-
目前用于惯性约束聚变研究的高功率激光装置如美国的国家点火装置(NIF)、法国兆焦耳激光装置(LMJ)等均采用了氙灯泵浦钕玻璃片的400 mm口径片状放大器系统[1-3],钕玻璃片与主激光呈布儒斯特角放置,可提供400 mm×400 mm的正方形通光口径,可将百mJ量级的1053 nm种子光放大至20000 J左右。钕玻璃片是片状放大器系统的核心组件之一,其特性参数对整个装置的激光输出特性有着直接而重要的影响:比如钕玻璃片掺杂浓度、吸收损耗、上能级荧光寿命、1053 nm线性折射率、受激发射截面、包边剩余反射率等激光物理参数将影响装置的增益能力[4-7];钕玻璃片波面质量、表面质量、光学均匀性、非线性折射率系数等将影响激光输出能量与光束质量 [8-10];钕玻璃片化学稳定性、损伤特性与包边寿命将影响整个装置的可靠性[11-13];钕玻璃的热导率、线膨胀系数等将影响装置的运行频率[14]。
文中介绍了用于高功率大能量激光装置的新型JG2钕玻璃片的增益与激光输出性能的实验研究结果,钕玻璃片尺寸为810 mm×460 mm×40 mm,其小信号净增益系数为5.37%/cm,小信号增益倍数为1.284倍/片/程,热恢复时间约为2 h,最高输出能量达到21.3 kJ/1053 nm。
-
JG2钕玻璃为典型四能级固体激光增益介质,主要用于脉冲激光放大,基本激光物理参数如表1所示,具有高储能、1053 nm吸收损耗低、非线性折射率系数低等特点,尺寸为810 mm×460 mm×40 mm,四周各有约12 mm厚度的包边用于吸收放大自发辐射荧光。
Parameter Value Typical size/mm3 810×460×40 Thickness of cladding glass/mm ~12 Coefficient of absorption of cladding glass
(1 053 nm)/cm−12.8±0.2 Nd concentration/1020 ions·cm−3 4.2±0.1 Cross section/10−20 cm−2 3.6±0.1 Fluorescence lifetime/μs 305 n linear refractive index (1053 nm) 1.520 n2 nonlinear refractive index/10−13 esu 1.05 Table 1. Main laser physical parameters of JG2 Nd:glass
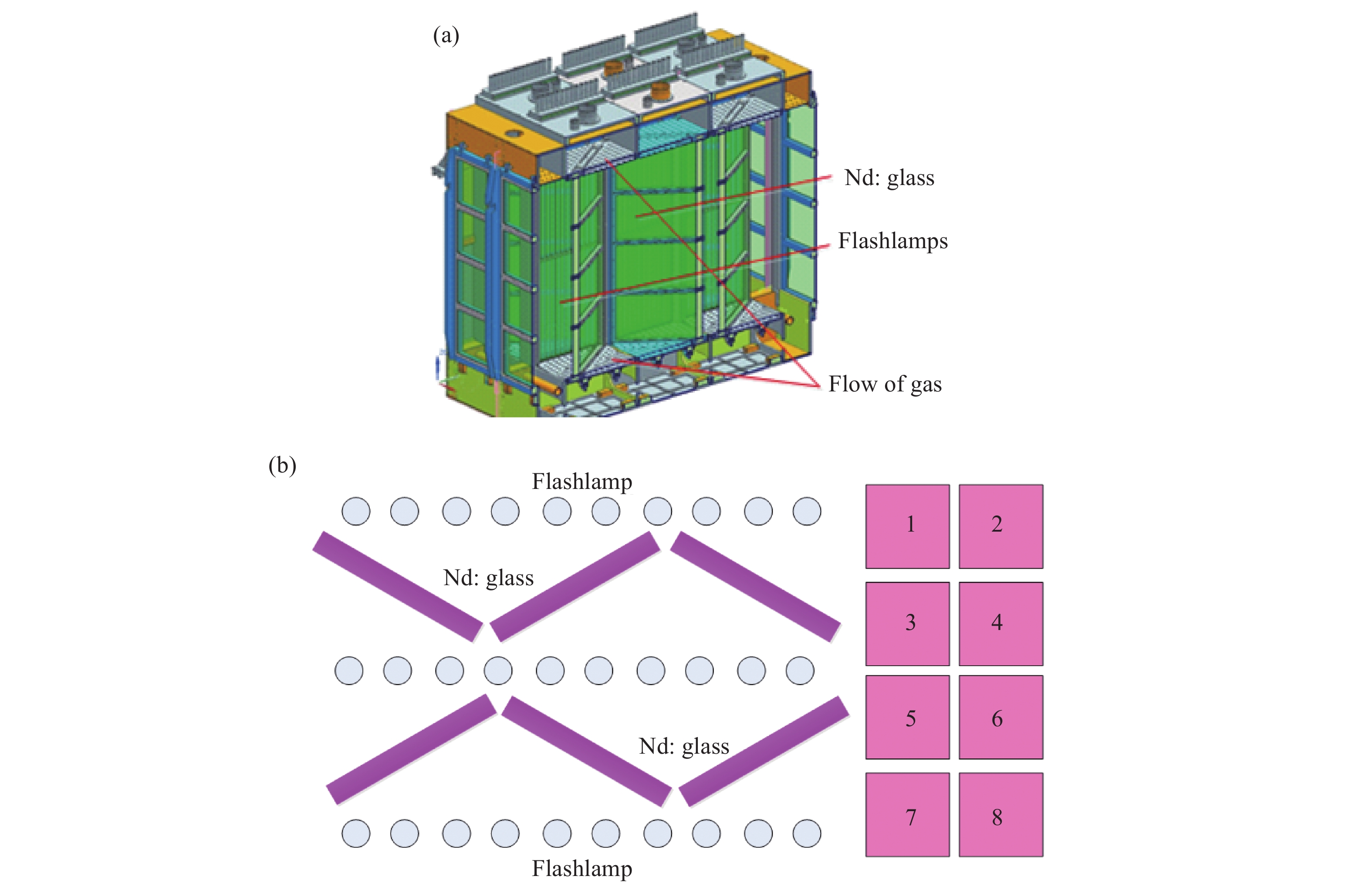
用于增益性能实验研究的装置为一组三片长的400 mm口径4×2组合式片状放大器, 如图1所示。放大器高度方向为四片钕玻璃片叠加,形成四个通光子口径,宽度方向有两个通光子口径,总体形成4×2的通光口径,氙灯从两侧对钕玻璃片进行泵浦。为提高氙灯光利用率,侧灯箱采用了镀银渐开线反射器,中灯箱采用了镀银菱形反射器,对400~1000 nm氙灯光平均反射率约为92%。隔板玻璃置于灯箱与钕玻璃片之间,镀有宽带的增透膜,对400~1000 nm氙灯光平均透过率约为96%。发次完成后气流从顶部至底部进行吹扫和冷却,实现洁净与热效应的快速恢复。装置基本方案如表2所示(1 Torr =133.322 Pa)。

Figure 1. (a) Scheme of the 4×2 multi-slab amplifiers (MSA) with 400 mm aperture and (b) section view of the MSA
Parameter Value Pre-ionized voltage/kV 26 Work voltage/kV 31 Peak current/kA 17 Delay between work and pre-ionization/μs 250 Current pulse width(10%-10%) 450 Flashlamp numbers every circuit 2 Pumping circuit numbers every amplifier 20 Flashlamp diameter/mm 37 Flashlamp arc length/mm 1 850 Flashlamp gas pressure/Torr 180 Table 2. Technical parameters of the scheme
JG2钕玻璃的增益储能动力学过程[15]如公式(1)所示。将整个钕玻璃片空间上划分为N个网格,整个泵浦过程分割为时间步长为
$\Delta {{{t}}}$ 的片段。钕玻璃激光介质在吸收氙灯辐射的泵浦光后获得泵浦储能(如公式(1)所示)的同时又以荧光形式随机向$ 4\mathrm{\pi } $ 空间辐射能量,在泵浦开始后t时刻介质单元$ \Delta {V} $ 的储能密度为$ {E}_{st}(x,y,{\textit{z}}) $ ,根据爱因斯坦关系,有一部分储能会以荧光形式衰减掉,在$ \Delta {t} $ 间隔内自发辐射荧光(SE)能量密度$ {E}_{SE}(x,y,{\textit{z}}) $ 如公式(2)所示。自发辐射荧光在经过另一体积元时,自发辐射光被放大(形成ASE),荧光的能量如公式(3)所示,此时初始储能密度变为$ {E}_{st} $ ,如公式(4)所示。式中:τ为钕玻璃上能级荧光寿命;
$ {\alpha }_{ns} $ 为钕玻璃介质对1053 nm工作波长的损耗系数,主要与材料本征特性相关;$ {g}_{0} $ 为瞬态小信号增益系数,与储能密度的关系如公式(5)所示:式中:σ为钕玻璃受激发射截面;h为普朗克常量;v为激光频率。
根据表2所示的技术方案及以上理论储能模型,计算JG2钕玻璃片38.6 mm厚度时小信号增益系数最高约为5.35%/cm,小信号增益倍数为1.281倍/片/程。
小信号增益系数实验光路如图2所示。利用一台单模激光器作为种子光,经过整形、扩束成为385 mm的方形光束通过片状放大器并经腔镜反射后返回,钕玻璃安装的表面法线与种子光的夹角为56.7°(布儒斯特角)。
利用能量卡计Ein处测注入能量,在能量卡计Eout处测输出能量。首先调整能量卡计位置使得本底为0(注入能量卡计与输出能量卡计在没有激光注入且放大器正常工作时读数均为0);然后测量静态(让激光通过放大器而放大器氙灯不工作)时的放大器的输入能量
Eini和输出能量Eouti,Eouti和Eini之比可得出静态透过率Ti,测试20组Ti取算术平均值,得到静态透过率T,如公式(6)所示: 最后测量动态(探针激光通过放大器且放大器氙灯正常工作)时的放大器的输入能量Ein和输出能量Eout,通过公式(7)可以得到六张钕玻璃片的平均小信号增益系数
$\;\overline \beta $ :六片钕玻璃的净增益倍数G用公式(8)进行计算:
小信号增益系数β定义为:
式中:n为钕玻璃的折射率,n=1.520;L为钕玻璃的厚度,三片JG2钕玻璃片平均厚度L=3.86 cm;N为激光经过的等效钕玻璃片数,N=6。系统运行于设计工作电压为31 kV时,测量光束口径为385 mm×385 mm,小信号增益系数为5.37%/cm,小信号增益倍数为1.28倍/片/程,储能密度达到0.282 J/cm3,与理论计算结果具有较好的一致性。
发次运行完成后利用洁净气体进行钕玻璃片吹扫冷却,气体基本参数为洁净度10级(ISO4级)、相对湿度低于0.1%RH、钕玻璃表面风速约为0.3 m/s,吹扫冷却时间为45 min。以2 h/发的频率连续运行六发,六片钕玻璃片累积的动态波前畸变稳定于1.4 λ±0.1 λ(λ=1053 nm)范围内,没有因多发次运行累积的残余热畸变,因此钕玻璃发次前已实现热恢复。
-
开展输出性能研究的大口径高通量验证实验平台为一台单束激光输出的激光装置,与美国NIF装置的一束激光类似,由前端、预放、空间滤波器、频率转换、片状放大器等分系统组成,其主要性能参数如表3所示。
Parameter Value Number of the laser beam 1 Laser aperture Square,max: 375 mm×375 mm Number of the amplifers Main amplifier: 9,booster amplifier: 7 Working voltage/kV Convention: 21 kV,max: 24 kV Work pattern Impulse work,the interval of
delivery is about 2 hOperating wavelength/nm 1053 nm,after the frequency
doubling is 351 nmTime waveform The typical working waveform is
square pulse, and the pulse can
be shaped arbitrarilyTable 3. Main characteristic parameters of Integration-Test-Bed (ITB) laser facility
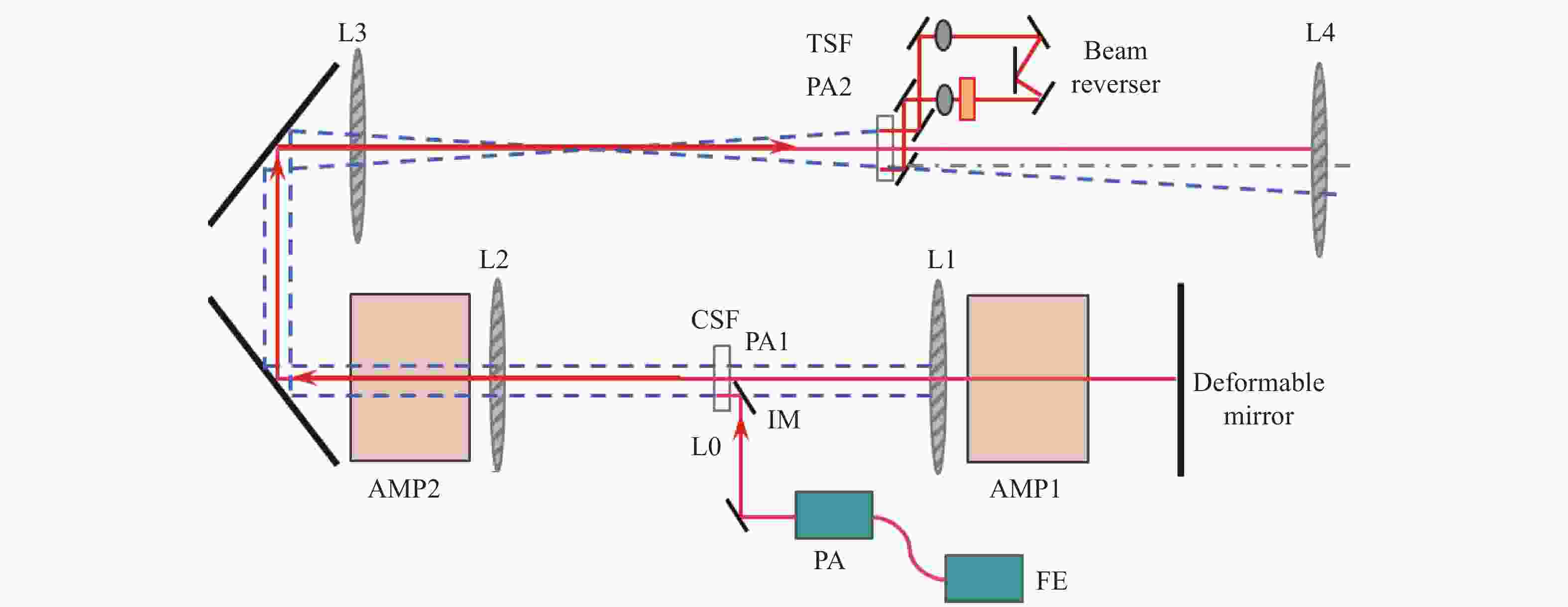
大口径高通量验证实验平台光路构型为“四程主放+三程助推”,如图3所示。从前端(FE)中产生的种子激光经预放大器(PA)放大后,经由注入透镜和SFL1透镜扩束后进入腔内放大器(Main),然后被变形镜(Deformable mirror)反射,第二次经过腔内放大器,随后经过腔内空间滤波器(CSF)首次进入助推放大器(AMP2)到达反转器(Beam reverser)进行光斑旋转90°后返回,第二次进入助推放大器和第三次进入腔内放大器,被变形镜反射后第四次进入腔内放大器,第三次进入助推放大器后经由传输空间滤波器(TSF)单向传输后滤波后输出。整个过程中,共计三次经过助推放大器,四次经过腔内放大器,等效经过57片钕玻璃。
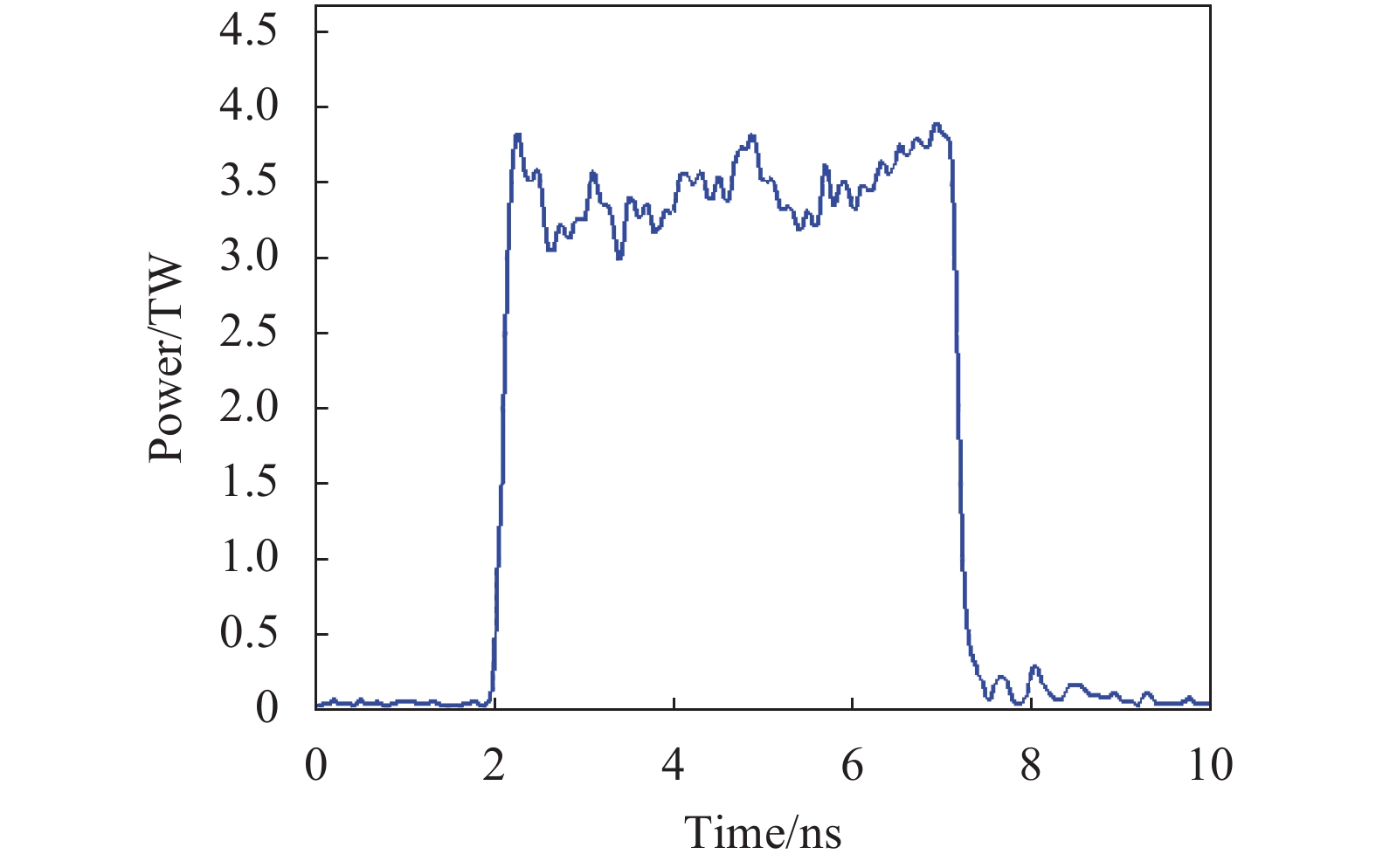
三片JG2钕玻璃片安装于助推放大器末级,在装置多程放大构型中等效为九片,其余位置为N41钕玻璃片。JG2钕玻璃具有储能密度大、损耗系数低、化学稳定性好等特点,而N41钕玻璃具有增益能力强、非线性系数低等特点,二者的激光物理特性接近于美国NIF 装置组合使用的LHG-8钕玻璃与LG770钕玻璃,可有效实现大能量激光输出。二者组合使用时,常规运行输出激光为18 kJ/5 ns/1053 nm方形脉冲波形,其典型脉冲波形与近场分布如图4和图5所示,近场调制度1.32∶1,近场对比度0.072,近场调制得到良好控制,最高输出能量达到21.3 kJ/1 053 nm。经过500余发次运行,JG2钕玻璃未出现包边玻璃破裂及包边胶层喷胶、脱胶等异常,钕玻璃片材料体内也未出现由于铂金颗粒、杂质、气泡等导致的炸裂等异常。
-
文中介绍了一种新型大口径JG2钕玻璃片的激光增益、热恢复与激光输出等激光物理性能的实验结果,达到了与美国NIF装置单束激光基本一致的性能,如表4所示。在400 mm口径4×2组合式片状放大器系统设计工作电压31 kV时,小信号净增益系数为5.37%/cm,小信号增益倍数为1.284倍/片/程,发次运行完成后利用风速为0.3 m/s的洁净气体进行冷却,热恢复时间约为2 h;基于JG2与N41钕玻璃片的优化组合使用,激光装置单束最高输出能量达到21.3 kJ/1053 nm,目前已稳定运行500余发。
Parameter JG2 NIF laser facility in USA(LHG8/LG770) Aperture Square,max:400 mm×400 mm Square,max: 400 mm×400 mm Nd concentration/1020 ions·cm−3 4.2±0.1 4.2±0.1 Cross section/10−20 cm−2 3.6±0.1 3.6±0.1(LHG-8);3.9±0.1(LG770) Fluorescence lifetime/μs 305 ≥300 Small gain coefficient/cm−1 5.37% ~5% (convention);~5.3% (max) Multiple of small gain/slab·pass−1 1.284 1.29 Energy density/J·cm−3 0.282 0.252 (convention);0.267 (max) Output energy for conventional operation/kJ (1053 nm) 18 18 Maximum output energy/kJ (1053 nm) 21.3 ~22 Thermal recovery time/h 2 h (Operating frequency of the device is 4 h) (Operating frequency of the device is 4 h) Table 4. Comparison of main performance parameters
Gain and laser output performance of JG2 Nd: glass in 400 mm aperture slab amplifier
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200461
- Received Date: 2020-11-30
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-02-08
- Publish Date: 2021-10-20
-
Key words:
- 400 mm aperture slab amplifier /
- small signal gain coefficient /
- laser output performance /
- experimental study
Abstract: The experiment result of gain performance of JG2 Nd:glass and the output of whole furniture was introduced which would be applied in 400 mm aperture slab amplifiers from high power inertial confinement fusion laser equipment. A 4×2 combined slab amplifier system of three-pieces-length and 400 mm-aperture was used to study the gain function. The gain and output experiment results of JG2 Nd: glass show that the small signal gain coefficient reaches 5.37%/cm, and the gain multiple of small signal is 1.284 times/pass when the system operating voltage is 31 kV. The thermal recovery time is about 2 h after cooling with clean and dry gas at a velocity of 0.3 m/s. Besides, experimental results acquired by Integration-Test-Bed (ITB) laser facility show that the optimal combination of JG2 and N41 Nd: glass reaches the maximum output energy of 21.3 kJ/1053 nm, and has been operated stably for more than 500 shots, without any faults such as abnormal cladding layer and material body damage.























 DownLoad:
DownLoad: