-
随着光纤入户的不断推进,我国光纤互联网的规模与日俱增,而对网络数据通畅和网络安全的需求也越来越高[1-3]。为高效维护光纤网络中的正常数据通信,研究网络异常数据快速识别方法具有重要意义。
针对光纤网络异常有多种检测方法,例如免疫算法(Immune Algorithm, IA)[4]、统计分类(Statistical Classification, SC)[5]算法、聚类分析(Cluster Analysis, CA)[6]算法、人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Network, ANN) [7]算法等。免疫算法将异常数据作为“抗原”提取其数据特征,从而形成具有针对性的选择依据,其具有收敛速度快、准确性高的优点,但通常适用于具有明显特征的异常数据类型,普适性差;统计分类算法是由大量数据统计结果分类得到的,对异常数据的特征要求不高,具有更好的普适性,但处理数据量大,仅适用于统计数据集合限定的异常数据类型;聚类分析算法对不完整、不精确数据具有较好的包容性,但其稳定性差,易受干扰;人工神经网络算法具有学习能力,可以通过自组织完成异常数据的分类,同样具有较好的普适性,但数据量增大时陷入局部极值的可能性大幅提升。可见,每种算法各有所长,而实际需求往往是在识别精度与算法收敛速度之间选取最优点。参考文献[8]采用抽样融合改进算法对光纤网络数据进行分段聚类,该种方法进行多次随机抽样,虽然解决了数据属性分类的问题,但是分段效率较低。参考文献[9]通过不平衡数据分类实现不同权重数据的聚类,达到了很好的数据分类效果,但趋势预测过程时间较长。
综上所述,为了实现异常数据的快速识别与精确定位,文中借助机器学习(Machine Learning, ML) [10]的交互功能将深度学习(Deep Learning, DL) [11]与遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm, GA)[12-13]相融合,利用GA扩展性好,对非线性数据包容性强的特点降低异常数据不确定性导致的识别困难,再通过DL的分类模式解决GA编码困难的问题,并利用DL自适应学习的特性提高算法的收敛速度。
-
由于光纤网络中数据量巨大[14],所以选择提取异常数据的合适范围对算法的时效性具有重要意义。由于异常数据与信号数据之间存在不相关的特性,所以采用相关运算可以完成对异常数据的鉴别,但是若对所有数据进行遍历对比时,计算量非常大,算法效率大幅下降,故文中采用深度学习技术完成异常数据特征的数据挖掘,完成对不相关数据剔除的降维处理。
首先对数据进行分段处理,对获取的光纤数据分段处理,将数据划分为五级,1级表示最大,5级表示最小,其中对于数据变化明显的敏感区域进行加权处理,利用组合和量化的手段完成数据提取侧重的偏向分析,这样可以在保证提取异常数据信息的同时降低算法运算量。对分段数据中所有数据点与故障状态条件的数据特征进行相关计算,当相关参数低于阈值时,将该数据点去掉,剩余数据构成相关数据集。
然后,构建相关特征邻域,由相关数据集采集的数据点特征计算得到,将相关数据集与特征集合并成光纤网络数据集合,其数据点就是网络故障变量参考值。再将数据集合中正常数据与异常数据之间的交界点作为焦点X,采用非线性离散的方法将数据分段,分段点可表示为:
式中:X为数据间的焦点;F为聚焦因子,F∈(0, 1);n为数据分段数。由此光纤网络中的数据经非线性离散成为2n+1份。
最后,将所有数据集合都通过非线性离散处理再统一单边取值,并以0值作为最优值,这样可以大幅提高故障数据的检出精度,提高数据挖掘精度。
-
在遗传算法模型[15]中,对交叉概率(Crossover Probability,Pc)与变异概率(Mutation Probability,Pm) [16]的设定直接决定了算法的解算效果,拟利用DL预处理完成数据分段,则在不同区间段中采用不同的Pc和Pm,从而实现个体适应度的自适应调节。这样由于不同分段数据具有不同的特性,而数据特征可以通过X和F进行表征,所以对Pc和Pm的赋值就具有针对性,避免了整体赋值时在分段数据中偏大导致不易收敛,而在另一些分段数据中偏小陷入局部最优的问题。在此设计思想的基础上,分别对应Kc和Km的调整参数有:
由此,Pc和Pm可表示为:
式中:X×Fn为其对应的分段区域;λ1,λ2,λ3,λ4为设置参数,取值范围为(0, 1];fmax为所选分段数据集合中适应度的最大值;f’为交叉运算中适应度更大一些的个体的适应度值;favg为群体的平均适应度值;f为待测个体的适应度值。由此可见,在不同的分段数据中采用不同的概率表征遗传特性,从而既保证了群体的多样性,又实现了算法的全局收敛。
-
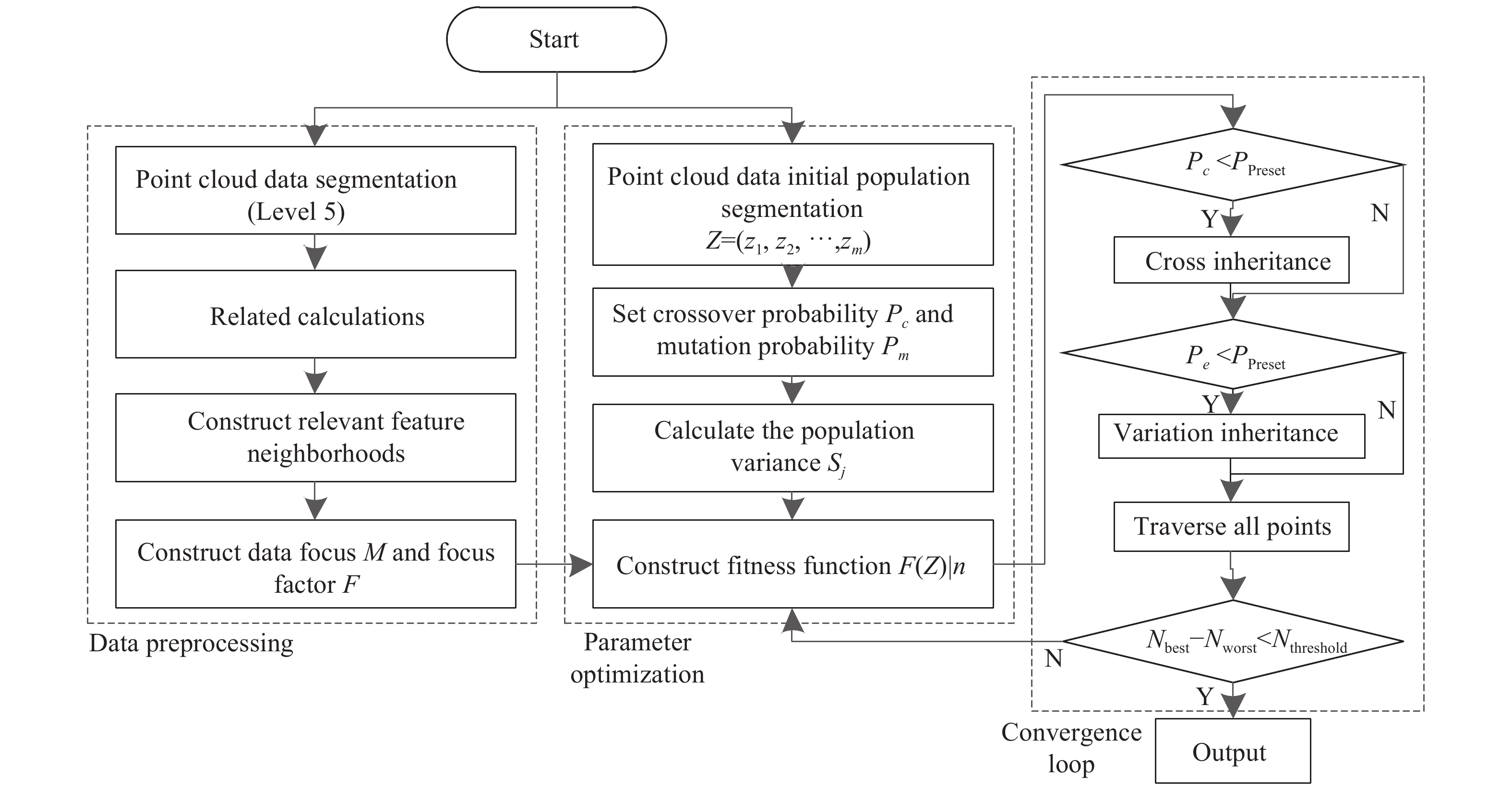
依据以上设计思路,利用基于深度学习获得的分段数据进行遗传算法改进,从而将异常数据识别转换为最优解问题,实现对网络中异常数据的监测。基于DL-GA算法的异常数据检测过程如下:
(1) 初始群体分段
对初始数据进行深度学习,完成分段处理,获得参数X、F和n(这个n就是分段表达中的数据分段数),则初始群体总数据量若为Q,则每一个数据层的数据量为Q/n。在一个分段数据区域中,由一个向量Z对种群染色体进行刻画,有Z = (z1, z2, ···, zi, ···, zl),l表示在该分段数据中的样本点数,zi为基因值。当zi=1时,该样本点为正常数据;当zi=0时,则该样本点为异常数据。
(2) 构造适应度函数
为了在遗传算法中匹配合适的适应度值,需要构造合适的适应度函数,在光纤网络数据中,个体的总体方差越小,则其适应度越大,遗传概率越高。光纤网络中的数据往往存在多个属性,设待测网络中数据属性有p个,将其表示为a1, a2, ···, ap。而每个属性表征的物理含义有所不同,所以为其设置不同的权重系数,有wj,调节分段数据中的比重关系,其范围有wj∈[0, 1],(j =1, 2, ···, p)。然后代入基因值zj,则总体方差Sj有:
式中:N为样本点数;zj为基因值;aji为第j种属性的第i 个样本值;avg(aj) 为正常样本点集合的第j个属性值对应的算术平均值;Nr为正常样本点总量。
将分段数据条件下的总体方差代入异常数据个体的适应度函数中,有:
式中:Fmax为预设的适应度最大值,可以选取max[F(Z)|n]作为其初始值循环迭代。由上式可知,分段数据中的总体方差越小,该区域内的样本点适应度值就越大,这样就能获得更好的遗传性。
(3) 交叉与变异
由于采用了分段数据,从而获得了具有一定自适应性的Pc和Pm,通过公式(5)计算每个个体的适应度值,并完成降序排列,再按照对应分段的交叉概率完成染色体交叉。将公式(1)中对应的参数带入交叉项中,与预设的交叉概率比较,当其低于预设值时完成交叉操作,反之忽略。
通过分段的变异概率实现新基因串的引入,从而对染色体数据进行变异处理,变异操作由变异位插入随机数实现。当染色体的适应度值大于群体平均值时,可以利用公式(2)求解个体的变异概率,并与预设变异概率初值进行对比。当其低于预设值时完成变异操作,反之忽略。
(4) 收敛条件设定
在前三步中完成了对数据分段、适应度函数构建以及交叉与变异方式的设定,最后只需要给出相应的限定条件就能够给出算法合适的终止条件了。将公式(5)中的F(Z)代入个体i下一代的期望值Ni中,有:
式中:F(Z)|n为适应度函数;favg为群体的平均适应度值。
当个体i被作为交叉或变异的对象时,其下一代的期望值Ni减去0.5;否则,减去1。当其和某个体的期望值Ni 小于零时,则该个体不遗传下一代。最终,以此依据完成群体所有数据点的遍历,将遍历后数据中的最优个体和最差个体的适应度值之差与预设阈值对比,小于阈值后终止迭代,其算法流程图如图1所示。
-
为验证DL-GA算法对光纤网络中异常数据的监测能力,从监测精度、算法稳定性与收敛时间三个方面对该算法与常用的两种传统异常数据检测算法(传统的遗传算法GA和聚类分析算法CA)进行了比较。
-
分别用三种算法对光纤网络中的异常数据进行检测,然后对比测试得到的异常数据量与实际异常数据量之间的关系(表1)。为了模拟真实网络中时而产生的异常数据情况,加载异常数据时没有采用定量加入的方法,比较机器学习和分类筛选时有规律可循。
Test time/s Actual abnormal data Test abnormal data GA CA DL-GA Test value Relative error Test value Relative error Test value Relative error 5 106 131 0.236 135 0.274 113 0.066 10 168 193 0.149 199 0.185 178 0.059 15 214 245 0.145 236 0.103 203 0.051 20 259 283 0.088 279 0.077 268 0.035 25 384 422 0.093 424 0.104 395 0.029 30 410 448 0.094 451 0.101 421 0.028 35 467 510 0.092 512 0.098 480 0.029 40 515 562 0.093 565 0.097 531 0.031 45 539 590 0.095 594 0.102 553 0.027 50 621 679 0.094 681 0.098 639 0.029 Table 1. Statistical table of test abnormal data volume and actual abnormal data volume
由表1看出,随着测试时间的增加,由人为引入的异常数据量也不断增加,实际异常数据量是已知的,然后对三种算法解算出的异常数据量进行统计分析。传统遗传算法的最小误差为0.092,最大误差为0.236,平均误差为0.117 9;传统聚类分析算法的最小误差为0.077,最大误差为0.274,平均误差为0.123 9;所提算法的最小误差为0.027,最大误差为0.066,平均误差为0.038 4。由此数据对比可以看出,所提算法在监测精度上明显优于两种传统方法,相同测试时刻的异常数据测试值更接近真实数量。并且随着测试时间增加,样本量增大,相对误差逐渐降低并趋于稳定。
-
算法的稳定性主要是算法在计算过程中出现的误差是否敏感,包括舍入误差、冗余能力等,也就是当输入数据中存在部分不符合规律的数据时,对于算法运算结果的影响程度。文中主要通过适应度值来反映算法的稳定性,因为适应度值可以表达不同数据条件下算法输出的结果,所以这里被用于评判算法的稳定性。分别采用三种算法对最优解进行迭代逼近,从而分析三种算法最大适应度的变化规律,结果见图2。
由图2(a)可知,随着迭代数的增加,三种算法的最大适应度值都将会趋于稳定,但相比之下,DL-GA算法大约在200次后就基本稳定了,而GA算法和CA算法分别在300次和350次趋于稳定,由此可见所提出算法的稳定性优于传统算法。由图2(b)可知,迭代过程中的样本个数越大,均值误差越平稳,对比三种算法的均值偏差可知,三种算法的偏差平均值分别为0.047、0.155和0.156,DL-GA的均值误差更集中且更小。通过均值误差可以有效地反映系统对异常数据的识别能力。
-
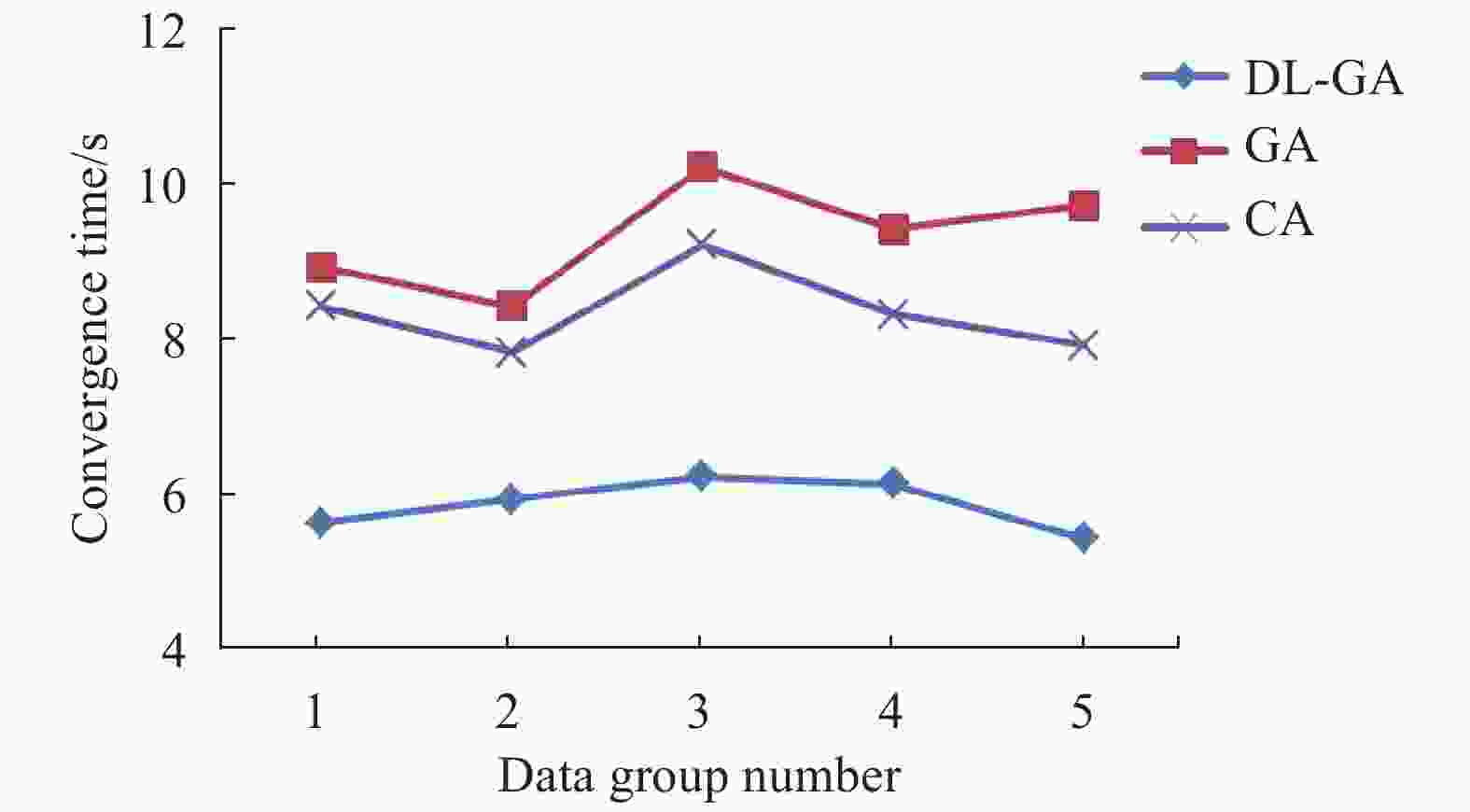
为了验证算法的时效性,针对相同数据集通过三种算法完成异常数据检测收敛时间的对比。为了使测试数据具有更好的普适性,分别设置了5组测试数据,这5组数据中混入不同比例的各类异常数据,而总数据量一致,从而排除了由于异常数据存在特征而导致某种算法收敛性好的可能。将5次不同数据测试结果进行了比较,结果如图3所示。
由图3可知,虽然测试数据中采用了不同的异常数据类型,但是DL-GA算法的收敛时间明显优于两种传统算法。通过在编译软件平台中调用时钟完成对算法运行时间的比较。DL-GA算法的收敛平均耗时为5.84 s,GA算法的收敛平均耗时为12.60 s,CA算法的收敛平均耗时为9.32 s。由此可见,在相同数据量的条件下,DL-GA具有更快的收敛速度,表示其具有更高的计算效率。
-
文中提出了一种基于DL-GA的光纤网络异常数据监测算法。通过对初始数据分段匹配交叉与变异概率,提高了异常数据特征的遗传效率。针对5组不同异常数据类型的光纤数据进行对比实验,实验结果显示:在监测精度、稳定性及收敛时间几个方面,所提到的算法均优于两种传统算法。总之,所提算法在光纤网络异常数据监测领域具有一定实用价值。
Optical fiber network abnormal data detection algorithm based on deep learning
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210029
- Received Date: 2021-01-18
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-02-04
- Publish Date: 2021-06-30
-
Key words:
- optical fiber network /
- network anomaly monitoring /
- deep learning /
- genetic algorithm /
- clustering algorithm
Abstract: The rapid identification of abnormal data from the massive data of large-scale optical fiber networks is a key issue of optical fiber communication technology. It is also an important research direction in optimizing optical fiber communication networks and improving communication accuracy in recent years. It mainly solves constraint relationship between the monitoring accuracy and convergence speed of abnormal data. Aiming at this problem, a monitoring algorithm based on the fusion of deep learning and genetic algorithm was proposed. The segmentation preprocessing of the initial data was completed through deep learning, and then the crossover probability and mutation probability with segmentation attributes was introduced into the genetic algorithm, thereby the retention of abnormal data features were enhanced. The original data was divided according to different attributes by segmentation preprocessing, thereby the amount of initial filtering data was reducing greatly, achieving the purpose of improving the detection speed of abnormal data; the segmentation attributes was introducd into the genetic factor of the genetic algorithm to make the results have a weighting effect, the separability of data was increased, thereby improving the monitoring accuracy. The proposed algorithm was compared with unoptimized genetic algorithm and clustering algorithm in the experiment. The results showed that the minimum relative errors of abnormal data volume of proposed algorithm, traditional genetic algorithm and clustering analysis algorithm were 0.029, 0.093 and 0.104, respectively; the average deviations were respectively 0.047, 0.155 and 0.156, the average convergence time were 5.84 s, 12.6 s and 9.32 s, respectively. It can be seen that this algorithm has been well optimized in terms of monitoring accuracy, stability and timeliness.











 DownLoad:
DownLoad:

