HTML
-
随着无人机的普及,无人机的无证飞行和随意飞行也越来越威胁到公共安全。如何解决无人机的“黑飞”问题成为研究热点。反无人机系统是检测无人机,反制无人机的系统。在反无人机系统中,图像识别是无人机识别的方法之一,而图像识别的关键在于图像特征的提取,使用显著对象作为图像内容表示。根据特征提取的方式不同,分为传统图像特征手动提取方法和神经网络自动提取特征两种图像识别方法,传统图像识别主要依靠手动提取图像中的颜色特征、形状特征、纹理特征等特征参数来对图像进行分类,但是由于传统图像识别方法本身的局限性,使得分类的精度不高。在基于神经网络的图像识别方法发展过程中,有许多模型被提来。付旻等设计的基于多分类支持向量机(SVM)的公交换乘识别方法取得了不错的效果[1]。在20世纪80年代,Le Cun等提出了基于卷积神经网络的手写数字识别网络Le Net-5[2]。2012年Krizhevsky等提出Alex Net模型,并在Image Net竞赛中取得了冠军。2016年Inception- v4被提出[3],它是基于Inception-v3的改进,模型简洁,计算量小。卷积神经网络具有自动提取特征和权值共享的特点,使得卷积神经网络也可用于图像识别。
文中提出了一种基于卷积神经网络的无人机识别方法。设计了适合无人机数据集的卷积神经网络。为验证提出的识别方法的可行性,分别对无人机和鸟的图片运用支持向量机和设计的卷积神经网络进行识别;并运用设计的卷积神经网络在MNIST数据集上进行测试[4]。
-
根据百强网和买购网的数据显示“低慢小”无人机排名前5为大疆、派诺特、AEE—电科技、零度智控等品牌,同时根据各个品牌无人机的销售情况,选取了以下5种型号的无人机进行采集,分别是大疆-御MAVIC 2,派诺特- Bebop 2.0,AEE—电科技AP10 Pro,零度智控- XPLORER V,极飞XAG-C2000。在拍摄过程中,拍摄条件没有任何限制,在自然光的照射下用自制光学系统对飞行中的无人机进行拍摄,如表1和图1所示。
UAV type Number of shots Number after amplification MAVIC 2 176 704 Bebop 2.0 176 704 AP10 Pro 176 704 XPLORER V 176 704 C2000 176 704 Total 880 3520 Table 1. 5 number of UAV pictures
-
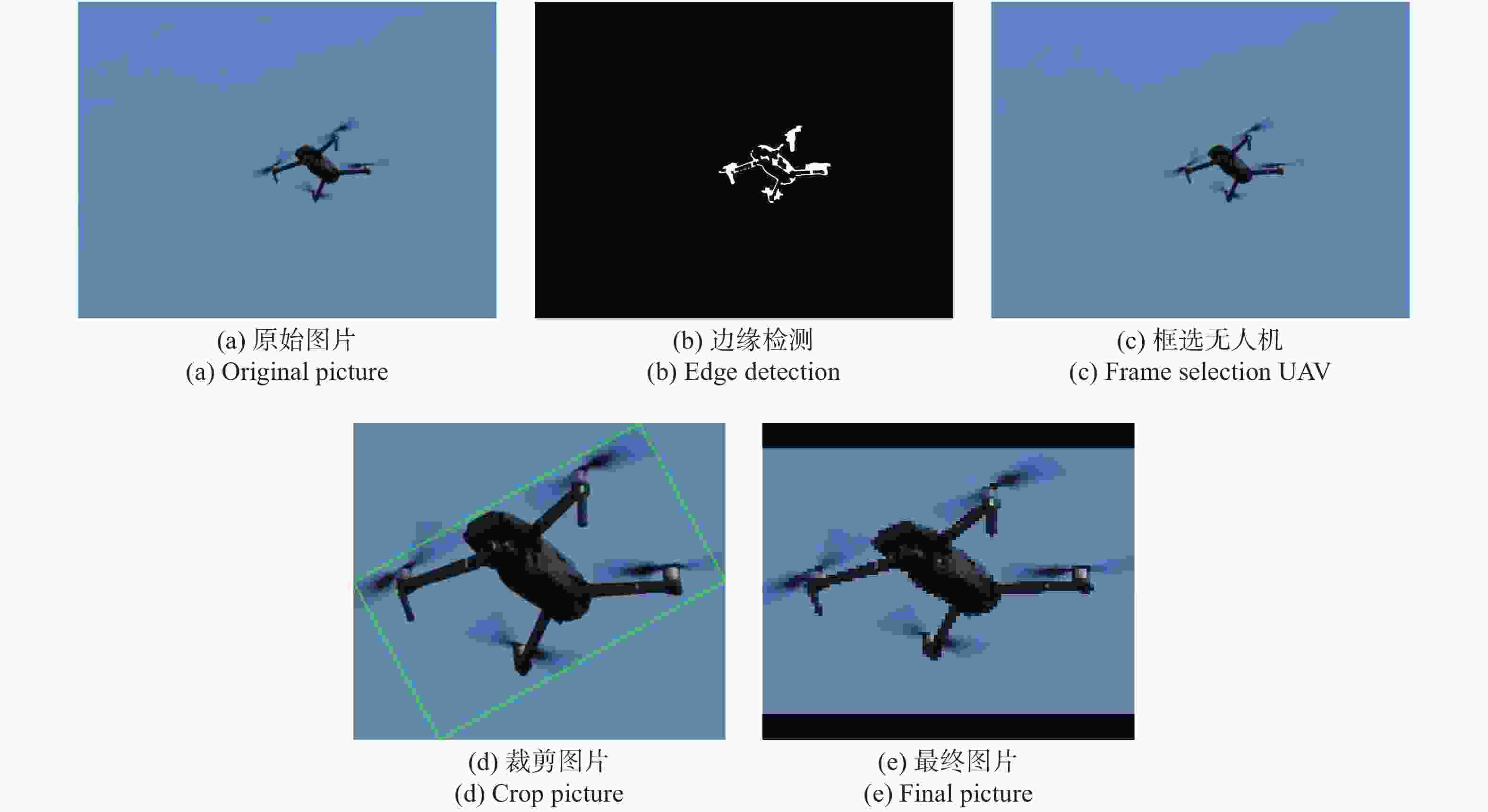
对采集的无人机样本首先进行预处理,即将图片缩放。将图片缩放至卷积神经网络要求的大小(100×100)。由于原始拍摄的图片宽高比不是1:1的,而且无人机所占图片的比例过小,所以不能直接把图片缩放至100×100,这样会使无人机发生形变,丢失原来的特征信息,导致识别的准确率降低。为此,对图片进行边缘检测,把图片中的无人机检测出来,去除大部分无关背景;然后,对裁剪下来的无人机图片进行缩放,缩放时保持原图片的宽高比,空白信息填充像素“0”(即为黑色),缩放过程如图2所示。
-
由于采集的样本数量较少,所以要对原始数据集进行扩增,常见的数据扩增方法有图像平移、图像旋转、图像镜像、图像亮度变化、图像裁剪、图像缩放、图像模糊等。为最大限度地保持原始图片的特征信息,采用图像旋转的方法来进行数据扩增,分别对图片进行顺时针90°、180°、270°的旋转(如图3所示),数据扩增后的数量如表1第3列所示。
-
由于数据集图像中目标的相似度较高,所以在对卷积神经网络进行训练前,要对数据集进行主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)的白化处理,来降低输入的冗余性[5],并且使得属性自身的方差尽可能大,而属性之间的协方差尽可能小,从而加快神经网络的学习速率。PCA作为一种典型的降维方法,它不仅能够搜索主要成分,还能够降低数据中的噪声,被广泛应用于识别领域。PCA算法的主要步骤如下:
计算样本的协方差矩阵如下式所示:
式中:n为样本个数;
${{{x}}}^{\left({{i}}\right)}$ 为经过零均值化的样本。计算协方差矩阵
${\rm{\varphi }}$ 的特征值及对应的特征向量,组成矩阵V如下式所示:式中:p为特征向量的总数;
${{{v}}}_{11}$ 为矩阵中向量对应的最大特征值;${{{v}}}_{22}$ 是次特征向量对应的最大特征值,依次类推。主成分个数的选择,选取主成分的个数q时,q的取值可以由保留的方差百分比
${{\alpha }}$ 来决定,${{\alpha }}$ 由下式所得:据以往的经验,应该保留99%以上的方差,即q的取值应为
${{\alpha }}$ ≥0.99的最小值。白化PCA白化后的数据如下式所示:
式中:
${{{x}}}_{rot,{{i}}}={{{{v}}}_{{{i}}}}^{{\rm{T}}}{{{x}}}_{{{i}}}$ ;${{\rm{\lambda }}}_{{{i}}}$ 为协方差矩阵${\rm{\varphi }}$ 的特征值;${{\rm{\beta }}}_{{\rm{P}}{\rm{C}}{\rm{A}}{{\rm{white}}}{,{{i}}}}$ 为经过PCA白化后的数据。 -
支持向量机和卷积神经网络都属于神经网络,是神经网络中的不同模型。两者都可以运用于图像识别,但是两者的识别原理,方法和效果都不同。
-
SVM是以最优化理论为基础来处理机器学习的方式。它的提出主要是用来解决两类分类的问题,在两类中寻找一个最优超分平面将两类分开,来提高分类的正确率。能使两类正确分开且使两类之间的距离最大的分类平面称为最优超平面,其方程记为:
对其进行归一化,使得样本:
满足约束条件:
支持向量机实现非线性分类是通过某种事先选择的非线性映射(核函数)将输入向量映射到一个高维特征空间,在这个空间中构造最优分类超平面。使用SVM进行数据集分类工作的过程中,首先通过预先选定的一些非线性映射将输入空间映射到高维特征空间。
变换后空间的分类平面为:
优化方程为:
式中:
${a}_{{{i}}}$ 为约束的拉格朗日乘子,$[{{\varphi }}\left({x}_{{{i}}}\right),{\varphi}({x}_{{{j}}}\left)\right]$ 是变换后的空间内积,此时,并不知道${\varphi}\left({x}\right)$ 的具体形式。所以在原空间构造一个函数${K}({x}_{{{i}}},{x}_{{{j}}})$ 使之等于变换后空间的内积运算$[{\varphi}\left({x}_{{{i}}}\right),{\rm{\varphi }}({x}_{{{j}}}\left)\right]$ ,通过非线性变换将样本数据映射到高维甚至无穷维空间,并在高维空间中构造最优分类超平面。但是,在求解最优化问题和计算分类平面时并不需要显式计算该非线性函数,甚至不需知道其具体形式,而只需计算函数${K}({x}_{{{i}}},{x}_{{{j}}})$ ,即核函数${K}({x}_{{{i}}},{x}_{{{j}}})$ ,因此支持向量机核函数的选择非常重要。经过对比分析,选用线性核函数,其公式为:SVM在解决小样本,非线性,高维数,局部极小值的图像识别的问题中表现出特有的优势,因此适合自制无人机数据集的识别。
SIFT(Scale Invariant Feature Transform) 是一种具有尺度不变性和光照不变性的特征描述子[5],也同时是一套特征提取的理论。SIFT特征对旋转、尺度缩放、亮度变化等保持不变性,是一种非常稳定的局部特征。因此,可以通过对图片提取SIFT特征作为SVM分类器的输入向量进行图片识别。主要识别步骤如下:
(1)按图片类别抽取训练集中所有图片的SIFT特征。
(2)将SIFT特征向量作为样本向量即可构建SVM的训练数据和测试数据。
SVM在面对小样本图像识别具有一定的优势。无人机图像的识别属于小样本识别,运用SVM可以很好地识别无人机样本。
-
输入层是用于数据的输入,经过输入层后会输出一个矩阵作为卷积层的输入值。文中的输入数据是100×100的RGB图像,以便进行卷积操作。
-
卷积层是通过一个
${X}\times {X}$ 的卷积核在输入层或者采样层图片的相应区域内进行局部感知[6],并提取出对应的局部特征,输入表达式如公式(5)所示。文中采用的卷积核是3×3,步长设置为1,卷积时考虑边界,不足的时候用0去填充周围。式中:
${{{z}}}_{{{j}}}^{{{l}}}$ 是卷积层的输出值;${{{x}}}_{{{i}}}^{{{l}}-1}$ 为第${{l}}-1$ 层的第i个特征映射图的激活值;${{{R}}}_{{{j}}}$ 为${{l}}-1$ 层对应${{l}}$ 层的第${{j}}$ 个映射图的映射图数量;${{{W}}}_{{{i}}{{j}}}^{{{l}}}$ 为第${{l}}$ 层的第${{j}}$ 个特征映射图与第${{l}}-1$ 层的第i个特征映射图相连的卷积核;${{{b}}}_{{{j}}}^{{{l}}}$ 为第${{l}}$ 层的第${{j}}$ 个特征映射图的偏置。 -
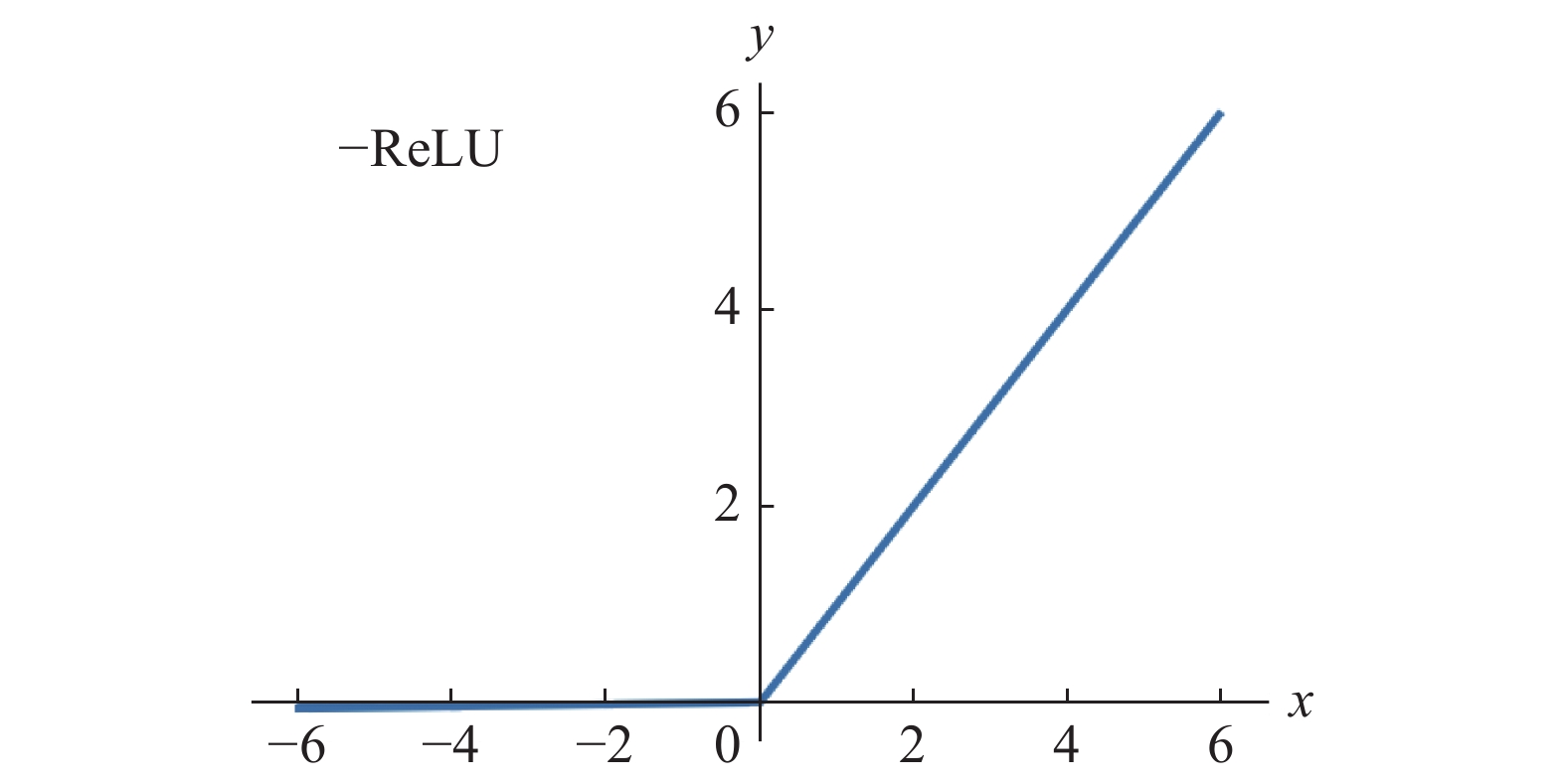
激活函数层主要对卷积层的输出进行一个非线性映射,由于卷积层的计算是一种线性计算,通过激活函数层的激励函数来加入非线性因素的,来增加模型的表达能力。文中使用的是ReLU激励函数(如图4所示)[7],其表达式如公式(6)所示:
-
池化层主要进行下采样,对特征图稀疏处理,减少数据运算量,加快模型的计算速度,同时也有减少过拟合的作用。常用的池化方法主要有最大池化和均值池化[8],文中运用最大池化方法,这样有利于保留更多的纹理信息和保证整个特征的稳定性。
-
全连接层可以看作是卷积、池化操作之后,将局部特征重新进行拟合,由于用到了全部的局部特征,故叫做全连接。文中设置2层全连接层,增强特征表达能力。
-
文中使用的是softmax分类器[9],它把一些输入映射为0~1之间的实数,并且归一化保证和为1,因此多分类的概率之和也刚好为1,其表达式如公式(14)所示:
式中:
${{{v}}}_{{{i}}}$ 是全连接层的输出;i表示类别索引;总的类别数为c;${S}_{i}$ 表示的是当前元素指数和的比值。 -
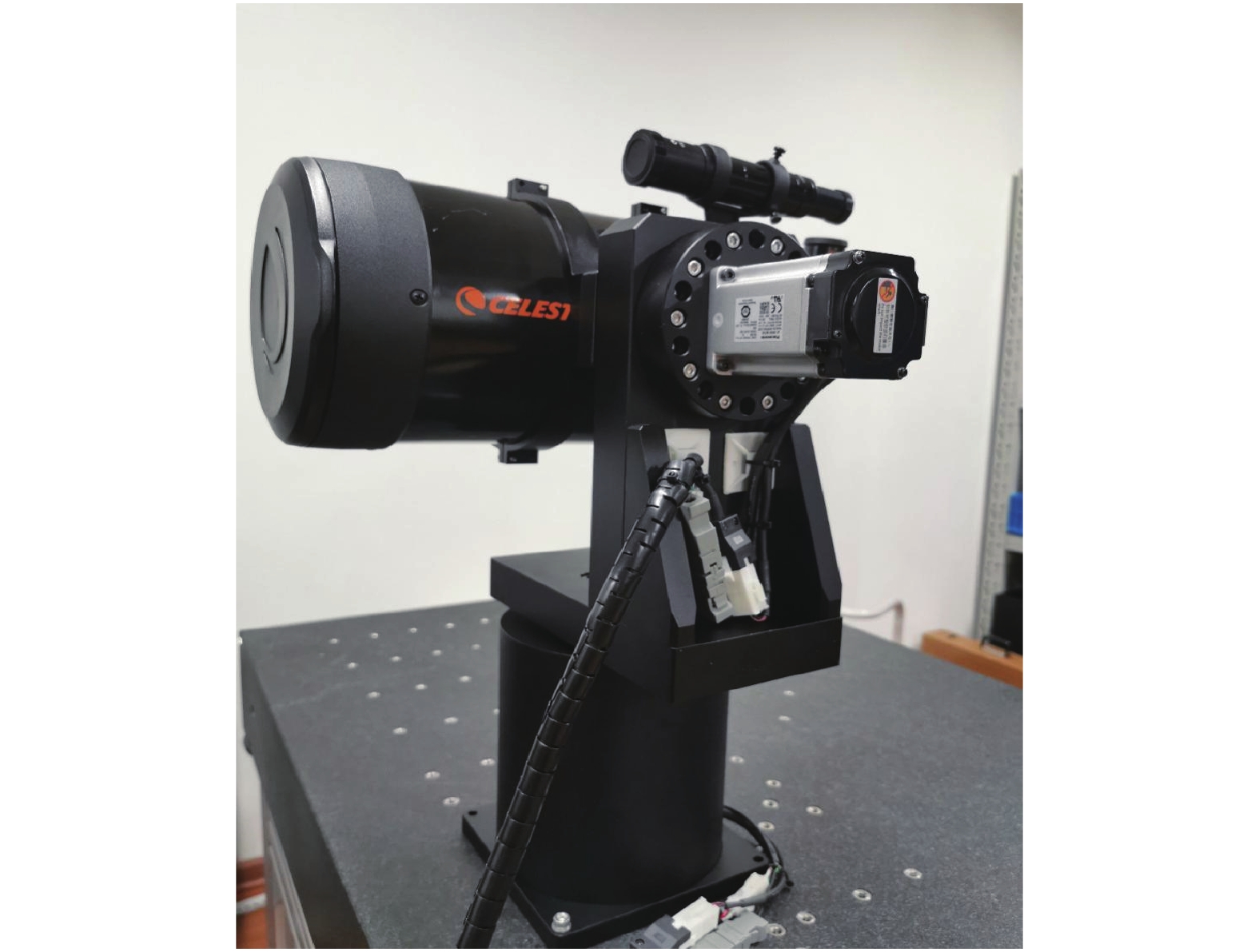
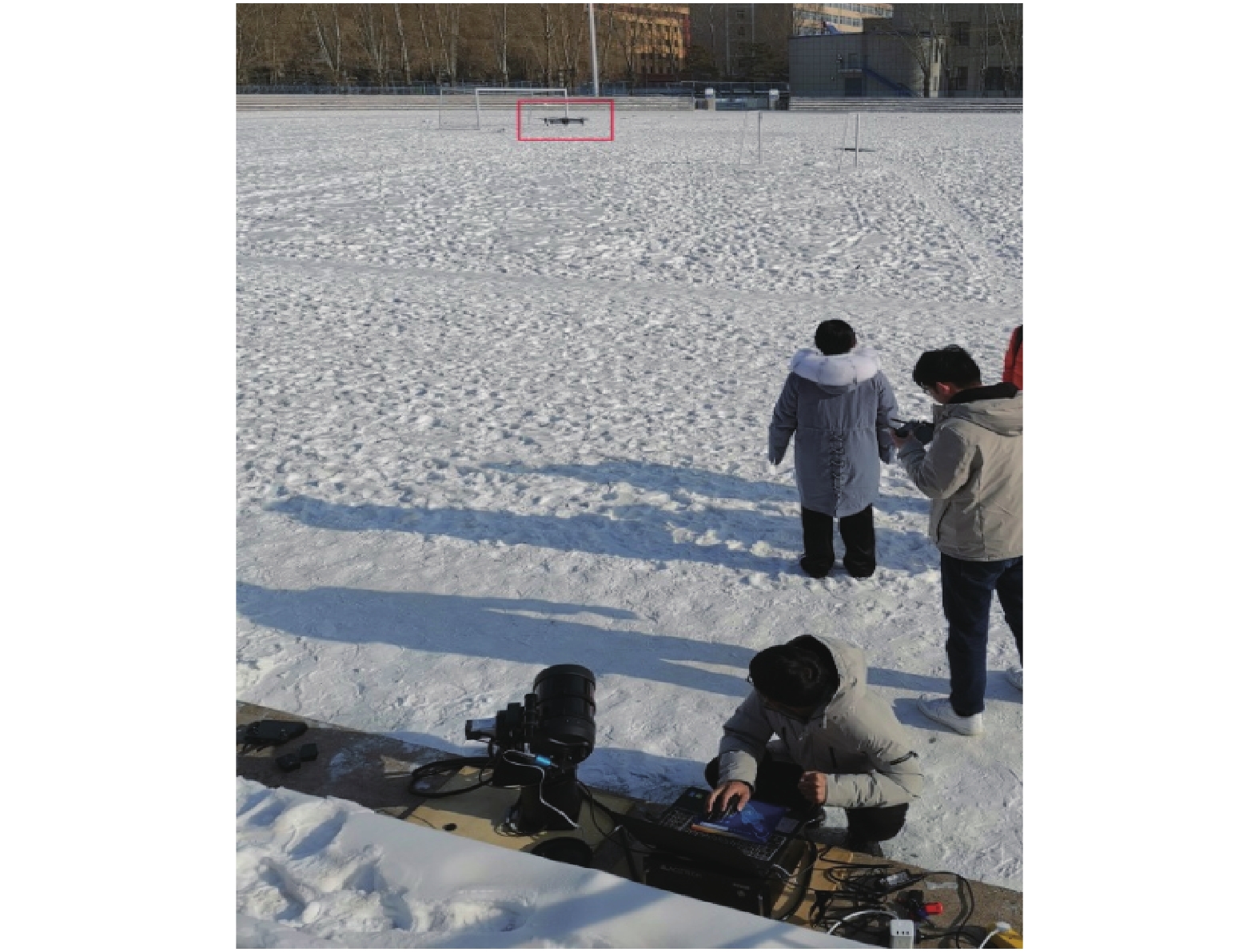
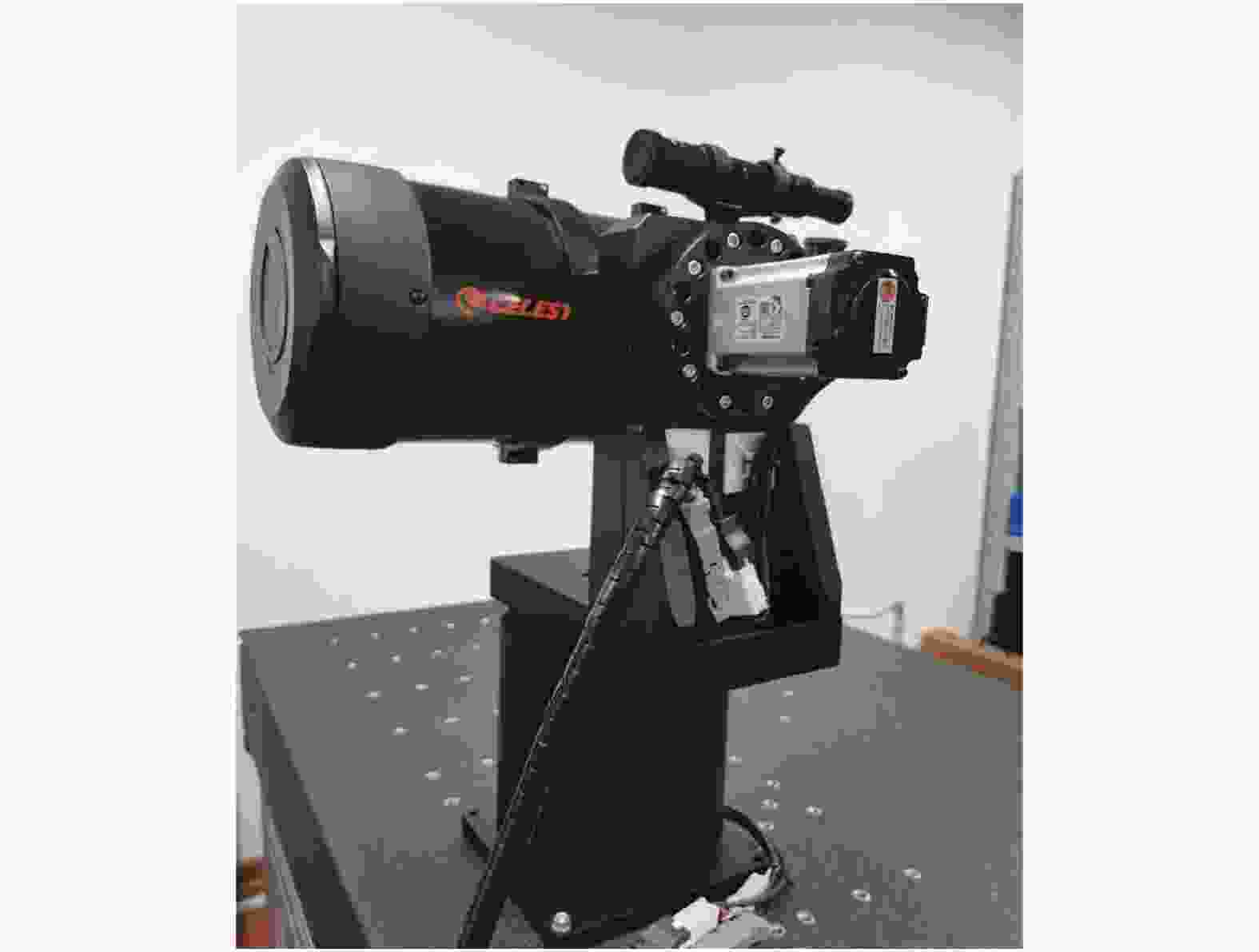
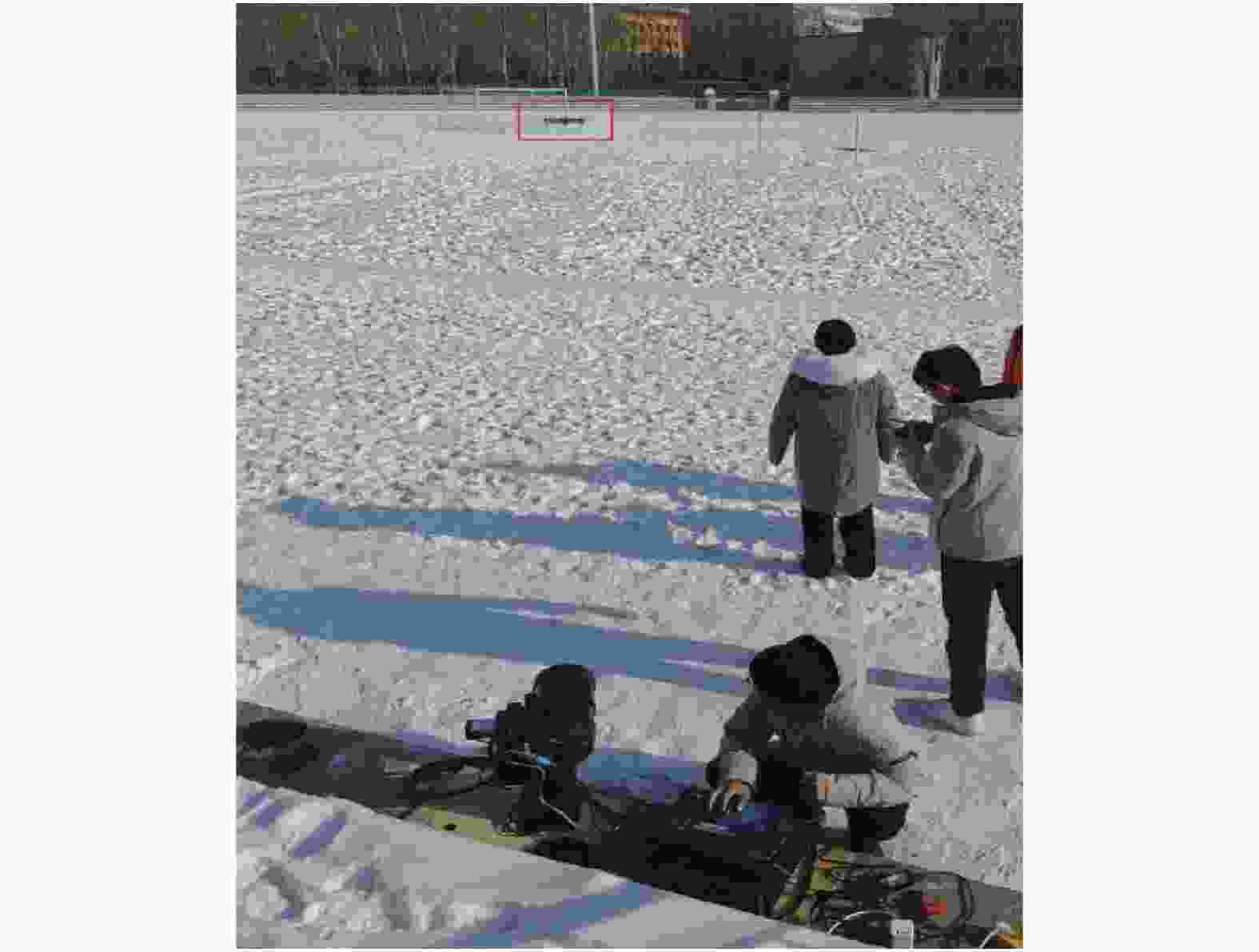
无人机样本图片是在长春理工大学操场运用自制光学系统(如图6所示)进行采集的(如图7所示),自制光学系统主要包括2轴伺服转台,反射式天文望远镜,彩色高清CMOS相机。此光学系统可以采集1000 m范围内的无人机图像,并将图片传给上位机进行处理。
-
文中实验采用的计算机环境是Windows 7系统Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-5500U CPU@2.40 GHz,16G内存,基于开源深度学习框架Tensorflow,采用Python3.7编写,代码运行平台Sublime。
-
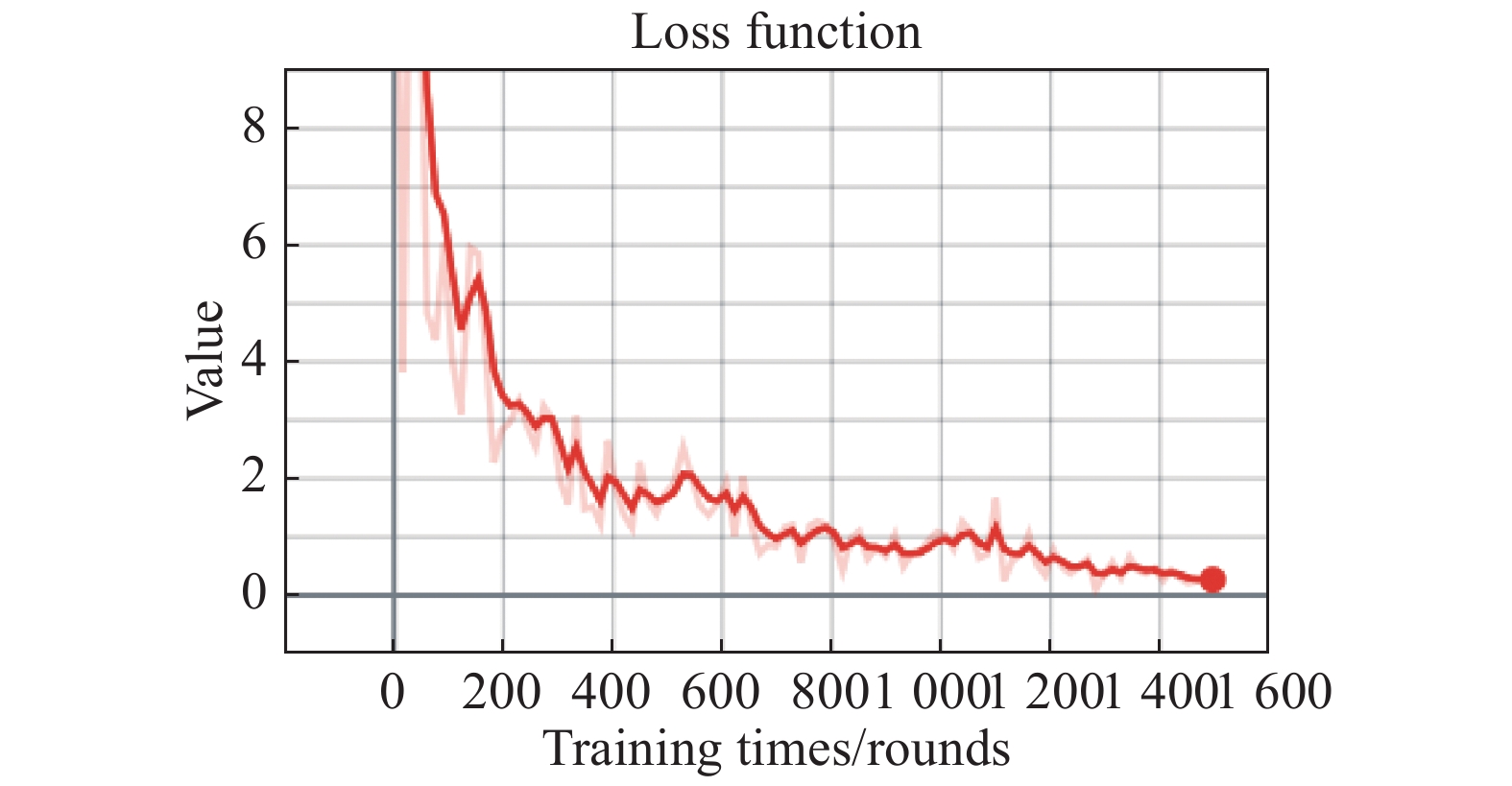
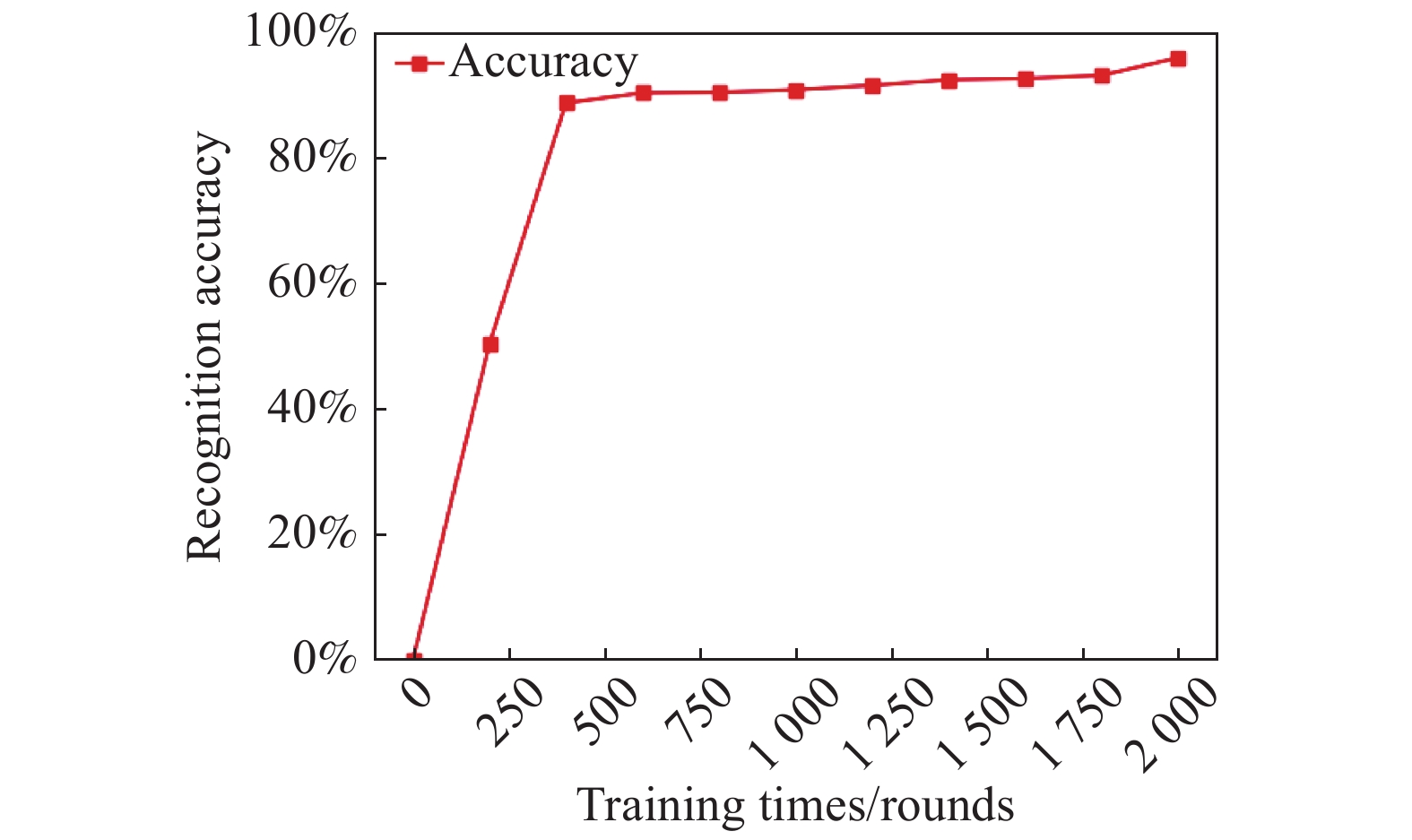
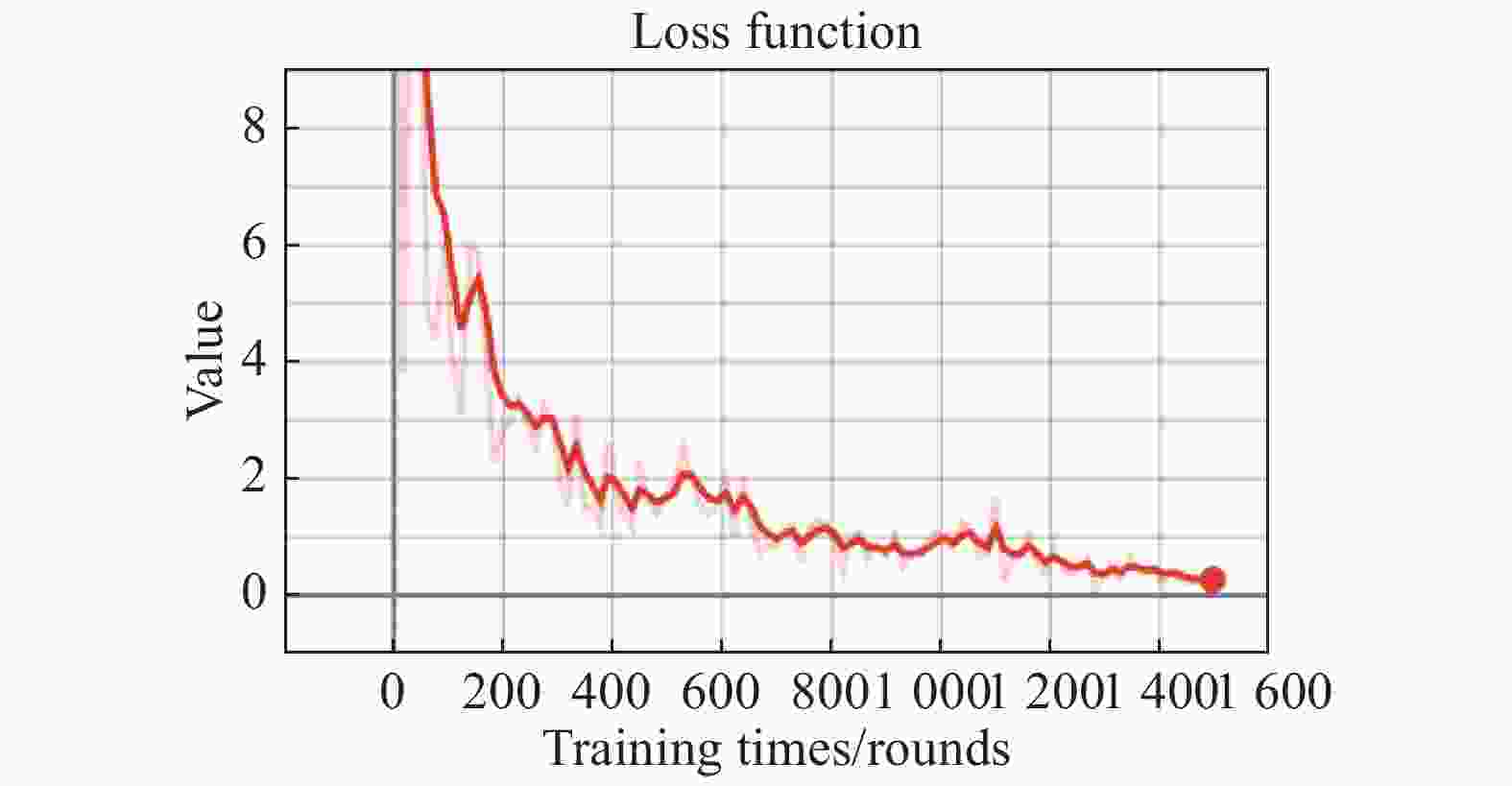
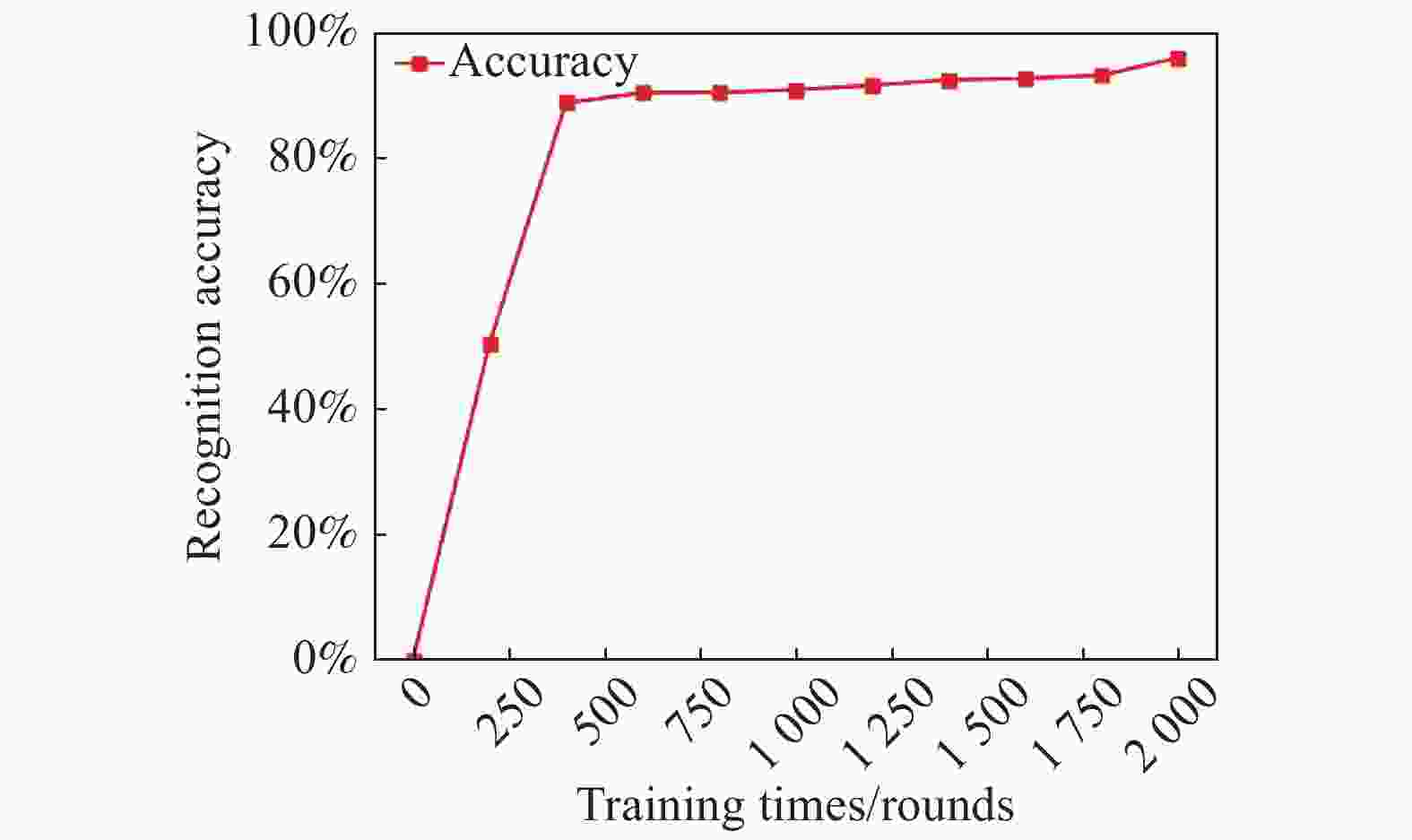
神经网络的识别的好坏不仅与网络的参数结构有关,而且与训练的次数有很大的关系;随着次数的增多,损失函数不断降低(如图8所示)[11-12],直到达到最优,同时识别的准确率不断地提升(如图9所示),经过2 000次的训练模型的准确率达到了95.9%。
-
为防止数据集训练时出现过拟合,在最后一层池化层后,加入了Dropout层。Dropout层设置的参数会很大程度上影响训练的结果,因此将参数分别设置为0.4、0.5、0.6、0.7,比较这四种参数,结果表明当参数设置为0.5时(如表2所示),训练的准确率达到95.9%,较其他三种参数有了很大提高。
Parameter setting Recognition accuracy 0.4 90.2% 0.5 95.9% 0.6 93.3% 0.7 88.4% Table 2. Results of different parameters of Dropout layer
-
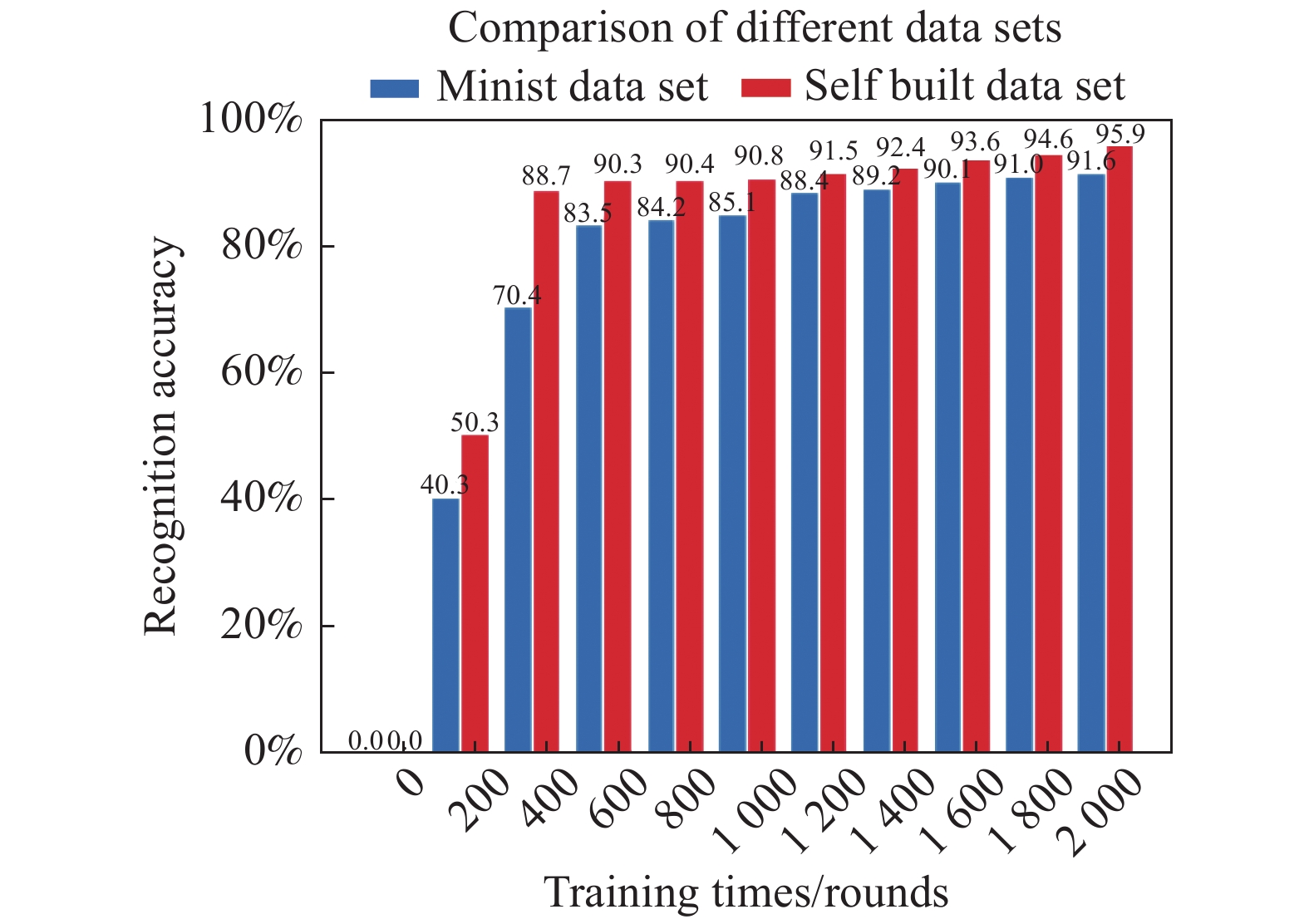
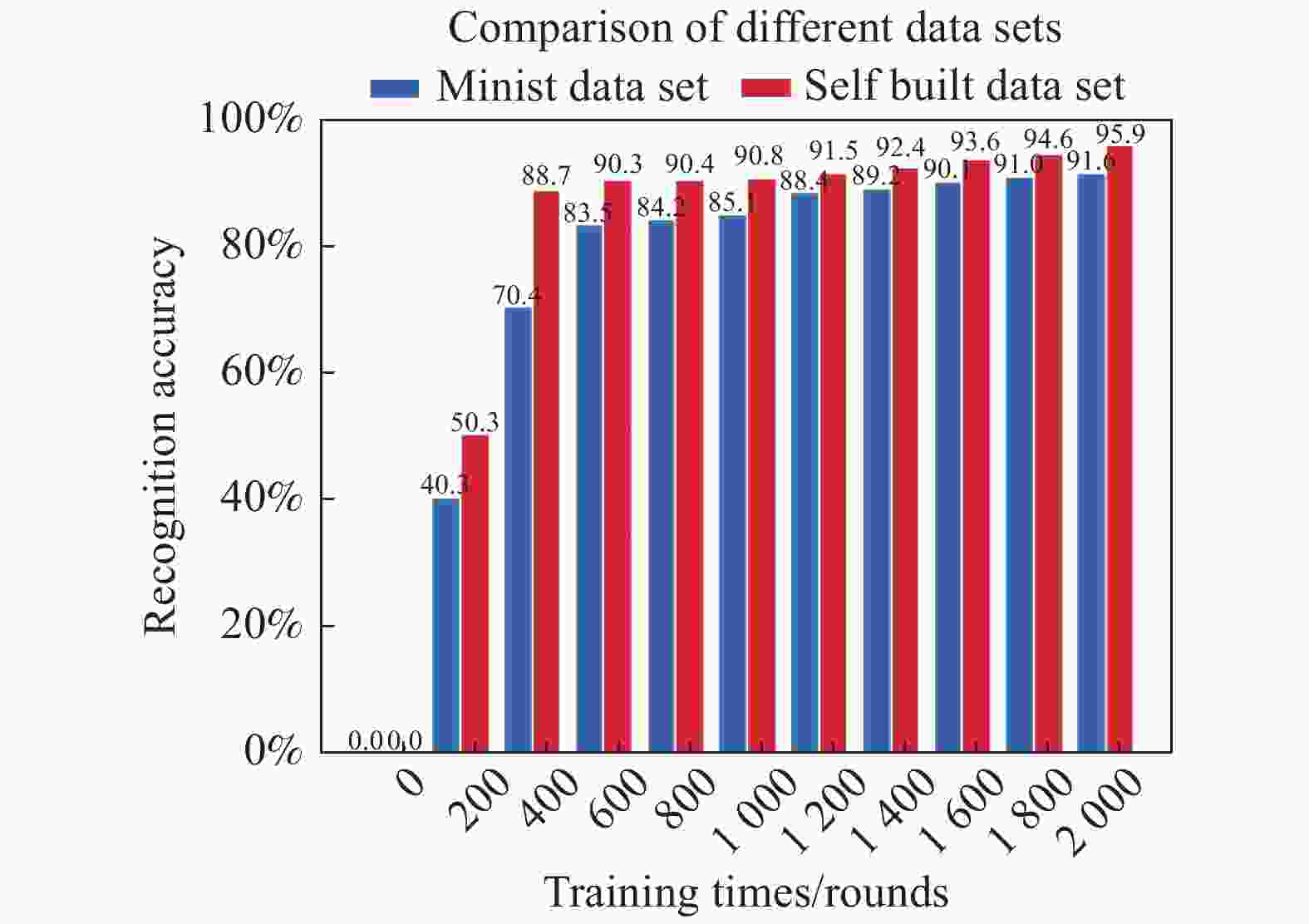
为验证文中所设计的卷积神经网络可行性,除在自行建立的数据集上进行测试外,还在MNIST数据集进行测试,MNIST数据集作为一个非常有名的手写体数字识别数据集,许多神经网络训练都会使用它[13]。实验结果表明(如图10所示),设计的卷积神经网络具有很高的可行性和较强的鲁棒性。
-
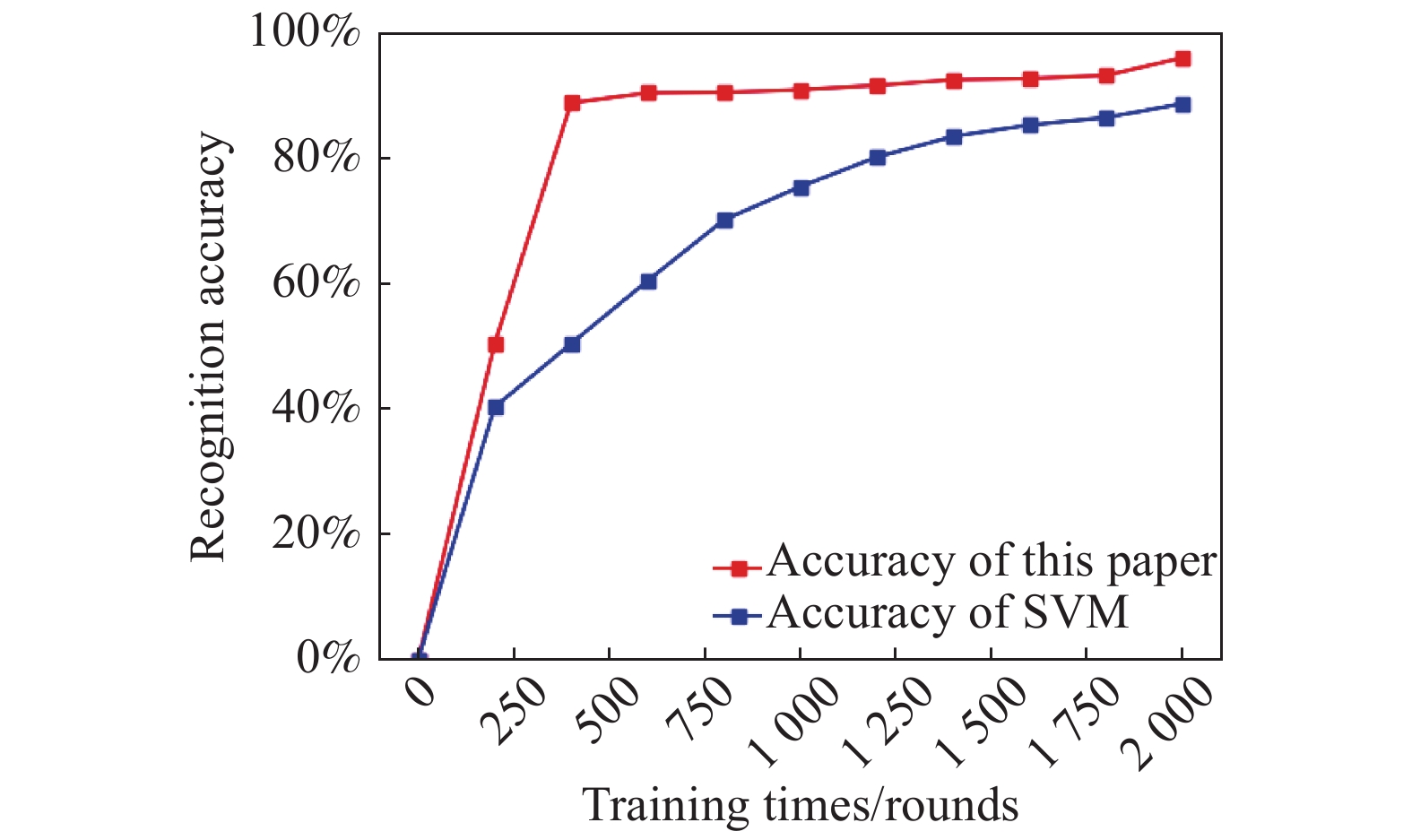
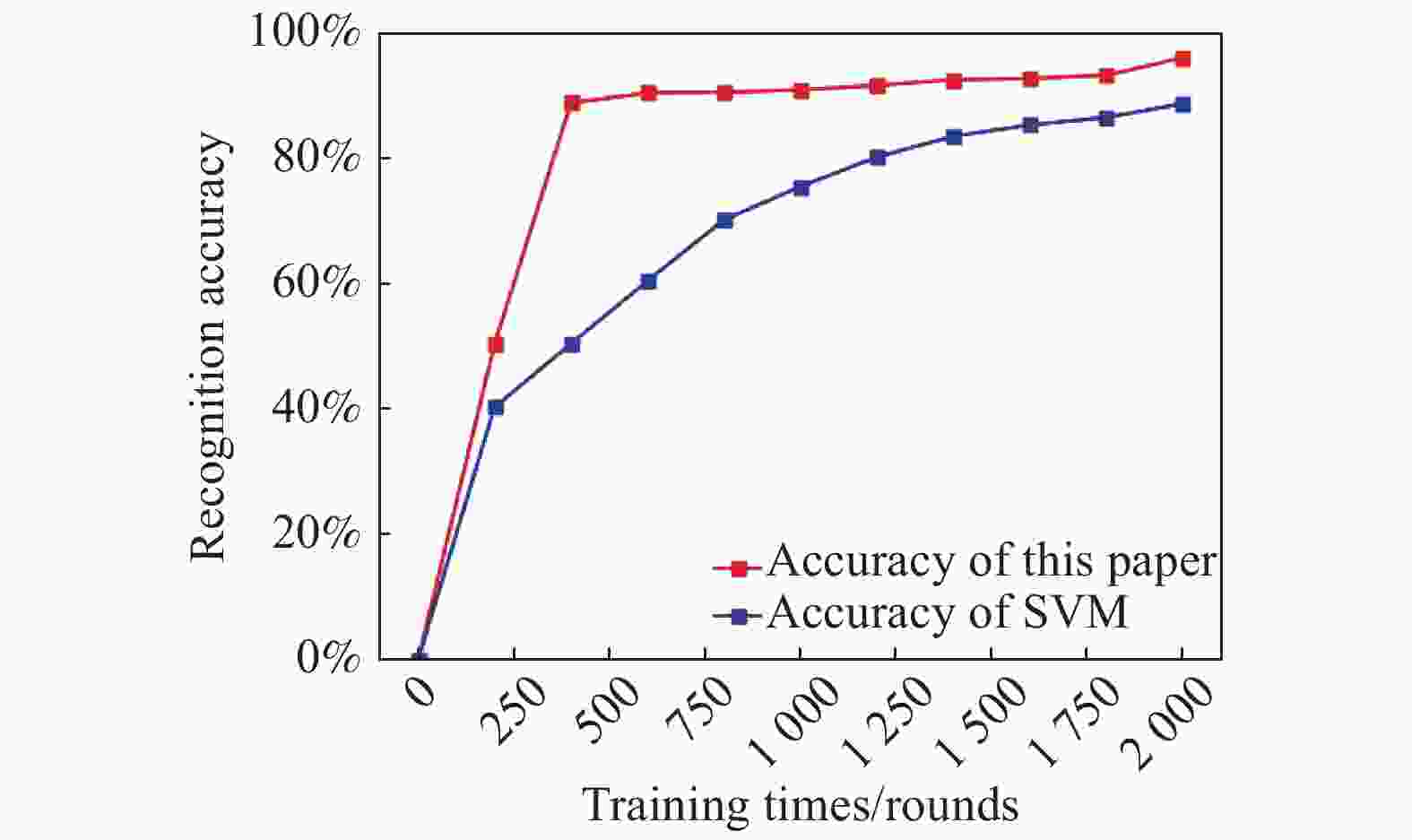
文中除使用设计的卷积神经网络模型外[14],还使用支持向量机(SVM)识别方法进行识别。由于在小样本的情况下,文中设计的卷积神经网络识别准确率为95.9%,支持向量机识别准确率为88.4%(如图11所示),经过对比(如图12所示)表明文中设计的卷积神经网络模型优于支持向量机。
-
综上所述:得出如下结论:
(1)针对反无人机系统图像识别“黑飞”无人机的问题,提出了一种运用卷积神经网络识别无人机的方法。运用自制光学系统采集了无人机图像样本;设计了针对无人机图像样本的卷积神经网络。
(2)分别运用支持向量机和设计的卷积神经网络识别无人机图片。实验结果表明基于卷积神经网络的识别方法的识别准确率更高。
(3)运用所设计的卷积神经网络分别识别了MNIST数据集和采集的无人机样本,识别结果表明运用卷积神经网络识别无人机样本具有可行性。



















































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: