三镜等多个光学元件,一般来说,光学系统中镜面的数量越多,装调难度越大,至少需要调整三个反射镜的位置量与角度量,工作量大,加工装调成本高。在生物成像TMA光学系统中,由于主镜和三镜的轴向位置非常接近,设计时将主镜和三镜进行一体化设计(以下简称主三镜或反射镜),形状为矩形轮廓,使一面镜子既具有主镜的功能,又具有三镜的功能,光学系统由原来的三镜变成二镜系统,减少了六个自由度的调整量,降低了装调难度和生产制造成本[7-8]。由于大口径矩形主三镜是生物成像系统的核心光学元件,它的面形精度对成像质量起着重要作用。决定反射镜面形精度的主要因素有材料、结构形式、制造质量、支撑方式及所受载荷等,其中支撑结构是影响反射镜最重要的因素,合理的支撑结构能够有效调整由于环境变化对反射镜面形造成的影响。因此,主三镜支撑结构设计是生物成像检测仪研制过程中的重要技术难点之一。
目前,国内外学者对大口径矩形反射镜的支撑结构设计进行了大量研究。朱俊青等提出集成参数优化设计方法,确定了长条形反射镜三点支撑结构[9];李海星等利用背部3点柔性支撑设计了矩形反射镜支撑组件[10]。刘福贺等采用背部九点的支撑方式设计了长条形反射镜的支撑结构[11];包奇红等对长条形反射镜中心支撑与多点支撑进行了对比研究[12]。王朋朋等采用中心支撑方法进行了长条形反射镜结构优化设计[13]。上述矩形反射镜支撑技术的研究受航空遥感器总体质量限制,多采用反射镜中心支撑或背部三点支撑。但是这两种支撑需在反射镜背面钻盲孔,镜面易变形,对于亚微米级细胞成像系统来说,反射镜镜面的微小形变将造成成像质量的急剧下降,因此需要设计一种新型支撑结构来满足生物成像系统的技术要求。
文中针对CTC细胞亚微米级成像、镜面面形精度高且持久稳定等技术指标要求,设计了大口径矩形主三反射镜支撑结构组件。首先设计了背部三点和侧面六点支撑的镜室结构,设计了当环境温度变化时具有良好调节能力的柔性铰链。然后对主三镜支撑组件进行循环迭代优化设计和有限元仿真分析,最后对支撑结构作用下的主三一体镜进行面形检测和系统波长差检测,检测结果基本满足了生物成像检测仪技术指标要求。
-
生物成像离轴三反光学系统主要由主三反射镜(非球面)、次镜(非球面)和折转镜及CCD等部分组成,如图1所示。为了使微弱荧光细胞成清晰像,光学系统采用物像等距共轭,光谱范围为350~1100 nm,光学系统焦距大于630 mm,采用反射式光学系统,成像视场为150 mm×20 mm,像元尺寸为2.8 μm×2.8 μm。对于2.8 μm探测器,Nyquist频率为178 lp/mm,在Nyquist频率处全波段传函平均为0.343,设计结果如图2所示,完全满足应用需求。
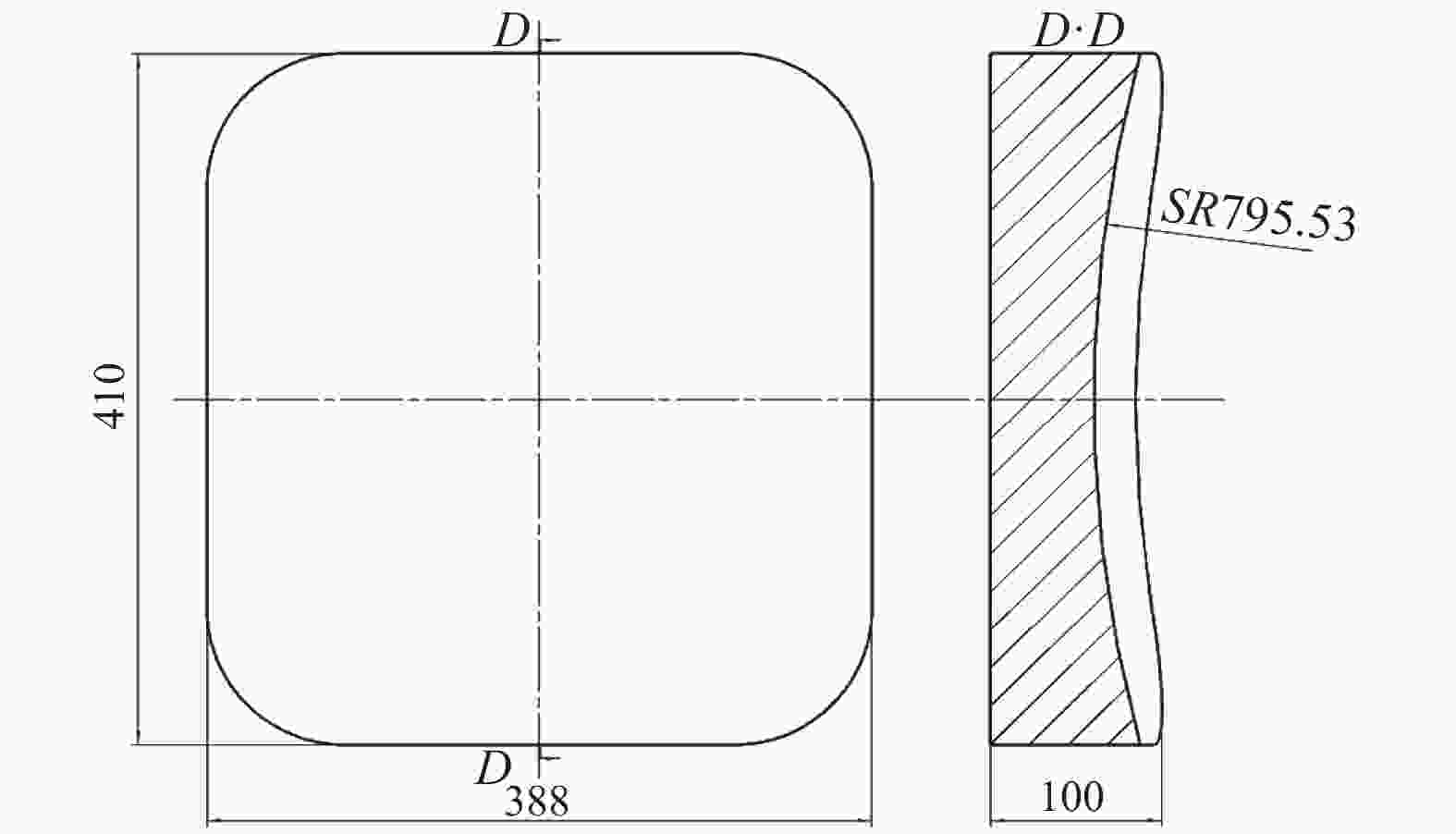
系统指标分配为:主三镜支撑组件总质量小于50 kg,重力工况下和4 ℃均匀温升载荷工况下,反射镜面形误差(RMS)≤λ/40(有效口径内),PV≤λ/10(有效口径内),主三镜和次镜系统波像差(RMS)≤λ/10,工作温度为20~24 ℃。主三镜尺寸为410 mm×388 mm,背部采用平背式,结构尺寸如图3所示,反射面为双曲面形式的非球面,其表达式为:
$$\left\{ \begin{gathered} s(r) = \dfrac{{C{r^2}}}{{1 + \sqrt {1 - (1 + k){C^2}{r^2}} }} \\ C = {1 / R} \\ {r^2} = {x^2} + {y^2} \\ \end{gathered} \right.$$ (1) 式中:
$C$ 为表面曲率;$R$ 为基圆的曲率半径,$R = {\rm{ - }}795.53$ mm;$r$ 为极坐标;$k$ 为二次曲面系数,$k = $ $ - 1.0623$ 。 -
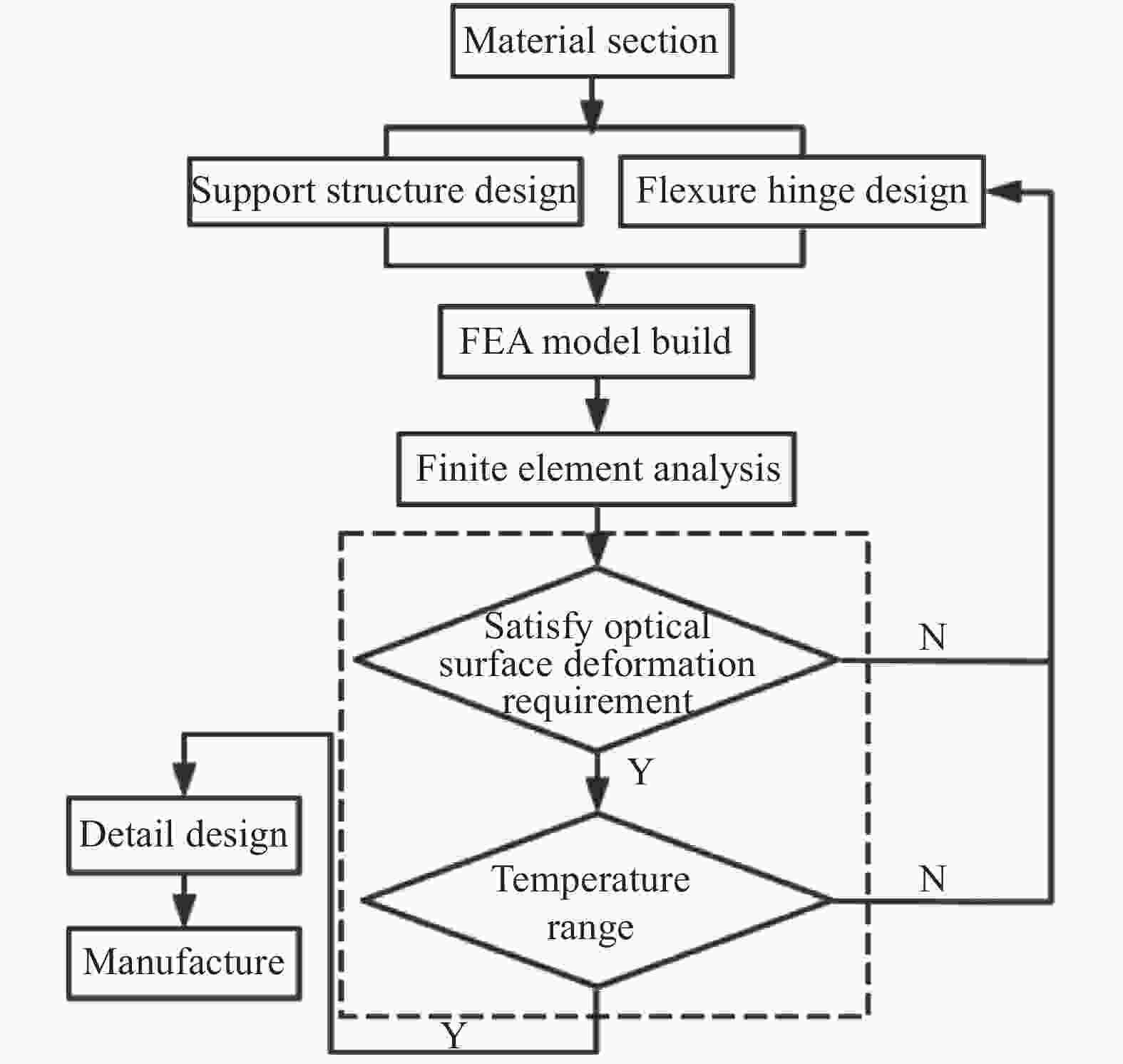
主三反射镜支撑结构设计是以镜面面形精度为主要设计目标的反复迭代优化设计过程,基本研制流程如图4所示。首先,根据光学设计技术要求,从材料物理特性及可加工性能、支撑结构的稳定性、温升适应性和经济性等方面选择反射镜及支撑组件材料。接着,采用机械动态设计的方法,利用三维设计软件建立实体几何模型;其次,根据所选材料赋予组成模型的各构件材料属性,分析设计要求精度、问题类型、考虑相应的边界条件建立有限元模型。然后,进行静态分析及热特性分析,根据静态特性及热特性的要求或预定的静态设计目标,进行综合评价。如果不满足设计要求则进行结构或材料的修改,再进行结构设计和有限元分析,直到系统结构满足设计指标要求为止。最后,确定符合静态特性及热特性的具体镜室结构和柔性支撑结构,并进行详细设计及加工制造装调。
-
反射镜材料选择需考虑以下几个方面:
(1)力学特性。主三反射镜需要加工、检测及装调时的搬运过程,因此反射镜应具有良好的稳定性和较高的面形精度。反射镜变形的经验公式为[14]:
$${\delta _{\max }} = \frac{{3\rho g{r^4}}}{{16E{t^2}}} = \frac{{3g{r^4}}}{{16(E/\rho ){t^4}}}$$ (2) 式中:
${\delta _{\max }}$ 为反射镜变形最大值;(${E / \rho }$ )为材料的比刚度;$\rho $ 为反射镜材料密度;$E$ 为弹性模量;$t$ 为反射镜厚度;$r$ 为反射镜半径;$g$ 为重力加速度。可以看出,镜面最大变形量与比刚度成反比,因此选择比刚度大的材料作为反射镜基体材料。(2)材料的可加工性及安全性。有毒的材料不仅对加工者身体健康有害,而且还将大大增加制造成本,因此反射镜材料应选择无毒并且加工性能优良的材料。
(3)热特性。反射镜处于温差大的环境时,内部将产生热应力,热应力扩散到镜面表面时,变形将使面形误差增大。
为了提高主三镜支撑结构的可靠性和对温度变化的适应性,选择支撑结构材料时需满足以下条件[11]:
(1)刚度和强度高,从而保证光机结构具有良好的尺寸稳定性。
(2)优良的热稳定性,在温度变化时,使支撑系统对反射镜面形的影响最小,一般选与反射镜膨胀系数接近的材料作为反射镜支撑材料。
在现有条件下,依据以上反射镜材料和支撑结构材料的选择原则,反射镜组件所选取的材料属性见表1。微晶玻璃加工工艺成熟,面形抛光时间相对较短,材料综合性能较好,在国内外反射镜中有着广泛的应用,因此主三镜选用微晶玻璃。由于铁镍合金的线膨胀系数可调节,能够制成与反射镜相匹配的线胀系数,因此柔性支撑和刚性支撑选用4J32材料。超硬铝结构刚度高、加工性好并且比较经济,因此主三镜镜室选用7A09超硬铝材料。
表 1 材料属性
Table 1. Performance parameters of materials
Material Modulous of clasticity, E/GPa Poission’s ratio, μ Density,ρ/g·cm−3 Coefficient of thermal expansion, α/℃ Zerodure 91 0.18 2.53 0.05×10−6 7A09 70 0.24 2.7 23.6×10−6 4J32 141 0.28 8.1 1.0×10−6 -
利用有限元软件Ansys参数化模块对支撑点位置进行合理化设置,优化目标为重力作用下镜面变形最小,主三镜镜室结构如图5所示。
优化的数学表达式及变量变化范围为:
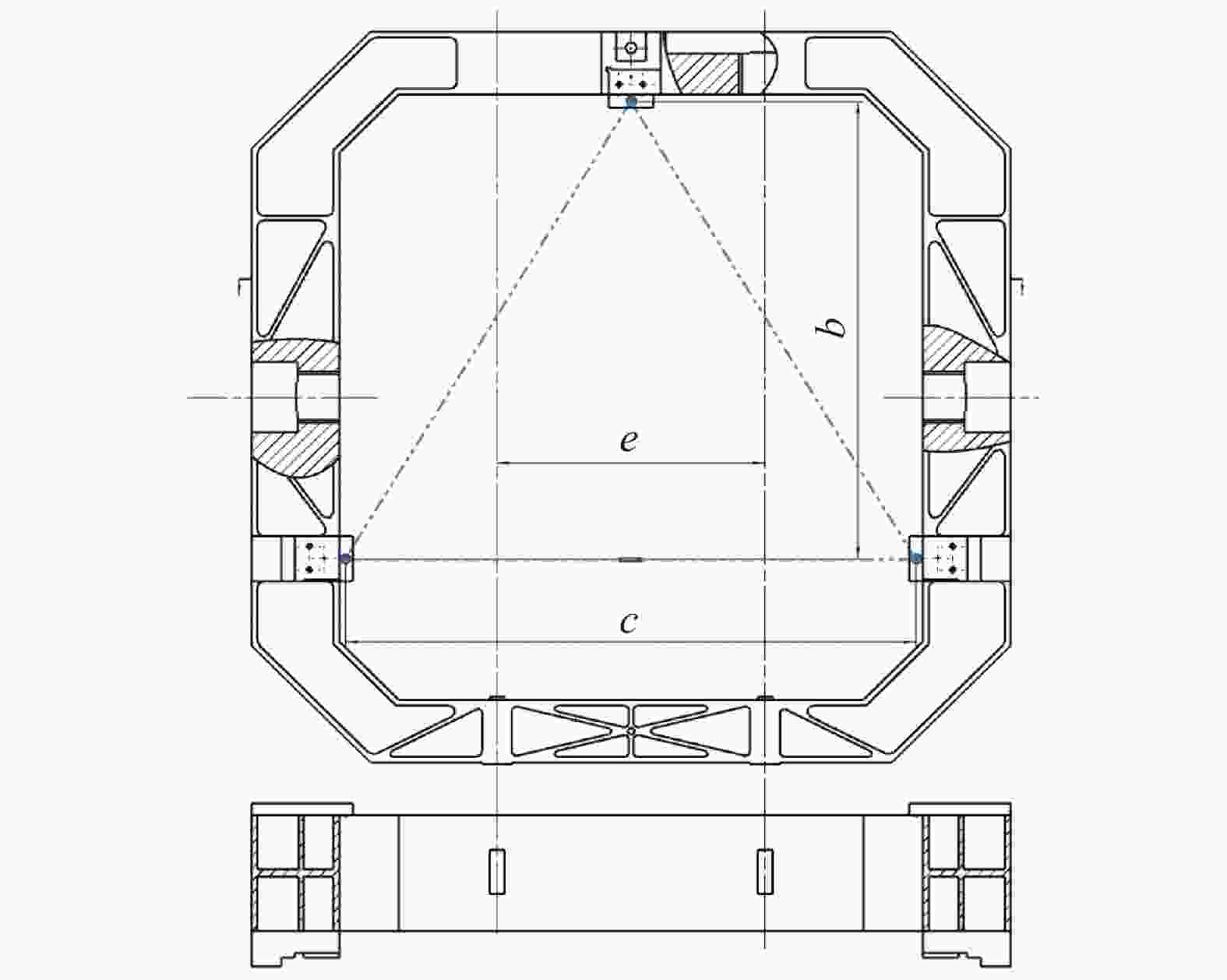
$$\left\{ \begin{gathered} {\rm Min}{{ C}}\left( {{x}} \right) = {X_{\rm RMS}} \\ { \rm Subject}\;{\rm { to : }} \\ {{ PV}} \leqslant \frac{\lambda }{{{\rm{10}}}} \\ {\rm{ 207}} \leqslant {{ b}} \leqslant 410 \\ {\rm{ 195}} \leqslant {{c}} \leqslant {\rm{3}}92 \\ {\rm{ }}0 \leqslant e \leqslant 264 \\ \end{gathered} \right.$$ (3) 在Ansys中建立优化模型,采用有限元优化方法进行迭代计算,其中当点的位置参数b=383 mm,c=313 mm,即图中三点支撑形成一个正三角支撑结构(图5中双点划线部分),光轴竖直时反射镜RMS有最小值为10.12 nm。当尺寸
$e = 188$ mm时,即光轴水平时,主三镜RMS有最小值为1.529 nm。三点支撑单元与镜室结构一体化设计,增强了三点支撑块的结构刚度。 -
为保证反射镜定位精度,支撑结构应满足静定机构支撑原理,实现六自由度定位,即满足[15]:
$$ F = 6(n - 1) - \sum\limits_{i = 1}^N ( 6 - {f_i}) = 0 $$ (4) 式中:
$F$ 为系统自由度总数;$n$ 为部件数;$N$ 为节点个数;${f_i}$ 为第$i$ 个节点的自由度。侧面支撑可以简化为平面机构,去掉虚约束,计算其自由度,F=6×(13−1)−72 = 0无过约束,也无欠约束。根据主三镜组件的设计目标和约束条件,综合考虑反射镜组件的功能需求、质量控制和空间尺寸限制,完成了主三镜镜室结构设计,如图5所示。主三镜镜室采用底部支撑和侧面支撑一体化设计,增加了支撑结构的整体刚度和稳定性,能够很好地抵抗外部变形对反射镜的作用,减轻了柔性支撑消除外界扰动变形的负担。镜室设计以轻量化和高刚度为目标,高度轻量化和高刚度本来就是相互矛盾的,还需通过有限元优化分析最终确定。考虑镜室的加工工艺性,将镜室设计成减重槽对称排布,如图5中的剖视图,这种排布能够使加工应力相互抵消,结构不易变形,刚度高,稳定性好。经有限元优化分析后最终确定镜室外形尺寸为520 mm×520 mm×110 mm,质量为13 kg,主三镜为32 kg,支撑组件总重为45 kg,满足指标要求(小于50 kg),镜室轻量化率按公式(5)计算得42.8%。
$$\eta = {{({M_s} - {M_l})} / {{M_s}}} \times 100{\text{%}} $$ (5) 式中:
$\eta $ 为轻量化率;${M_s}$ 为轻量化前的质量;${M_l}$ 为轻量化后的质量。主三反射镜立体模型如图6所示,反射镜组件装配关系如图7所示。侧面支撑约束反射镜的Tx,Ty,Rx,Ry共四个自由度,轴向约束限制Tz,Rz共两个自由度,因此共约束了主三镜六个自由度。由于需约束反射镜Z向平动,在镜室顶部用压块定位,因此顶部两个柔性支撑位置设计成关于中性面对称布局,并且顶部柔性支撑位置与底部支撑一一对应,两侧支撑点连线过镜室中心,使作用力关于质心对称布置,减少了额外作用力和力矩。反射镜与镜室有2 mm间隙,靠刚性和柔性支撑块支撑和定位,使反射镜“浮”在镜室里。
装配时将镜室平放(光轴竖直),把反射镜放到镜室装配基准面上,使背面与镜室三点组成的平面高精度接触,并且使反射镜每一个面到相邻镜室的内壁距离为(2±0.005) mm。通过修磨调整垫,调整右侧刚性支撑块位置,使反射镜处于镜室中的质心位置。然后调整左侧柔性支撑块的位置,使反射镜侧面施加微弱的预紧力,最后用螺钉紧固并用D04胶封固。同样方法装调反射镜上下两个方向的柔性支撑位置,使主三镜的质心尽量与镜室质心重合,最后安装反射镜镜面上的三个压块,镜面表面垫聚四氟乙烯垫,紧固压板螺钉后用D04胶封固,最后将主三镜组件处于竖直(光轴水平)状态,微调柔性支撑螺钉之后,在柔性支撑块和刚性支撑块上打定位销,进而保证反射镜在镜室中的位置精度。
采用刚性支撑与柔性支撑一一对应的支撑方法,刚性支撑起定位作用,柔性支撑起环境温度变化时自动调节功能。反射镜支撑组件竖直(工作状态)时,镜室两个凸台承担了反射镜的全部重力。
-
柔性支撑主要是为了消除反射镜与镜室热膨胀系数不同、装配应力或加工误差等引起的变形对反射镜面形的不利影响。柔性支撑结构一般为板簧型结构、十字交叉铰链结构、柔性杆上切槽或开圆弧铰链的形式和悬臂梁柔节等,柔性支撑设计时要遵循以下几个原则[16]:
(1)柔性支撑应以较小的附加作用力作用在反射镜上,以保证对镜面的影响最小;
(2)温度变化时,反射镜镜面变化很小;
(3)支撑系统应有足够高的刚度来满足反射镜的校准及姿态保持的要求。
-
柔性铰链的参数化设计为多目标优化过程,但优化目标一般无法同时达到最优,需将多目标优化转化为单一目标的优化,采用折衷规划化理论进行优化函数设置,多目标优化问题可表示为:
$$\left\{ \begin{gathered} {\rm{ find}}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{} \end{array}x = \left( {{x_1},{x_2},{x_3}, \cdots ,{x_m}} \right) \\ \min {f_i}\left( x \right),i = 1,2,3, \cdots ,n \\ s.t.\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{} \end{array}x \in X\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{} \end{array} \\ \end{gathered} \right.$$ (6) 式中:
$x$ 为优化变量;$m$ 为优化变量数目;${f_i}\left( x \right)$ 为第$i$ 个子目标函数;$n$ 为目标函数总数;$x$ 为优化变量的约束集合。针对大视场生物成像检测仪优化时,需考虑重力和温度载荷参数,柔性支撑单一目标的优化设计数学模型为[17]:
$$\left\{ \begin{gathered} {\rm{find}}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&x \end{array} \\ \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&\begin{gathered} \\ \min \sum\limits_{x = 1}^i {} F\left( {{x_i}} \right) = {\left\{ {\lambda _t^2\left[ {\frac{{{R_t}\left( x \right) - R_t^{\min }}}{{R_t^{\max } - R_t^{\min }}}} \right]} \right\}^{\frac{1}{2}}} + \\ {\left\{ {\lambda _g^2\left[ {\dfrac{{{R_g}\left( x \right) - R_g^{\min }}}{{R_g^{\max } - R_g^{\min }}}} \right]} \right\}^{\frac{1}{2}}} \\ \end{gathered} \end{array} \\ s.t.\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{x \in X} \end{array} \\ \end{gathered} \right.$$ (7) 式中:
$\lambda $ 为各个优化子目标的权重;${R_t}\left( x \right)$ 为温度变化引起的镜面$\rm RMS$ ;${R_g}\left( x \right)$ 为重力作用引起的镜面$\rm RMS$ 。 -
柔性支撑结构立体模型如图8所示,可以看作悬臂梁和圆弧铰链组合的结构。铰链的柔性由圆弧直径D、槽宽t、长度L和厚度b决定。铰链刚度越小,外力作用时变形越大,热应力释放的程度越高,对镜面的变形影响就越小。将这些几何参数分别作为设计变量,以反射镜在重力及4 ℃温升载荷作用下镜面的RMS值最小为优化目标进行柔性铰链参数设计。
由分析结果(图9(a))可以得出RMS值随圆弧直径D的增加而增加,在1~2 mm范围内变化不大,考虑加工工艺性,因此确定D为1.5 mm;由图9(b)得出RMS值随槽宽t值的增加而增加,并且增加幅度大,因此确定t为1 mm;由图9(c)得出RMS值随L增加稍有下降,确定L为11 mm,考虑空间位置及加工工艺性确定b为20 mm。
-
在主三镜镜室支撑结构中,通过支撑点与反射镜接触,用尽量少的接触面积来保证主三镜的装配精度,由于接触的非线性,为保证计算收敛,对网格进行细化。用有限元分析软件NASTRAN,采用自动划分网格的方式建立主三镜支撑系统(包括主三镜、镜室、柔性支撑块、刚性支撑块、压块及垫片等)有限元模型(图10),总单元数41677035,节点22370160,最后对主三镜支撑系统施加载荷和约束条件,根据项目实际工作环境要求,分别对组件Y向重力工况下和热载荷工况下的面形精度进行分析。
-
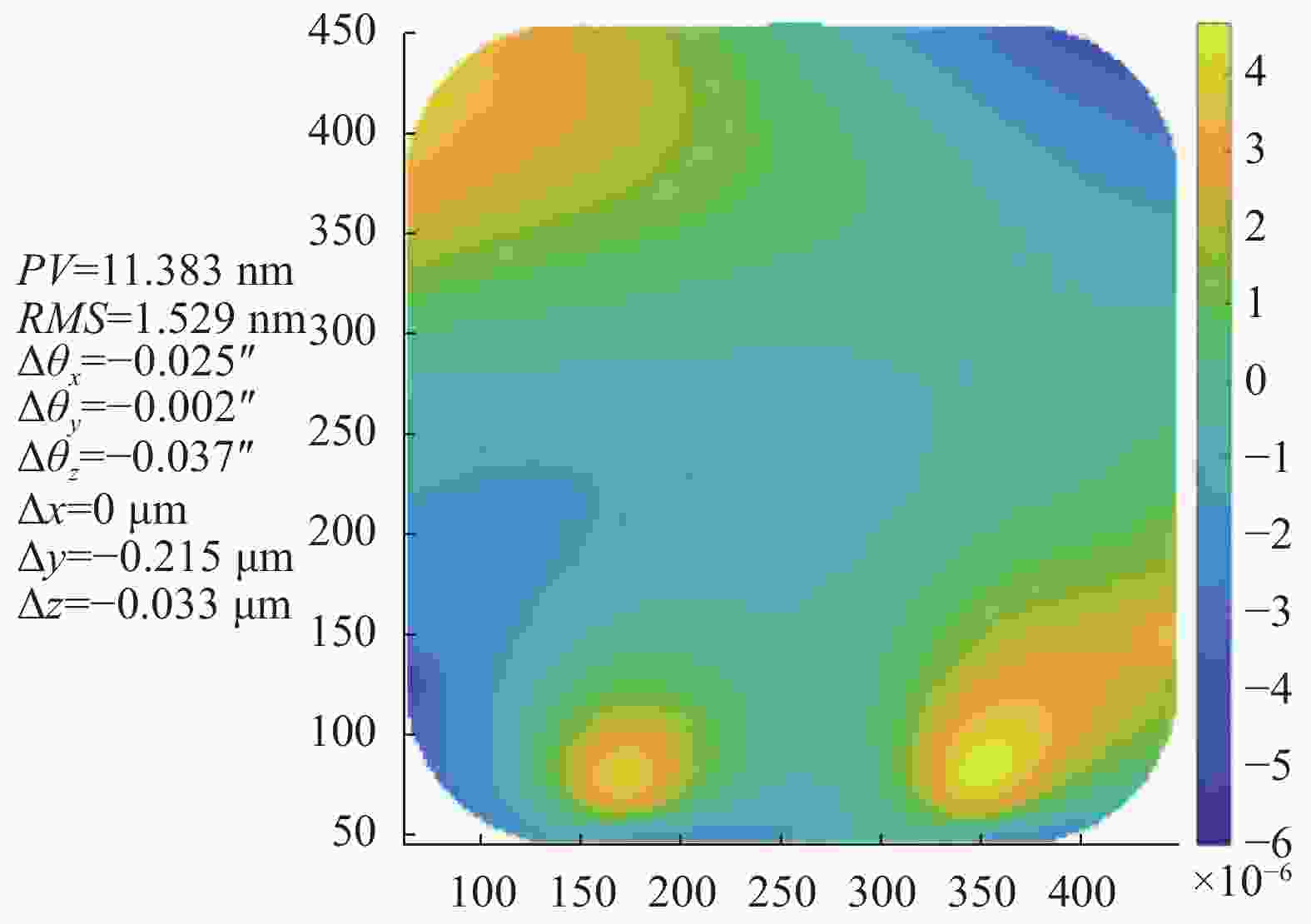
有限元分析了主三镜支撑系统光轴水平时(工作状态),Y向重力工况下,反射镜镜面变形云图如图11所示。主三一体镜镜面经Matlab拟合后RMS值为1.529 nm,PV值为11.383 nm,远小于设计要求,表明反射镜支撑系统具有很好的静态刚度。
-
一般情况下,热载荷变化引起反射镜的变形位移很小,但却给反射镜带来很大的应力,这种应力足以破坏反射镜的面形精度,从而产生像散、离焦、彗差等像差。要尽量减少热载荷对主三镜支撑组件的影响,需要对整个组件在加工制造前,利用有限元分析软件进行热特性仿真分析,进而保证主三镜支撑组件在环境温度发生改变时,对面形的影响降至最低,减少了反复制造实验的周期。对主三镜支撑系统热特性仿真分析时,以实际工作状态进行位置约束,对组件随机均匀分布三个网格点,分别进行自由度约束,其中一个点为全约束,另外两个点为半约束。
由于生物成像分析仪在恒温室使用,温差不会超过3 ℃,留取一定的设计余量,以温升4 ℃模拟温度变化;假设20 ℃时的面形误差为理想值,相当于给反射镜支撑系统预设一个恒定的温度场。因此20 ℃为初始温度,温度载荷为24 ℃时,进行仿真分析,反射镜镜面面形云图如图12所示。主三镜经Matlab拟合后RMS值为2.426 nm,PV值为14.13 nm,说明因支撑结构和主三镜材料的热膨胀系数不同带来的影响不大,在可接受的范围之内,表明支撑结构具有良好的热解耦能力。
-
光学元件(主三反射镜)和机械零件支撑组件(镜室、柔性铰链、刚性支撑块和压块等)加工完成后,对主三镜组件进行光机装调和检测,加工制造和装调后的主三镜组件现场照片如图13所示。
(1)主三反射镜面形检测
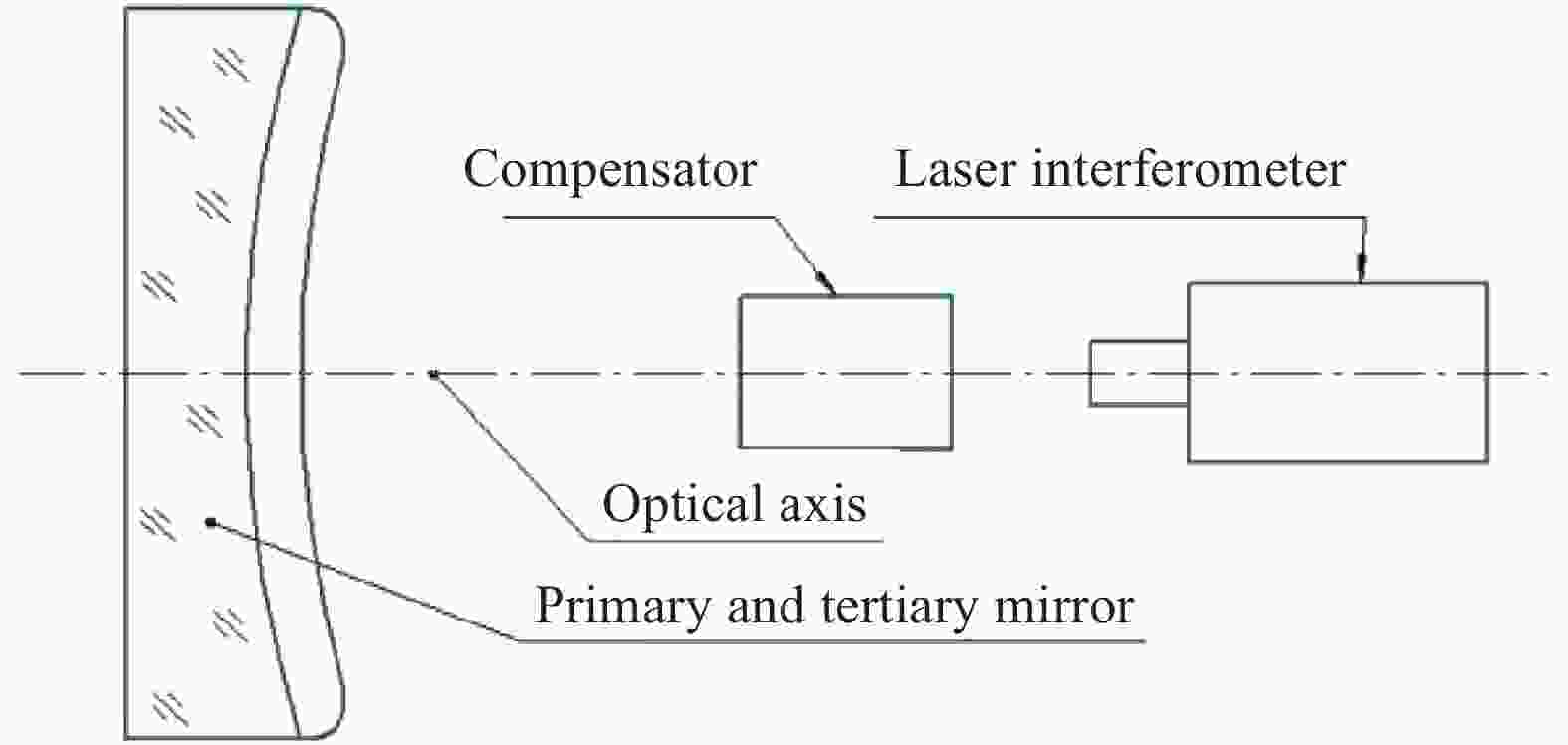
对主三镜组件采用Zygo激光干涉仪、补偿器对反射镜面形进行检测,检测原理如图14所示,激光干涉仪发射平面波,经补偿器投射到非球面主三镜镜面上,激光由主三镜反射后经补偿器再次回到干涉仪中并形成干涉条纹,然后转化为反映主三镜面形精度的云图。
主三镜面形检测是衡量反射镜支撑系统性能的最重要的手段之一,根据图14检测原理,环境温度约为24 ℃时,对主三镜支撑组件(光轴水平时)进行反射镜面形检测,检测结果如图15所示。从检测结果可以看出:主三反射镜面形误差RMS值为0.025 λ,PV值为0.376 λ(全口径),基本满足了生物成像分析仪技术指标要求(有效口径内,RMS≤λ/40)。
(2)主三镜、次镜系统波像差检测
将主三镜组件安装在主支撑框架上,精度调好后固定,然后安装次镜组件,在出光方向放置标准镜,在主三镜、次镜主点位置放置Zygo激光干涉仪检测系统波像差,通过反复调整次镜组件的位置量和姿态,使干涉条纹清晰,实测系统波像差为0.102 λ(RMS),基本满足生物成像系统波像差≤λ/10的技术要求。
-
文中针对离轴三反生物成像光学系统的矩形轮廓主三反射镜设计了其支撑结构和柔性铰链。通过循环迭代优化设计,确定了轻量化镜室结构。根据多目标优化数学模型,分析了在重力工况和4 ℃均匀温度载荷工况下各参数对镜面面形精度的影响,确定了以面形RMS最小为设计目标的柔性铰链各参数值。通过对反射镜支撑组件进行有限元仿真分析,得到了主三反射镜镜面的PV值和RMS值远小于技术指标要求(反射镜镜面PV≤λ/10,RMS≤λ/40)。最后对支撑作用下的主三反射镜进行了面形检测和光学系统波像差检测,测试结果基本满足了工程技术指标要求,验证了所述支撑方案的合理性及可行性,该项目的研究可为同类型反射镜支撑结构的设计和装调工作提供一定的借鉴和技术途径。
Supporting structure design for primary and tertiary mirror of off-axis TMA system
-
摘要: 主三反射镜支撑结构是离轴三反生物成像系统研制过程中的关键技术难点之一,为了减少工作环境下主三镜面形变化,满足支撑系统稳定性要求,利用有限元方法对主三镜组件进行了优化设计。首先,根据光学系统设计要求确定了反射镜及其支撑结构的材料和支撑方式。接着,优化布局了反射镜底部3点和侧面6点支撑位置,设计了轻量化镜室结构。根据优化数学模型设计了圆弧悬臂梁式柔性铰链结构,分析了在重力工况下和温度载荷工况下各参数对镜面面形精度的影响。然后,对反射镜支撑组件进行了静力学和热力学仿真分析,分析结果为重力工况下镜面均方根值RMS为1.529 nm,温度变化4 ℃时镜面均方根值RMS为2.426 nm。最后,采用Zygo干涉仪对支撑作用下的主三反射镜和系统波像差进行检测,实测反射镜镜面RMS值为0.025 λ,系统波像差RMS值为0.102 λ (λ=632.8 nm),基本满足了生物成像系统技术指标(主三镜镜面RMS≤λ/40,系统波像差RMS≤λ/10)要求。Abstract: Supporting structure for primary and tertiary mirror is one of the most challenging technical points during development of off-axis three-mirror anastigmatism (TMA) biological imaging system. In order to minish the shape error of the mirror and meet the stability of the supporting structure which was working, the mirror supporting structure was designed and optimized with finite element method. First, based on requirement of optical design, materials and supporting mode for the mirror and its supporting structure were decided. Then, a weight reduction structure of the mirror cell was designed which had three-point backside and six-point lateral support structure. The flexible hinge with circular and cantilever beam was made according to the optimized mathematical model. The influence of the parameters on the precision of mirror surface were analyzed under the load conditions of gravity and uniform temperature rise of 4 ℃. Then, the static analysis and thermal analysis for the mirror subassembly were performed. The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) indicated that the surface error (RMS) was 1.529 nm at self-weight. RMS value was 2.426 nm when the temperature rised 4 ℃. Finally, the surface figure test and the wavefront aberrations test were carried out by using Zygo interferometer. The test RMS value of the surface figure is 0.025 λ and the wavefront aberrations of the optical system is 0.102 λ (RMS). The results show that this supporting system could meet the technical indicator requirements of biological imaging system (RMS value of the shape error ≤λ/40, RMS value of the wavefront aberrations≤λ/10).
-
表 1 材料属性
Table 1. Performance parameters of materials
Material Modulous of clasticity, E/GPa Poission’s ratio, μ Density,ρ/g·cm−3 Coefficient of thermal expansion, α/℃ Zerodure 91 0.18 2.53 0.05×10−6 7A09 70 0.24 2.7 23.6×10−6 4J32 141 0.28 8.1 1.0×10−6 -
[1] Li Zhilai, Xu Hong, Guan Yingjun. Structural design of 1.5 m mirror subassembly for space camera [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(6): 1635-1641. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152306.1635 [2] Yang Libao, Li Yanhong, Wang Jing, et al. Alignment of Φ 1000 mm primary mirror for photoelectric tracking system [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(7): 1633-1641. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182607.1633 [3] Tang Wei, Liu Lisheng, Liu Yang, et al. Optimization anti analysis of a primary mirror fbr a laser incoherent combining system [J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(3): 442-450. (in Chinese) [4] Yu Funan, Zhang Chunyue. Support structure design of a hexagonal reflect mirror [J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 43(3): 1-6. (in Chinese) [5] Yao Yugang, Li Yaobin, San Xiaogang, et al. Multi-objective topological optimization of primary mirror of laser communication terminal [J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2019, 38(9): 1414-1419. (in Chinese) [6] Zhang Haidong, Yu Zhenkun. Enrichment and detection of circulating tumor cells and its application in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2017, 52(2): 147-151. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.02.020 [7] Meng Qingyu, Wang Wei, Ji Zhenhua, et al. Design of off-axis three-mirror system based on integration of primary and tertiary mirrors [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 4(2): 578-582. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.02.033 [8] Sha Wei, Chen Changzheng, Xu Yanjun, et al. Integrated primary and tertiary mirror components from common base line of off-axis TMA space camera [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(6): 1612-1619. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152306.1612 [9] Zhu Junqing, Sha Wei, Chen Changzheng, et al. Position layout of rear three point mounting for space rectangular mirror [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(9): 2562-2569. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152309.2562 [10] Li Haixing, Ding Yalin, Zhang Hongwen. Support system study of rectangular mirror [J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(5): 0523002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.0523002 [11] Liu Fuhe, Cheng Zhifeng, Shi Lei, et al. Design and analysis of supporting structure for rectangular mirror [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(5): 1512-1517. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.05.021 [12] Bao Qihong, Sha Wei, Chen Changzheng, et al. Lightweight and optimization design of rectangular reflective mirror supported in centre [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(7): 0718003. (in Chinese) [13] Wang Pengpeng, Xin Hongwei, Zhu Junqing, et al. Structural optimization design of lightweight rectangular reflective mirror [J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2020, 47(8): 200109. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.200109 [14] Zhai Yan, Mei Gui, Jiang Fan, et al. Ф2 020 mm aperture space infrared camera main reflector design [J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(8): 1170-1176. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183908.1170 [15] Shao Liang, Zhao Yongzhi, Ming Ming, et al. Novel support for 1.2 m zerodur primary mirror [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(10): 2462-2470. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162410.2462 [16] Han Linchu, Zhang Jingxu, Yang Fei. Summarization of lateral flexural flexure support in large telescope [J]. Laser & Infrared, 2014, 44(12): 1306-1311. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2014.12.003 [17] Hu Jianing, Dong Jihong, Zhou Pingwei. Parametric design of flexure supporting for optical space remote sensor primary mirror [J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(11): 1128001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.1128001 -







 下载:
下载: