-
液晶偏振光栅是近些年发展起来的基于几何相位实现光束偏转的超薄衍射光学元件,相较于其他衍射光学元件,具有尺寸小、质量轻、响应速度快等优势[1-3]。在激光雷达、空间光通信、激光对抗和激光武器等领域具有广泛的应用前景[4-7]。
液晶偏振光栅作为激光相控阵雷达的核心器件,其光束衍射效率过低会造成探测距离下降和目标检测概率降低[8],由于单片液晶偏振光栅光束偏转角度小且单一,因此,在实际使用过程中,需要将多片液晶偏振光栅级联[9-11],实现大角度光束偏转。光栅的级联结构会造成光束倾斜入射,影响光栅衍射效率。目前,国内外已有学者对斜入射下液晶偏振光栅的衍射效率进行了定性研究。2013年,李天等人[12]利用矢量傅里叶系数描述了斜入射下液晶偏振光栅的光束泄露问题并用实验测出了不同入射角度下液晶偏振光栅的衍射效率。2016年,赵祥杰等人[13]分析了斜入射对液晶偏振光栅转向效率的影响,表明了过度倾斜的入射会消除入射光束的转向作用,将光束能量衍射到非闪耀级次。以上针对斜入射的研究,并没有给出具体模型,均是定性分析了光束斜入射对液晶偏振光栅衍射效率的影响,不能量化斜入射角度、电压、衍射效率三者的关系。因此,为了准确研究斜入射对液晶偏振光栅的电压和衍射效率的影响,文中通过对液晶分子指向矢求解和斜入射下液晶偏振光栅的扩展琼斯矩阵计算方法的研究,建立了液晶偏振光栅斜入射角度-驱动电压-衍射效率的三维模型。利用该模型可计算出液晶偏振光栅衍射效率最优时的驱动电压,实现光栅快速标定,并且能对不同入射角度下液晶偏振光栅衍射效率进行量化分析。斜入射下液晶偏振光栅光束衍射效率的研究,对未来实现远距离、高精度的激光雷达具有重要意义。
-
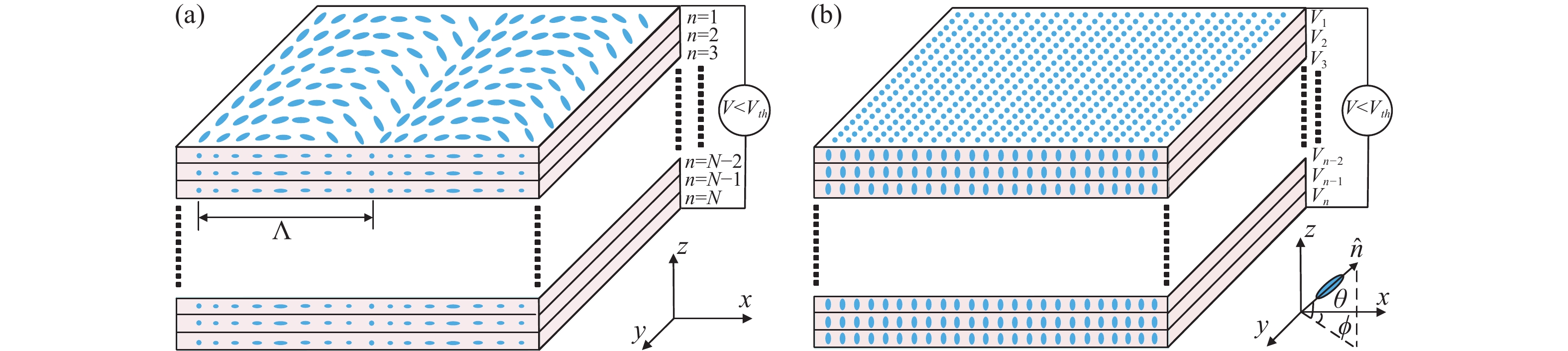
液晶偏振光栅是由电控制双折射液晶材料组成。其基本原理是光束在通过液晶层时,液晶折射率呈现周期性差异分布,使得入射光的相位发生周期性变化,最终产生光栅效果[14-15]。液晶指向矢是指在时间无限小的范围内液晶分子长轴的排列方向。在施加电压小于阈值电压的情况下,如图1(a)所示,液晶分子平行排列,其中
$ \phi $ 是液晶分子方位角,它是液晶分子在xy平面上投影与x轴夹角,其角度呈周期性变化,$ \theta $ 为液晶分子倾斜角,它是液晶分子指向式与z轴夹角。在电场的作用下,液晶分子倾角发生变化,液晶分子从平行排列转变为沿电场方向排列,如图1(b)所示。
图 1 (a)无驱动电压下液晶分子排布图;(b)驱动电压下液晶分子排布图
Figure 1. (a) Molecular arrangement of liquid crystal without driving voltage; (b) Molecular arrangement of liquid crystal at driving voltage
液晶指向矢的数学表达式为:
$ \vec n =( \cos \theta \cos \phi , \cos \theta \sin \phi ,\sin \theta ) $ ,其中$ \theta $ 、$ \phi $ 分别为液晶分子的倾斜角和方位角。由图1(b)可知,在外加电场时,液晶分子指向矢会随倾斜角和方位角发生改变。根据液晶连续体弹性形变理论,将指向矢代入液晶吉布斯自由能密度方程,可得液晶吉布斯自由能密度具体表达式为:$$ \begin{split} &f = \dfrac{1}{2}\left\{ {m\left( \theta \right){{\left( {\frac{{\partial \theta }}{{\partial {\textit{z}}}}} \right)}^2} + g\left( {\theta ,\phi } \right){{\left( {\frac{{\partial \phi }}{{\partial x}}} \right)}^2} + } \right.\\ &\quad\left. {h\left( {\theta ,\phi } \right) - \left( {{\varepsilon _ \bot } + \Delta \varepsilon {{\sin }^2}\theta } \right){{\left( {\frac{{{\rm{d}}v}}{{{\rm{d}}{\textit{z}}}}} \right)}^2}} \right\} \end{split}$$ (1) 式中:
$m(\theta ) = \left( {{k_{11}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta {{ + }}{k_{33}}si{n^{2}}\theta } \right)$ ;$g\left( {\theta ,\phi } \right) = {\cos ^{2}}\theta ({k_{11}}{\sin ^{2}}\phi + {k_{22}}{\cos ^{2}}\phi {\sin ^{2}}\theta \;+\; {k_{33}}{\cos ^{2}}\phi {\cos ^{2}}\theta )$ ;$h\left( {\theta ,\phi } \right) = \left( {{k_{22}}{{ \;-\; }}{k_{11}}} \right){\cos ^{2}}\theta \sin \phi$ ;$ {k_{11}} $ 、$ {k_{22}} $ 、$ {k_{33}} $ 为展曲、扭曲、弯曲弹性系数,在驱动电压作用下,液晶层中的自由能发生变化,液晶分子发生重排。当液晶分子处于平衡状态时,其吉布斯自由能密度最小。通过非线性最小二乘差分迭代法对指向矢求解[16]可以得到液晶分子倾斜角和位置关系,如图2所示。
图 2 不同电压下液晶分子倾斜角分布
Figure 2. Distribution of liquid crystal molecular inclination angle at different voltages
由图可得液晶分子倾斜角是关于电压和位置的函数,可将其记为
$ \theta ({\textit{z}},v) $ ,若要研究电压与液晶分子倾斜角的关系就必须选定某一位置,因此需要对液晶偏振光栅进行分层,而在利用最小二乘差分迭代法求解液晶指向矢的过程中,已将厚度为d的液晶偏振光栅分成了N层,每一层的电压都对应了一个液晶倾斜角,因此第n层液晶分子倾斜角和电压的关系可表示为:$$ {\theta _n} = \theta {}_{\textit{z}}(v) ,\left({\textit{z}} = \dfrac{d}{N}×n,n = 1,2,3\cdots N\right) $$ (2) 由此可以求出每层不同电压对应的液晶分子倾斜角,基于上述的分析与推导,即可建立液晶分子在外电场作用下倾斜角与电势分布的关系。
-
当光束垂直入射在液晶层上时,由于液晶分子寻常折射率
${n_{{o}}}$ 和非寻常折射率$ {n_e} $ 的不同,光束分成两部分,即寻常光(e光)和非寻常光(o光)[17]。正常情况下,入射光束必须垂直于液晶偏振光栅,但是由于级联结构和实际使用环境,入射光束很难时刻保证与光栅垂直,必然会有斜入射的情况发生,此时入射光与液晶分子夹角会发生变化。一般认为液晶分子是长棒状结构[14],其示意图如图1所示,由于液晶分子形貌对入射光束影响较小,在实际计算过程中,可将其简化为图3中形式,这样简化的好处是:在垂直入射时,可以近似认为液晶分子与入射光束夹角等于液晶分子倾斜角,即$ \theta {\text{ = }}\theta ' $ ,斜入射时,入射光束与液晶分子夹角就可以用倾斜角和斜入射角度来表示。从图3可以看出,斜入射时,入射光束与液晶分子夹角发生了变化,该情况下可以认为等同于液晶分子发生旋转。
图 3 (a)光束垂直入射模型;(b)光束斜入射模型
Figure 3. (a) Vertical incident beam model;(b) Beam oblique incident model
若圆偏光以入射角
$ {\theta _0} $ 倾斜入射在光栅上,通过上述分析可知斜入射改变了液晶分子倾斜角,此时,光束通过液晶分子的相位延迟将发生改变。为了研究斜入射下液晶分子相位延迟量的变化,建立坐标系使入射光在光栅x轴和z轴组成的平面上,坐标系如图4所示。图中,
$\hat n$ 为液晶分子指向矢,$ {K_i} $ 为入射光束矢量,根据图3可得斜入射下e光和o光的z分量为[18-20]:$$\begin{split} &{k_{e{\textit{z}}}} = \dfrac{{\left( {n_e^2 - n_o^2} \right)\sin \theta \cos \theta \cos \phi \sin {\theta _0}}}{{{n^2}}} + \dfrac{{{n_o}{n_e}}}{{{n^2}}} \times\\ &\quad{\left\{ {\left. {{n^2} - \left[ {1 - \dfrac{{n_e^2 - n_o^2}}{{n_e^2}}{{\cos }^2}\theta {{\sin }^2}\phi } \right]{{\sin }^2}{\theta _0}} \right\}} \right.^{\frac{1}{2}}} \end{split} $$ (3) $$ {k_{o{\textit{z}}}} = \sqrt {n_0^2 - {{\sin }^2}{\theta _0}} $$ (4) 式中:
$ \theta $ 为液晶分子在电场作用下的倾斜角;$ {\theta _0} $ 为斜入射角度。斜入射时实际光程大于液晶盒厚度,在图4中,液晶盒厚度为d,入射光束矢量$ {K_i} $ 在液晶中的传播角度为$ {\theta _e} $ ,由此关系图可得光束在实际传播过程中的光程为:$$ L = \dfrac{d}{{\cos {\theta _e}}} $$ (5) 通过公式(3)~(5)可以求出不同角度入射下液晶偏振光栅双折射相位延迟量:
$$ \varGamma = \left| {{k_{e{\textit{z}}}} - {k_{o{\textit{z}}}}} \right|L $$ (6) -
琼斯矩阵可以为研究光在各向异性介质中传播提供一种数值解法,但是由于其不考虑光在液晶表面的Fresnel折射和反射问题,因此其只适用于光垂直入射和近光轴传播情况,当光束斜入射时,使用常规的琼斯矩阵无法准确计算出入射光的状态变化。因此,需要使用扩展琼斯矩阵描述光束在液晶偏振光栅中的传播过程[12-13, 18-22],在对光栅的光学特性进行数值模拟时,将其分解成N层双折射晶体,再假设在每层晶体之间有一个厚度为0的各向同性的介质,当N足够大时,每一层都可以被认为是具有特定光轴方向的单轴晶体,入射在单轴晶体界面上的o光和e光在各向同性介质和单轴晶体的界面上,光的折射可以用矩阵形式表示[20]:
$$ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{E_e}} \\ {{E_o}} \end{array}} \right] = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {R\left( {p,e} \right)}&{R\left( {s,e} \right)} \\ {R\left( {p,o} \right)}&{R\left( {s,o} \right)} \end{array}} \right]\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{E_p}} \\ {{E_s}} \end{array}} \right] $$ (7) 式中:
$ {E_e} $ ,$ {E_o} $ 为单轴晶体中的e向量和o向量;$ {E_p} $ ,$ {E_s} $ 为个各向同性介质中电场分量的p向量和s向量;$ R\left(e,p\right),R\left(o,p\right),R\left(e,s\right),R\left(o,s\right) $ 为从液晶到各向同性介质的传播系数。因此,当光束从各向同性介质到单轴晶体,然后又到另一个各向同性介质的光波传输矩阵为[15,20]:
$$ J = {R_1}G{R_2} $$ (8) 式中:
$ {R_1} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {R\left( {e,p} \right)}&{R\left( {o,p} \right)} \\ {R\left( {e,s} \right)}&{R\left( {o,s} \right)} \end{array}} \right]\; $ ;$ {R_2} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {R\left( {p,e} \right)}&{R\left( {s,e} \right)} \\ {R\left( {p,o} \right)}&{R\left( {s,o} \right)} \end{array}} \right] $ ;G=$ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0 \\ 0&{{e^{i\Gamma }}} \end{array}} \right] $ ;$ {R_1} $ 和$ {R_2} $ 分别为入射矩阵和折射矩阵;$ G $ 为单层液晶的传输矩阵。矩阵传播系数表示为:$$ R(e,p) = R(p,e) = \dfrac{1}{{{A_e}}}(m + v) \cdot (n - u) $$ (9) $$ R(p,o) = R(o,p) = \frac{1}{{{A_o}}}\cos \theta \sin \phi $$ (10) $$ R(e,s) = - \frac{1}{{{A_e}}}\cos \theta \sin \theta (m + v) $$ (11) $$ R(s,o) = R(o,s) = \frac{1}{{{A_o}}}(n - u) $$ (12) 式中:
$ m = {n_e}({\theta _e})\cos {\theta _0}\cos {\theta _e} $ ;$ v = {n_0}{\sin ^2}{\theta _0} $ ;$ u = \sin {\theta _0} \sin \theta $ ;$ n = \cos {\theta _0}\cos \theta \cos \phi $ ;$ {\theta _e} $ 为$ e $ 光在液晶中的折射角;$ {n_e}({\theta _e}) $ 为$ e $ 光在$ {\theta _e} $ 方向上的折射率,$ \cos {\theta _e} = {{{k_{e{\textit{z}}}}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{k_{ez}}} {{n_e}}}} \right. } {{n_e}}}({\theta _e}) $ ;$ \theta $ 为液晶指向矢的倾斜角;$ \phi $ 为液晶偏振光栅方位角;${A_o}$ 和$ {A_e} $ 是归一化常量。则:$$ {A_o} = {[{\sin ^2}\phi {\cos ^2}\theta {\text{ + (}}u - n{)^2}]^{\frac{1}{2}}} $$ (13) $$ {A_e} = {\{ [{n_e^2}({\theta _e}){\cos ^2}{\theta _e} + v]{(n - u)^2} \times {\cos ^2}\theta {\sin ^2}\phi {[m + v]^2}\} ^{\frac{1}{2}}} $$ (14) 实际计算过程中,选择各向同性介质的折射率为
$ {n_o} $ ,由折射定律可知当o光从各向同性介质到液晶层的时候不发生折射。因一般情况下液晶的$ {n_\parallel } $ 和$ {n_ \bot } $ 差别较小,由折射率椭球公式可知e光的折射率和o光的折射率是相等的,因此上述各式中$ {\theta _e} $ 和$ {\theta _0} $ 也可以近似认为是相等的[13, 20],即:$ {n_e} \approx {n_o} $ ,$ {\theta _e} \approx {\theta _0} $ ,这样可以简化计算且可将琼斯矩阵中各元素全部都用液晶参数和入射角来表示。基于上述分析将入射界面传输矩阵化简得:$$ {R_1} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\dfrac{{n - u}}{{{A_o}}}}&{\dfrac{{\sin \phi \cos \theta }}{{{A_o}}}} \\ { - \dfrac{{\sin \phi \cos \theta }}{{{A_o}}}}&{\dfrac{{{n_o} - u}}{{{A_o}}}} \end{array}} \right] $$ (15) 最终可将第n层液晶偏振光栅的扩展琼斯矩阵化简为:
$$\begin{split} & {J_n} =\\ & {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{\left( {\dfrac{\Delta }{{{A_o}}}} \right)}^2}\exp \left( {i\Gamma } \right) + {{\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \phi \cos {\theta _n}}}{{{A_o}}}} \right)}^2}} & {\left( {\dfrac{{\Delta \sin \phi \cos {\theta _n}}}{{{A_o}^2}}} \right)\left( {1 - \exp \left( {i\varGamma } \right)} \right)} \\ {\left( {\dfrac{{\Delta \sin \phi \cos {\theta _n}}}{{{A_o}^2}}} \right)\left( {1 - \exp \left( {i\varGamma } \right)} \right)} & {{{\left( {\dfrac{\Delta }{{{A_o}}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \phi \cos {\theta _n}}}{{{A_o}}}} \right)}^2} \exp \left( {i\varGamma } \right)} \end{array}} \right] } \end{split}$$ (16) 式中:
$\Delta = \cos \phi \cos {\theta _n}\cos {\theta _0} - \sin {\theta _n}\sin {\theta _0}$ 。$ N $ 层液晶的总的琼斯矩阵为:$$ T{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {{ = }}{\kern 1pt} J = {J_N}{J_{N - 1}} \times \cdot \cdot \cdot {J_n} \times \cdot \cdot \cdot {J_3}{J_2}{J_1} $$ (17) 若入射光的琼斯矢量表达式为
${[{E_{in\_p{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} }}{E_{in\_s}}]^{\rm{T} }}$ ,则出射光的琼斯矩阵为:$$ \left[ \begin{gathered} {E_{out\_p{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} }} \\ {E_{out\_s}} \\ \end{gathered} \right] = T\left[ \begin{gathered} {E_{in\_p{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} }} \\ {E_{in\_s}} \\ \end{gathered} \right] $$ (18) 基于上述的分析与推导可以看出,斜入射角度不同时,液晶偏振光栅的透过率也会发生变化,从而影响光栅衍射效率。值得注意的是,斜入射不仅会改变透过率,同时会改变入射光的偏振态并增加入射光束在光栅上的界面反射,对于级联系统,这些变化都会影响整个系统的衍射效率。
-
根据光栅的矢量衍射理论[13],光栅m级次的偏振特性和衍射效率由透射光场的矢量傅里叶变换系数决定。
$$ {D_m} = \dfrac{1}{\varLambda }\int_0^\varLambda T \exp (i2{\text{π}} mx/\varLambda ){\rm{d}}x $$ (19) 式中:
$ \varLambda $ 为光栅周期;$ T $ 为光栅的透过率矩阵。通常将液晶偏振光栅
$ m $ 级次光束能量与各级衍射光束能量之和的比值作为光栅$ m $ 级次的衍射效率,而第$ m $ 级次光束能量的大小与$ {\left| {{D_m}} \right|^2} $ 成正比,因此,液晶偏振光栅第$ m $ 级的衍射效率可以表示为[23]:$$ {\eta _m} = \dfrac{{{{\left| {{D_m}} \right|}^2}}}{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = - \infty }^\infty {{{\left| {{D_m}} \right|}^2}} }} $$ (20) 式中:
$ {\eta _m} $ 为$ m $ 级衍射效率。通过对上式求解可得,对于$ m > 1 $ 的级次,其矢量傅里叶系数均为零,所以液晶偏振光栅衍射级次分布在:0级和$ \pm 1 $ 级。而在实验中,衍射级次的实际分布,取决于入射光的偏振态;衍射强度大小,则取决于光栅的透过率。垂直入射时,右旋圆偏光通过液晶偏振光栅会被衍射到+1级,左旋圆偏光则会被衍射到−1级,理论上衍射效率可达100%。斜入射时,液晶偏振光栅透过率会发生变化,从而导致$ \pm 1 $ 级衍射效率也会随之改变。基于上述理论推导,结合公式(2)、(16)、(17)即可建立斜入射角度、驱动电压与衍射效率模型:$$ {\eta _m} = \dfrac{{{{\left| {\displaystyle\int_0^\varLambda T \exp \left(\dfrac{{i2\pi mx}}{\varLambda }\right){\rm{d}}x} \right|}^2}}}{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m= - \infty }^\infty {{{\left| {T\exp \left(\dfrac{{i2\pi mx}}{\varLambda }\right){\rm{d}}x} \right|}^2}} }} $$ (21) 通过该模型可以定量计算出液晶偏振光栅不同入射角度下的电压、衍射效率,进而简化标定过程,提高衍射效率。
-
根据上述模型,文中选择向列型混合液晶材料,分别对液晶偏振光栅的光束入射角、电压和衍射效率进行了仿真和分析。其中物理参量
${K_{11}}{\text{ = }} 11.1 \times {10^{{{ - }}12}}\;{{N}}$ ,${K_{22}} = 7.4 \times {10^{ - 12}}\;{{N}}$ ,${K_{33}} = 17.1 \times {10^{ - 12}}\;{{N}}$ ,真空介电常数为$ {\varepsilon _0}{\text{ = }}8.854 \times {10^{ - 12}}\;{{\rm{F / m}}} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _\parallel }{\text{ = }}19.0{\varepsilon _0} $ ,$ {\varepsilon _ \bot }{\text{ = }}5.2{\varepsilon _0} $ ,折射率为$ {n_o}{\text{ = }}1.521 $ ,$ {n_e}{\text{ = }}1.746 $ ,液晶相控阵厚度$ d = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}}\;{\rm{m}} $ ,激光波长为$ \lambda = 1\;064 \times {10^{ - 6}}\;{\rm{m }}$ 。为了分析斜入射下液晶偏振光栅的衍射特性,对光束入射角从−10°~+10°,电压从0~20 V的情况进行仿真,结果如图5所示。

图 5 斜入射角度,电压和+1级衍射效率关系
Figure 5. Relationship between oblique incident angle, voltage and +1 diffraction efficiency
图5为液晶偏振光栅+1级衍射效率与斜入射角度和电压之间的关系。通过图5可以看出,+1级衍射效率受电压和斜入射角度影响。入射光束角度从−10°倾斜到10°时,其中0°入射时光栅+1级衍射效率最高,随着入射角度增大,+1级衍射效率逐渐下降;当驱动电压大于阈值电压时,+1级衍射效率先随电压升高而升高,衍射效率达到最大值之后,如果电压继续升高,+1级衍射效率逐渐下降最终降为0,这与液晶偏振光栅的光束偏转原理是相吻合。由此可以看出,用液晶偏振光栅斜入射角度-驱动电压-衍射效率模型来表征光束斜入射时的传播过程是可行的,有效的。
若光束以固定角度倾斜入射液晶偏振光栅,便可得到在某个斜入射角度下电压和衍射效率关系,如图6所示,图(a)~(c)分别为正入射、斜入射−10°、斜入射+10°时,电压与+1级光束衍射效率关系图。
液晶偏振光栅在实际使用过程中需要对其驱动电压进行标定,传统标定方法是在光束垂直入射光栅时,从光栅阈值电压开始对进行调整,直到达到最佳偏转效果才停止调整,这种方法导致标定速度较慢。从图6(a)电压与衍射效率模型可以看出,垂直入射时液晶偏振光栅光束偏转+1级的最优驱动电压为2.2 V,由于制备工艺的限制,光栅的最优驱动电压会有所偏差,在实际标定过程中只需在2.2 V附近微调电压,即可得到光栅实际的最优驱动电压,该模型可避免现有复杂标定过程,有效提高标定效率。对比图6(a)~(c),倾斜入射时,最优电压会在2.2 V附近发生小幅度的变化,而+10°入射时,最优偏转电压由原来的2.2 V变为2.0 V;−10°入射时,最优偏转电压由原来的2.2 V变为2.4 V。通过该模型可求出不同入射角度下驱动电压,实现衍射效率最优时驱动电压的快速标定。
通过上述分析,求出不同入射角度下光栅最优驱动电压,可得到斜入射角度和衍射效率的关系,如图7所示。
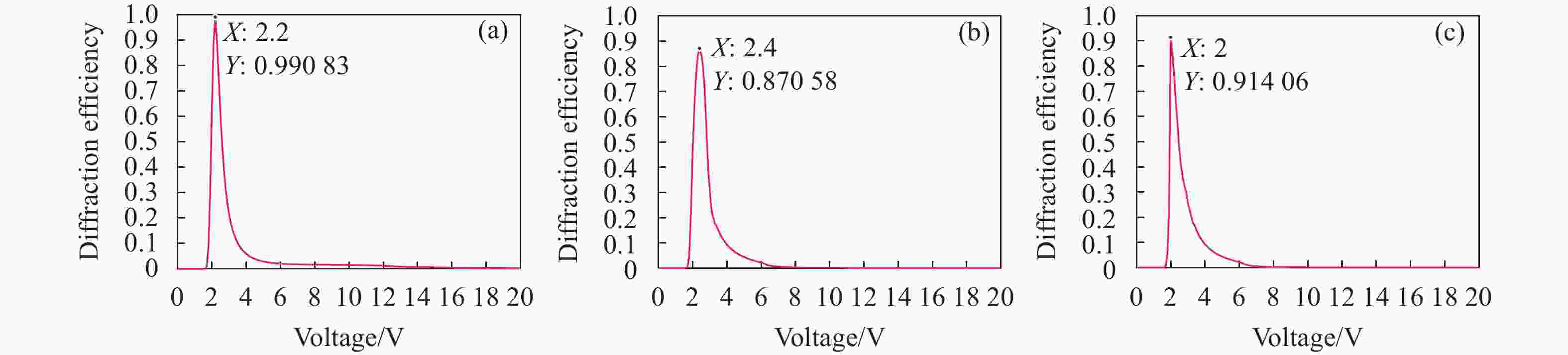
图 6 (a) 垂直入射;(b) 斜入射−10°;(c) 斜入射+10°
Figure 6. (a) Vertical incident; (b) Oblique incident −10°; (c) Oblique incident +10°

图 7 (a) +1级衍射效率;(b) 0级衍射效率
Figure 7. (a) +1 order diffraction efficiency; (b) 0 order diffraction efficiency
从图7液晶偏振光栅+1级和0级衍射效率的变化趋势可以明显看出,当光束垂直入射时,一级衍射效率较高,但随着入射角度增加,一级衍射效率逐渐降低,零级衍射效率逐渐上升,光束能量发生泄露。通过上述模型可定量计算出驱动电压、斜入射角度、衍射效率的关系,如表1和表2所示。
表 1 光束0°~10°入射时驱动电压、衍射效率之间对应关系
Table 1. Corresponding relationship between driving voltage and diffraction efficiency when the beam is incident at 0°-10°
Oblique incidence
angle/(°)0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Driving voltage/V 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.1 2.1 2.1 2.0 2.0 Diffraction efficiency 99.3% 99.1% 98.9% 98.5% 98.1% 97.4% 96.5% 95.5% 94.3% 92.9% 91.4% 表 2 光束−10°~ 0°入射时驱动电压、衍射效率之间对应关系
Table 2. Corresponding relationship between driving voltage and diffraction efficiency when the beam is incident at −10°-0°
Oblique incidence angle/(°) 0 −1 −2 −3 −4 −5 −6 −7 −8 −9 −10 Driving voltage/V 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.4 Diffraction efficiency 99.3% 99.1% 98.8% 98.3% 97.5% 96.5% 95.3% 93.7% 91.9% 89.8% 87.1% 通过以上分析可得,当斜入射角度达到−10°时,驱动电压变为2.4 V,一级衍射效率为87%,此时衍射效率下降了12%左右,随着斜入射角度增加,光束衍射效率逐渐下降,光束会被衍射其他级次,因此在实际使用过程中要尽量避免斜入射。
-
针对上述仿真分析,搭建实验平台对其进行验证,实验装置如图8所示,实验系统主要包括:激光器、1/4波片,偏转角为5°液晶偏振光栅、观察屏和CCD相机等部分。实验中激光器产生1064 nm的激光,出射光经过准直扩束镜,入射到QWP上,使用QWP 将线偏光转化为圆偏光,然后经过液晶偏振光栅发生光束偏转,照射到观察屏上,最后利用 PC 控制驱动器产生驱动电压,施加给液晶偏振光栅。改变入射光束角度,同时用CCD相机记录零级、正一级光强分布随入射角度的变化,通过对采集的光斑进行处理即可得到斜入射角度对衍射效率的影响。
利用CCD相机采集的几组斜入射下光束分布图案如图9所示。图(a)中的光斑为+1级光斑,在图(b)和图(c)亮的光斑为+1级光斑,暗的光斑为0级光斑。由于液晶偏振光栅偏转角度为5°,因此当光束垂直入射时,+1级光斑偏转角度为5°,5°和10°入射时,+1级光斑分别会偏转到10°和15°位置,如图(b)和(c)所示。

图 9 (a) 垂直入射下+1级光斑图;(b) 5°入射下+1级光斑图;(c) 10°入射下+1级光斑图
Figure 9. (a) Light spot pattern of +1 under vertical incidence; (b) Light spot pattern of +1 at 5° incidence; (c) Light spot pattern of +1 at 10° incidence
从图9可以看出,对比垂直入射的光强分布,当光束以5°、10°入射时,0级光斑则明显增强。10°入射时,光栅衍射效率低于5°和垂直入射。根据公式(18)衍射效率计算公式,可得到不同斜入射角度下的衍射效率,如图10所示。
由于液晶偏振光栅形貌缺陷、液晶盒厚度误差、菲涅耳损耗等因素的影响,液晶偏振光栅实际衍射效率低于理论值,但根据测量所得衍射效率的变化趋势可以明显看出,随着斜入射角度增大,一级衍射效率逐渐降低,零级衍射效率逐渐升高。光束入射角从−10°~+10°变化时,衍射效率出现了不对称性,这是因为液晶偏振光栅的真实结构并不是完全对称。当光束入射角度为0°~10°入射时,一级光束能量损失了10%,零级光束能量上升了6%;而当光束入射角度从−10°~0°变化时,一级光束能量损失了13%,零级光束能量上升了8%。通过实验结果可以看出,仿真结果和实验结果基本吻合。
-
文中从液晶偏振光栅的结构出发,推导建立了液晶偏振光栅斜入射角度-驱动电压-衍射效率的三维模型。通过求解液晶分子指向矢分布,得到了倾斜角和电压之间的关系,将扩展琼斯矩阵和矢量衍射理论相结合,表征了斜入射时液晶偏振光栅第
$ m $ 级的衍射特性,并对光束入射角度为−10°~+10°的情况进行了仿真和实验验证。仿真和实验结果表明,斜入射会使光束偏转的最优电压发生变化,衍射效率随入射角度的增大而减小,入射角过大时,会明显出现其他衍射级。光束正入射时,最优驱动电压为2.2 V,10°入射时,最优驱动电压变为2.0 V,−10°入射时,最优驱动电压变为2.4 V;且光束入射角从−10°倾斜到−10°时,衍射效率最大下降了13%。因此,在实际应用环境中需对入射光束的角度进行控制,该研究为提高液晶偏振光栅的衍射效率提供了技术指导。
Research on diffraction characteristics of liquid crystal polarization grating under oblique incidence
-
摘要: 为了表征光束倾斜入射下液晶偏振光栅的衍射特性,提出了液晶偏振光栅斜入射角度-驱动电压-衍射效率的三维模型建模方法。该方法利用吉布斯自由能方程,求解液晶分子指向矢,得到驱动电压与液晶分子倾斜角的表达式,推导出斜入射角度与相位延迟量之间的关系,结合扩展琼斯矩阵表征不同入射角度下液晶偏振光栅的透过率,通过矢量衍射理论,建立了斜入射角度-驱动电压-衍射效率的三维模型。该模型不仅可以定量求解不同斜入射角度下液晶偏振光栅衍射效率,而且能够实现衍射效率最优时驱动电压的标定。通过仿真分析和实验对该模型的有效性进行了验证,结果表明:光束入射角度从0°倾斜到10°时,最优驱动电压由2.2 V降低到2.0 V,液晶偏振光栅衍射效率从85%下降到78%;光束入射角度从0°倾斜到−10°时,最优驱动电压由2.2 V升高到2.4 V,液晶偏振光栅衍射效率从85%下降到74%。Abstract: To characterize the diffraction characteristics of the liquid crystal polarization grating when the beam is incident obliquely, a three-dimensional model modelling method of liquid crystal polarization grating oblique incident angle-driving voltage-diffraction efficiency was proposed. This method uses the Gibbs free energy equation to solve the director of the liquid crystal molecule, obtains the expression of the driving voltage and the tilt angle of the liquid crystal molecule, derives the relationship between the oblique incident angle and the phase retardation, and combines the extended Jones matrix to characterize different incident angles. The transmittance of the lower liquid crystal polarization grating, through the vector diffraction theory, establishes a three-dimensional model of oblique incident angle-driving voltage-diffraction efficiency. This model can not only quantitatively solve the diffraction efficiency of liquid crystal polarization gratings at different oblique incident angles, but also realize the calibration of the driving voltage when the diffraction efficiency is optimal. The effectiveness of the model was verified by simulation analysis and experiments. The results show that when the beam incident angle is tilted from 0° to 10°, the optimal driving voltage is reduced from 2.2 V to 2.0 V, and the diffraction efficiency of the liquid crystal polarization grating is reduced from 85% to 78%; when the beam incident angle is tilted from 0° to −10°, the optimal driving voltage is increased from 2.2 V to 2.4 V, and the diffraction efficiency of the liquid crystal polarization grating drops from 85% to 74%.
-
表 1 光束0°~10°入射时驱动电压、衍射效率之间对应关系
Table 1. Corresponding relationship between driving voltage and diffraction efficiency when the beam is incident at 0°-10°
Oblique incidence
angle/(°)0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Driving voltage/V 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.1 2.1 2.1 2.0 2.0 Diffraction efficiency 99.3% 99.1% 98.9% 98.5% 98.1% 97.4% 96.5% 95.5% 94.3% 92.9% 91.4% 表 2 光束−10°~ 0°入射时驱动电压、衍射效率之间对应关系
Table 2. Corresponding relationship between driving voltage and diffraction efficiency when the beam is incident at −10°-0°
Oblique incidence angle/(°) 0 −1 −2 −3 −4 −5 −6 −7 −8 −9 −10 Driving voltage/V 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.4 Diffraction efficiency 99.3% 99.1% 98.8% 98.3% 97.5% 96.5% 95.3% 93.7% 91.9% 89.8% 87.1% -
[1] Hoy C, Stockley J, Shane J, et al. Non-mechanical beam steering with polarization gratings: A review [J]. Crystals, 2021, 11(4): 361. doi: 10.3390/cryst11040361 [2] Wang Lina, Li Mingqiu, Wang Chunyang. Diffraction characteristics of cascaded liquid crystal polarizing gratings [J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(3): 88-92. (in Chinese) [3] Kim J, Miskiewicz M N, Serati S, et al. Nonmechanical laser beam steering based on polymer polarization gratings: Design optimizationand demonstration [J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2015, 33(10): 2068-2077. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2015.2392694 [4] Kim J, Miskiewicz M N, Serati S, et al. Demonstration of large angle nonmechanical laser beam steering based on LC polymer polarization gratings[C]//Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2011, 8052: 8052T. [5] Escuti M J, Jones W M. 39.4: Polarization‐independent switching with high contrast from a liquid crystal polarization grating [J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2006, 37(1): 1443-1446. doi: https://doi.org/10.1889/1.2433259 [6] Zhang Tianyi, Wang Xiangru, Hang Zhiqiang. Application of liquid crystal optical phase technologyin satellite multiple access communication [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 44(11): 1122004. (in Chinese) [7] Zhang Dai, Hao S, Zhao Q, et al. Wavefront reconstruction method based on wavelet fractal interpolation for coherent free space optical communication [J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 410: 723-729. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.11.021 [8] Xiao Feng. Research on key technology of liquid crystal optical phased array[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018. (in Chinese) [9] Zhao Zhiwei. Study on polarization grating of liquid crystal with large deviation angle[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. (in Chinese) [10] Serati S, Hoy C L, Hosting L, et al. Large-aperture, wide-angle nonmechanical beam steering using polarization gratings [J]. Optical Engineering, 2017, 56(3): 031211. [11] Li Songzhen. Design of liquid crystal polarization grating and its optical deflection characteristics[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese) [12] Tan L, Ho J Y. P. 92: Characterization of complex liquid crystal polarization gratings at oblique incidence using extended Jones matrix method [J]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2013, 44(1): 1335-1337. doi: 10.1002/j.2168-0159.2013.tb06484.x [13] Xiangjie Z, Jiazhu D, Dayong Z, et al. Oblique incidence effect on steering efficiency of liquid crystal polarization gratings used for optical phased array beam steering amplification [J]. Optical Review, 2016, 23(5): 1-10. [14] Liu Chunjie. The study on the fabrication of active liquid crystal polarization grating[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese) [15] Li Jiyang, Tan Yidong, Wu Ji, et al. Birefringence measurement of liquid crystals based on laser feedback effect [J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(3): 0306003. (in Chinese) [16] Niu Qifeng, Wang Chunyang, Zhang Guangping, et al. Solution of liquid ctystal phased array director and its beam defiection [J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(12): 27-34. (in Chinese) [17] Panezai S, Wang D, Zhao J, et al. Study of oblique incidence characterization of parallel aligned liquid crystal on silicon [J]. Optical Engineering, 2015, 54(3): 037109. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.54.3.037109 [18] Yeh P. Extended Jones matrix method [J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1982, 72: 507-513. [19] Gu C, Yeh P. Extended Jones matrix method II [J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1993, 10: 966-973. [20] Yu F H, Kwok H S. Comparison of extended Jones matrices for twisted nematic liquid crystal displays at oblique angles of incidence [J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1999, 16: 2772-2780. [21] Tan L, Ho J Y, Kwok H S. Extended Jones matrix method for oblique incidence study of polarization gratings [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(5): 324-490. [22] Niu Qifeng, Wang C, Shi H. Phase modulation characteristics analysis of liquid crystal spatial light modulator under oblique incidence [J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90(5): 055001. doi: 10.1063/1.5087535 [23] Niu Qifeng. Research on the key technology of liquid crystal phased array beam deflection[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: