-
2011年,Cao提出了棱镜掩膜式多光谱成像系统 (PMVIS, Prism-Mask Multispectral Video Imaging System)[1-2],该系统采用空间信息复用的方法,通过空间维和光谱维双路信息获取,实现了高动态高辨率的光谱视频采集。相比传统扫描式光谱仪,不依赖于复杂光学和机械装置,可以更好适应新型平台的快速发展和搭载需求。目前首个比较成熟的PMVIS光学系统是中科院长春光机所刘冰在2015年设计研制的可见/近红外视频型成像光谱仪光学系统,该系统采用传统棱镜形式,实现了平均光谱分辨率为10 nm的设计[3],对进一步验证和推广PMVIS型光谱仪起到了重要作用。
为了使PMVIS更具实际应用价值,本文针对轻小型化这一核心要解决的问题,提出采用光栅优化分光方式以及光学系统精简优化设计等方法,实现了400~1 000 nm光谱范围下,平均分辨率小于5 nm,全视场MTF在奈奎斯特频率处平均调制传递函数(MTF)均大于0.4,系统光学总长度为165.36 mm,使光谱仪在高性能前提下更加趋于小型化。同时分析了新的分光形式可能带来杂散光的问题,最终信噪比为0.06,在光谱采集可容忍范围内。
-
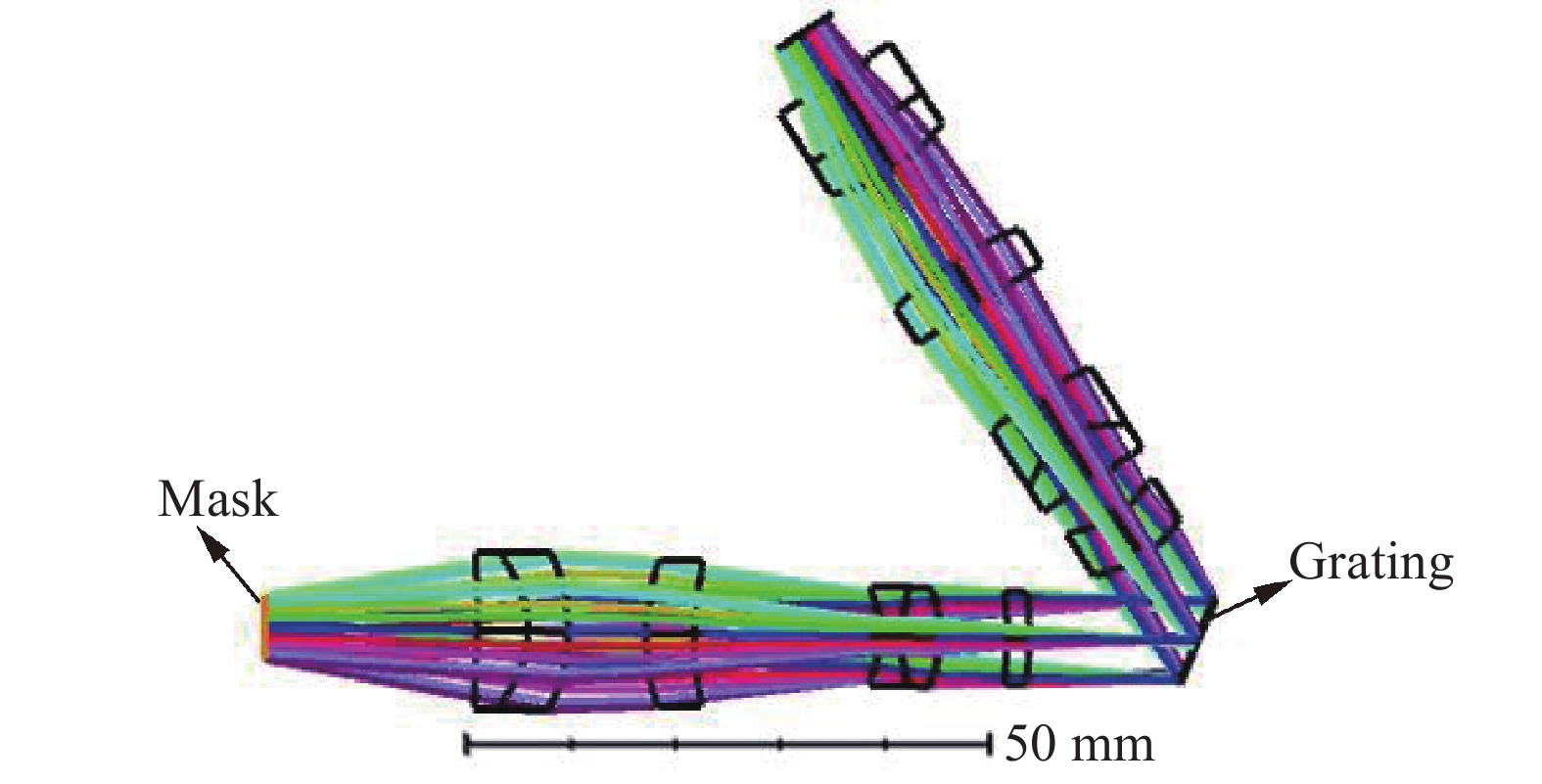
PMVIS系统包括1)物镜、2)分光棱镜、3)掩膜板、4)准直模块、5)分光模块、6)会聚模块六个部分。为了同时获取空间高分辨率的实时视频监控和高光谱分辨率,物镜对远处所成的像由分束棱镜按一定能量比例分为两路,两路系统具有相同的目标视场,如图1所示。一路透过分束棱镜进入RGB相机,生成目标的彩色视频,另一路通过分束棱镜的反射后,成像在掩膜板(掩膜板上刻有狭缝)上,再经过准直模块、分光模块、会聚模块后,进入灰度相机,生成含光谱信息的灰度视频图像,最后通过图像处理算法获得清晰的光谱视频图像。掩膜板的尺寸与RGB相机的靶面尺寸一致,保证光谱面和成像面具有相同的观察视场,用于实现光谱维和空间维的信息融合。
系统中物镜可以选择现有成熟的商业产品,而光谱分光光学系统较为复杂,设计难度较大,在整体中起决定性作用,因此本文主要承担的设计是光谱分光系统,物镜不作为本次研究重点。
棱镜的体积较笨重,其色散具有很大的非线性且不均匀,而光栅色散均匀,分辨率高,可以调制特定级次衍射光的出射角度和能量等特点,在小型化设计中具有极大的优势。因此在本研究中选择闪耀光栅作为分光元件,在保证色散的前提下,避免了二级衍射谱线干扰问题,并且折转光路有利于整个结构轻小型化。
光栅色散是衍射和干涉现象的综合作用,通过控制光栅常数d和光束入射角度θ来计算光栅刻痕密度,而光栅刻痕密度对光谱成像系统的光谱分辨率起决定性作用,光谱分辨率会随着光栅刻痕密度的增大而增大,光栅刻痕密度满足光栅方程:
因光栅衍射角度θ的限制,且光栅的刻痕密度p为光栅常数d的倒数,则有[4-5]:
在公式(3)中,闪耀光栅工作衍射级次为一级则m=1。系统设计时为保证所有工作谱段都能达到光谱分辨率的要求,选用边缘条件λ=1 000 nm,由以上公式可计算出p≤1 000 lp/mm。光栅的总刻痕数目直接决定光栅的光谱分辨率,总刻痕数目大,光谱分辨率就高,总刻痕数目少,可覆盖更宽的工作光谱范围,则有:
式中:δλ为光谱分辨率;N为光栅的总刻痕数。在光谱系统的设计过程中,设计应用的光栅分辨率应高于光谱系统的光谱分辨率,系统工作波长在400 ~1 000 nm,根据需求分辨率达到5 nm即δλ=5 nm,则通过公式(4)得到N>200 lp。
经过上述计算,刻线数目太少则分光本领太低,刻线数太大又造成单一衍射级次光能不足,且后面光学系统体积会相应增大,为减小整体系统的体积以及现有商业产品规格,综合考虑之后,选择254 lp/mm的反射闪耀光栅[6],线宽约为3.9 nm,光栅的总刻线数选择2 032 lp,可计算光栅的尺寸大小约为8 mm。该系统选用灰度相机探测像元尺寸为3.45 μm。由经验公式(5)可以计算出会聚模块焦距f:
δ为分开的像元大小,经过计算选择会聚模块的焦距为30 mm。
光谱分辨率由准直模块前掩膜板的入射狭缝和分光模块的角色散率共同决定。文中所选用光谱维探测相机分辨率为2 480×2 048 pixel,像素尺寸为3.45 μm。因光谱带宽为600 nm,为实现平均光谱分辨率5 nm,理论上最低需要获取120个光谱通道,所以设置掩膜板上光谱维方向狭缝阵列为10个,可计算出每个狭缝宽度方向对应像素为2 480/10/120≈2 pixel,即狭缝宽度为6.9 μm。为使探测器能够接受到足够的能量,刻划狭缝大小为10×2像元区间,即34.5×6.9 μm2。
-
光谱分光系统采用反向设计思路,由探测器性能和光栅线对数计算会聚模块和准直模块设计参数。会聚模块的初始结构在专利结构中选择,较小的系统F数,可以保证得到的图像不失真也能保证接收到较多的光谱信息[7],会聚模块设计参数如表1所示。
Parameter Value Wavelength range/nm 400 -1 000 Pixel/pixel 2 480×2 048 Pixel size/μm 3.45 Focus of convergence module/mm 30 Grating notch density/lp·mm-1 254 F number 4 Resolving power/nm 5 Field angle/(°) ±7.5 Table 1. Convergence module system parameters
由于系统包含光栅元件,使得视场非对称,所以设计时设置全视场进行优化。为达到轻小型化的目的需控制镜片数量及大小,系统中存在较大的球差和色差,矫正难度高。因此系统使用两组胶合镜对色差及球差进行矫正,两片单透镜使用消色差材料。设计完成的会聚模块系统如图2所示。由此可以看出使用较少的镜片会聚模块仍达到良好像质且系统体积较小,满足轻小型化的目的[8]。
为保证与空间维视场一致,需要放大倍率为1,因此选用与会聚模块对称结构,系统参数如表2所示。同时为与光栅及会聚模块更好的拼接,准直模块设计要考虑到光瞳匹配以及装调等问题[9],准直模块光学系统采用像方远心系统。考虑到系统中光谱范围较大,会存在较大的色差,因此准直模块还需要重点校正色差。上述几个问题叠加在一起均增加了系统总体设计难度。设计完成的准直模块如图3所示。图3(a)为准直模块结构图;图3(b)显示在截至频率处MTF接近衍射极限;从图3(c)可以看出掩膜板处点列图光斑最大RMS为3.1 μm小于掩膜板狭缝宽度,满足对掩膜版空间分辨的的要求,同时系统像质良好,MTF接近衍射极限。
Parameter Value Wavelength range/nm 400 -1000 Focus of collimation module/mm 30 F number 4 Field angle/(°) ±7.5 Mask slit width/μm 6.9 Table 2. Collimation module system parameters
-
将准直模块、分光模块、会聚模块三部分进行拼接,这里着重考虑准直模块与会聚模块在分光面上的光瞳匹配问题,具体采用像方远心光路设计来实现。拼接后的系统整体结构图如图4所示。系统的焦距为−18.5 mm,F数为3.9。
图5(a)表示光学系统各波段传递函数(MTF)均大于0.4;从图5(b)中可以看出光学系统在1 000、700、500、400 nm处的分辨率分别为2、2、2、4 nm,在400 nm处达到最低分辨率,450 nm处分辨率可达3 nm,其余个波段均可达到2 nm分辨率;图5(c)中目标能量的80%包含在3.45 μm半径内,并且如图5(d)所示像面照度均匀高于0.9,图5(e)中畸变小于3%,光学系统像质良好。系统使用四个胶合镜组和四片单透镜完成设计,光学总长度为165.36 mm。
-
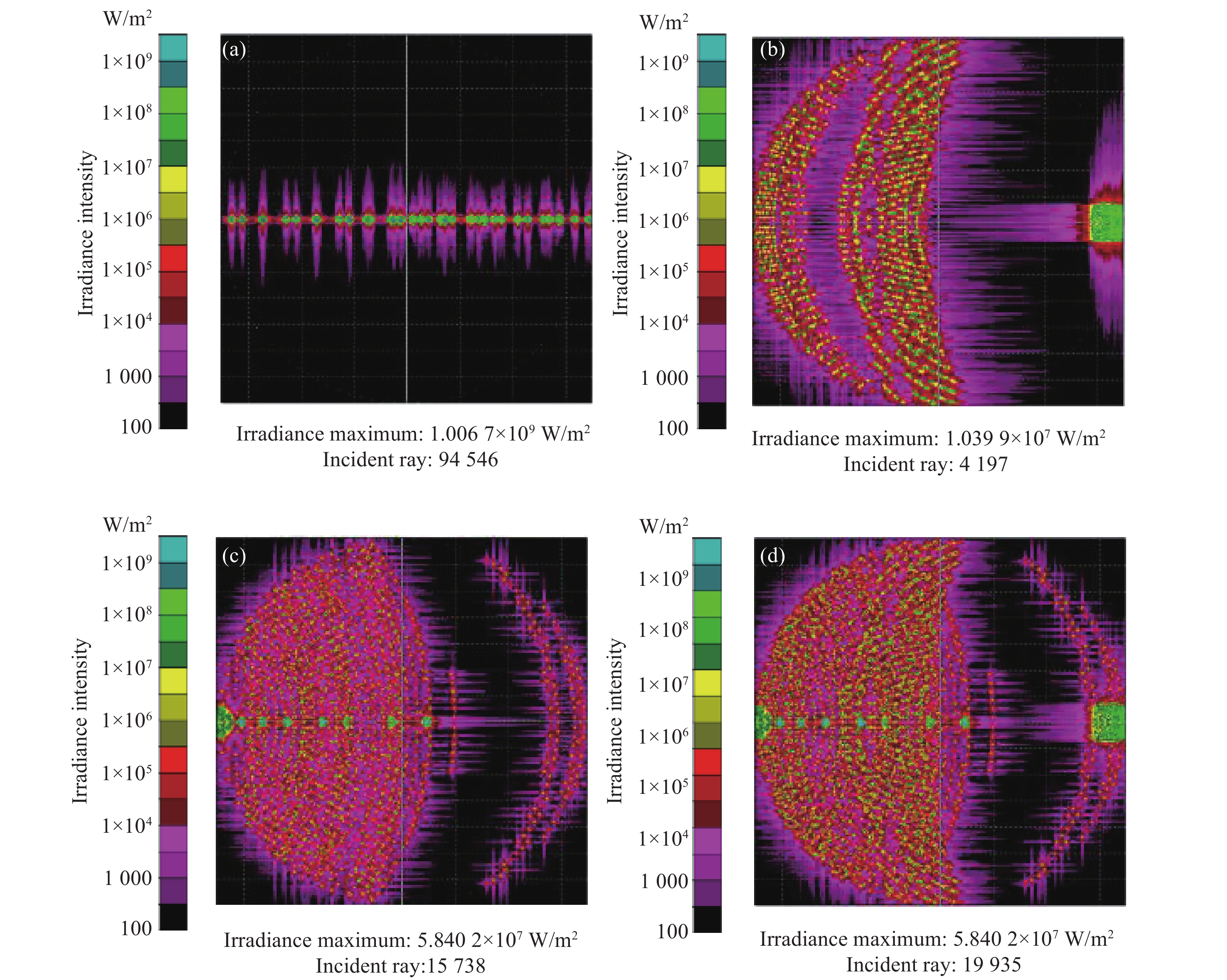
采用光栅作为分光元件的缺点是无用的衍射级次将产生杂散光对像面产生影响,即使是闪耀光栅也只有约80%的能量集中在工作级次,因此建立光学系统杂散光分析模型,分析光栅无用级次的杂散光影响。根据闪耀光栅目前的工艺水平,无用级次零级、二级的反射率均为为10%;光栅工作级次一级衍射反射率为80%。运用蒙特卡洛方法追迹光线127 939条,分析光栅无用级次产生杂散光对一级衍射的信噪比[10],到达像面的辐照度如图6所示。
Figure 6. Image surface irradiance analysis diagram. (a) First order diffraction; (b) Zero order diffraction; (c) Second order diffraction; (d) Zero order and second order diffraction
由图6可以看出无用级次产生的杂散光能量集中在工作级次,但由图6(a)可以看出工作级次到达像面的最大辐照度值为1.006 7e+009 W/m2;图6(b)零级衍射到达像面的最大辐照度值为1.039 9e+007 W/m2,能量主要集中在工作级次的右边;图6(c)二级衍射到达像面的最大辐照度值为5.840 2e+007 W/m2,产生的能量主要集中在工作级次的左边。图6(d)为零级衍射和二级衍射共同产生的杂散光最大辐照度值为5.840 2e+007 W/m2。可以分析出二级衍射对工作级次影响较大信噪比为5.8%,零级衍射的信噪比为1%,产生的杂散光在可接受范围之内。
-
文中设计了结构更为简单,重量更为轻便的轻小型掩膜式光谱分光系统。文中运用的模块化设计,简化的优化系统的环节,减小了各个部分像差的互相影响,使像质更为优良。在球面设计时使镜片数量的得到简化并且像质良好,使系统达到轻小型化的目地并进行杂散光分析验证了光栅在小型化的可行性。文中设计的系统平均分辨率均在4 nm以下,全波段MTF在奈奎斯特频率处平均调制传递函数(MTF)均大于0.4,系统光学总长度为165.36 mm,占空间面积为93 mm×6.4 mm,总重量30.32 g。并且具有结构简单,光谱分辨均匀,能量集中,便于携带等特点。
Light and small mask spectral optical system
doi: 10.3788/IRLA202049.0414001
- Received Date: 2019-12-02
- Rev Recd Date: 2020-01-09
- Available Online: 2020-04-14
- Publish Date: 2020-04-24
-
Key words:
- mask type /
- spectrometer /
- optical design /
- grating /
- miniaturization
Abstract: The mask spectrometer uses the beam splitter to separate the incident scene into two dimensions: spatial dimension and spectral dimension, then information fusion is used to achieve high spectral resolution of dynamic video signal acquisition. It has wide application value in the field of dynamic hyperspectral imaging. In order to solve the problem of miniaturization of mask spectrometer, for the part of the spectral optical system simplified design of the number of lenses, and the conventional prism was replaced by the grating, the linear dispersion was realized while the structure was further compacted. The problem of stray light generated by the unwanted stages of the grating was analyzed, and the feasibility of the system design was demonstrated. Finally, in the range of 400-1 000 nm, the spectral resolution was less than 4 nm, the average modulation transfer function (MTF) at the full field of view Nyquist frequency was greater than 0.4, and the image illumination uniformity was higher than 0.9, achieved good image quality. Meanwhile, the SNR generated by stray light was 0.06, which did not affect the collection of spectral information.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: