-
目前用于激光雷达等空间激光通信技术的光学天线主要有两种形式:透射式和反射式。反射式光学系统由于没有色差而受到人们的青睐,典型的反射式接收望远镜有牛顿(Newton)式、卡塞格林(Gassegrain)式和格里高利(Gregory)式。卡塞格林式光学系统广泛应用于激光通信、遥感和光谱仪器等领域[1-3],其中共口径收发一体光学天线多采用卡塞格林式光学望远镜[4]。
光学天线本质上是一个前置望远系统,其收发共用,相当于是一个扩束和缩束系统,发射时扩大光束口径,接收时缩小光束口径。卡塞格林式光学系统具有以下优点:(1)天线口径较大、无色差,适用波段范围广泛;(2)主次镜面式使用非球面后,消像差能力强;(3)光学结构简单、像质优良等。但共口径收发一体光学天线由于输入输出光束形式的多变不容易进行初始结构的确定。潘君骅和庞志海等人[5-6]通过分析卡塞格林式光学系统的像差特性,给出了一组有用的计算公式,但是并未考虑光学系统的体积尺寸要求和光学天线的收发效率问题。为了解决这一问题,得到合理的光学天线初始结构参数。文中在考虑光学天线三级像差的基础上,提出了一种通过优化遮挡比获得光学初始结构参数的计算方法,既满足共口径光学天线的体积尺寸要求及主镜口径要求又兼顾光学天线的光学收发效率。
-
常用的卡塞格林式光学天线是由主次反射镜组成,其中主反射镜中央开孔,成像在主镜后面。根据主次反射镜面型的不同有不同的分类,经典卡塞格林光学天线的主镜为抛物面,次镜为双曲面,理论上能够很好地的消除球差,其他种类型的卡塞格林光学天线也具有消像差的能力,笔者将在下面进行分析。
-
如图1所示为卡塞格林式光学天线结构,图中定义了大部分光学天线的基本符号,根据高斯光学[7]可以得到如下关系式:
式中:
${R_1}$ 为主镜曲率半径;$f$ 为卡塞格林光学天线的系统焦距;${R_2}$ 为次镜曲率半径;$\beta $ 为次镜放大率;$\alpha $ 为遮挡比。由公式(1)和(2)可得:由公式(3)和(4)可以得到次镜放大率
$\beta $ 与遮挡比$\alpha $ 的关系为:对于光阑在主镜上的光学系统,单色像差共有五种:球差、彗差、像散、场曲和畸变,其三级像差分别表示为
${S_1}$ 、${S_{\rm{2}}}$ 、${S_{\rm{3}}}$ 、${S_{\rm{4}}}$ 、${S_{\rm{5}}}$ 。根据三级像差理论,对于两镜反射光学系统,折射率${n_1} = n_2^{'} = 1$ ,$n_1^{'} = {n_2} = - 1$ ,对系统归一化,令入射高度${h_1} = 1$ ,系统焦距$f = 1$ 及视场角$\theta = 1$ ,则得出这五种像差的归一化表达式为:将公式(5)代入公式(6)可得到:
式中:
${k_1}$ 、${k_2}$ 分别为主镜和次镜的面型非球面系数,公式(7)是各种像差和系统焦距$f$ ,主次镜间距$d$ 和遮挡比$\alpha $ 之间的关系式。从上式可以看出,光学天线各结构参数必须取合适的值才能消除像差,并且最多只能同时消除四种像差,可以根据非球面系数得到一些典型的卡塞格林式光学天线。 -
根据主镜和次镜面型,笔者简单讨论以下几种典型卡塞格林式光学天线对应的非球面系数及特性。
(1) 经典卡塞格林(Cassegrain)光学天线
经典卡塞格林光学天线的主镜为抛物面镜,次镜为双曲面。该天线利用了抛物面和双曲面的反射特性,抛物面的焦点和双曲面的虚焦点重合,经双曲面后成像在是焦点处。主次镜面型结构能够很好地消除球差,故
${S_1} = 0$ ,可得主次反射镜的非球面系数${k_1}$ 、${k_2}$ 分别为:此种光学设计是最常用的,该系统的优点是像质好、结构简单并且加工制造工艺成熟,可用于空间成像和多用途激光通信天线方案[8-9]中。但是存在彗差,放大率会随着光线的发散而下降,视场会比施密特光学天线(Schmit-Cassegrain)和R-C(Ritchey-chretien)光学天线小。
(2) 达-客(Dall-kirkham)光学天线
达-客(Dall-kirkham)光学天线本质上是经典卡塞格林光学天线的简化版,其主次镜面型曲线更易于磨制。这是一种主镜面型为椭圆面,次镜面型为球面的能够消除球差的光学系统结构,即
${S_1} = 0$ 。这种面型结构没有修正离轴的彗差和视场畸变,但对长焦比的影响较小。可得主次反射镜的非球面系数${k_1}$ 、${k_2}$ 分别为:在工程设计中,考虑到制造成本和主次镜检测成本,此种光学天线做了设计上的简化,没有修正离轴的彗差和场曲,故离开轴心的影像品质便会很快地变差。但彗差和场曲与次镜的放大率会因系统的焦比变小而减小,故主镜焦比在4或更低时,此光学天线所产生的彗差和场曲可忽略。同样,长焦比会导致视场非常小,焦比在15以上的反射镜仍会采用此种设计。
(3) 施密特(Schmit-Cassegrain)光学天线
这是一种以普雷斯曼-卡米歇尔卡塞格林式的折叠光路与施密特修正板组成的紧密型光学天线。主镜面型为球面,次镜面型为椭圆面,并以施密特修正板来校正球差,即
${S_1} = 0$ 。故可得主次反射镜的非球面系数${k_1}$ 、${k_2}$ 分别为:此种光学系统结构相比其他卡塞格林式光学天线最容易制造,成像品质略差,视场较大。美国Celestron和Meade两家公司的镜筒产品均有采用此种光学结构,而通过对国内外激光通信项目的调研,光学天线系统多借鉴天文望远镜[10]。
(4) R-C(Ritchey-chretien)光学天线
R-C(Ritchey-chretien)光学天线的主镜和次镜均为双曲面,这样既可以完全消除球差,还可以完全消除彗差,不仅为目镜提供了更好的一次像面,还可以扩大整个系统的视场。故可得主次反射镜的非球面系数
${k_1}$ 、${k_2}$ 分别为:R-C(Ritchey-chretien)光学天线实际上是一种对经典卡塞格林光学天线改进的光学版本。美国PlaneWave Instruments公司的RC Telescopes产品就是采用此类型的光学系统。在实际操作中,R-C光学天线较难对准,且造价成本相对其他类型天线高。
总之,由公式(8)~(11)可以看出,在已知系统焦距
$f$ 、两镜间距$d$ 和遮挡比$\alpha $ 的情况下,笔者能够求出以上讨论的光学系统的不同的非球面系数,其中前三种光学系统主要纠正球差,第四种光学系统能够近似地消除三级球差和彗差。在工程化设计中,会根据成本、检测费用和不同的实际应用要求选择不同的天线。 -
在激光通信和成像系统中对卡塞格林式光学天线的遮挡比要求较高,遮挡比越小,激光发射和接收效率越高,可得到增益因子和遮挡比之间的关系[11]:
式中:
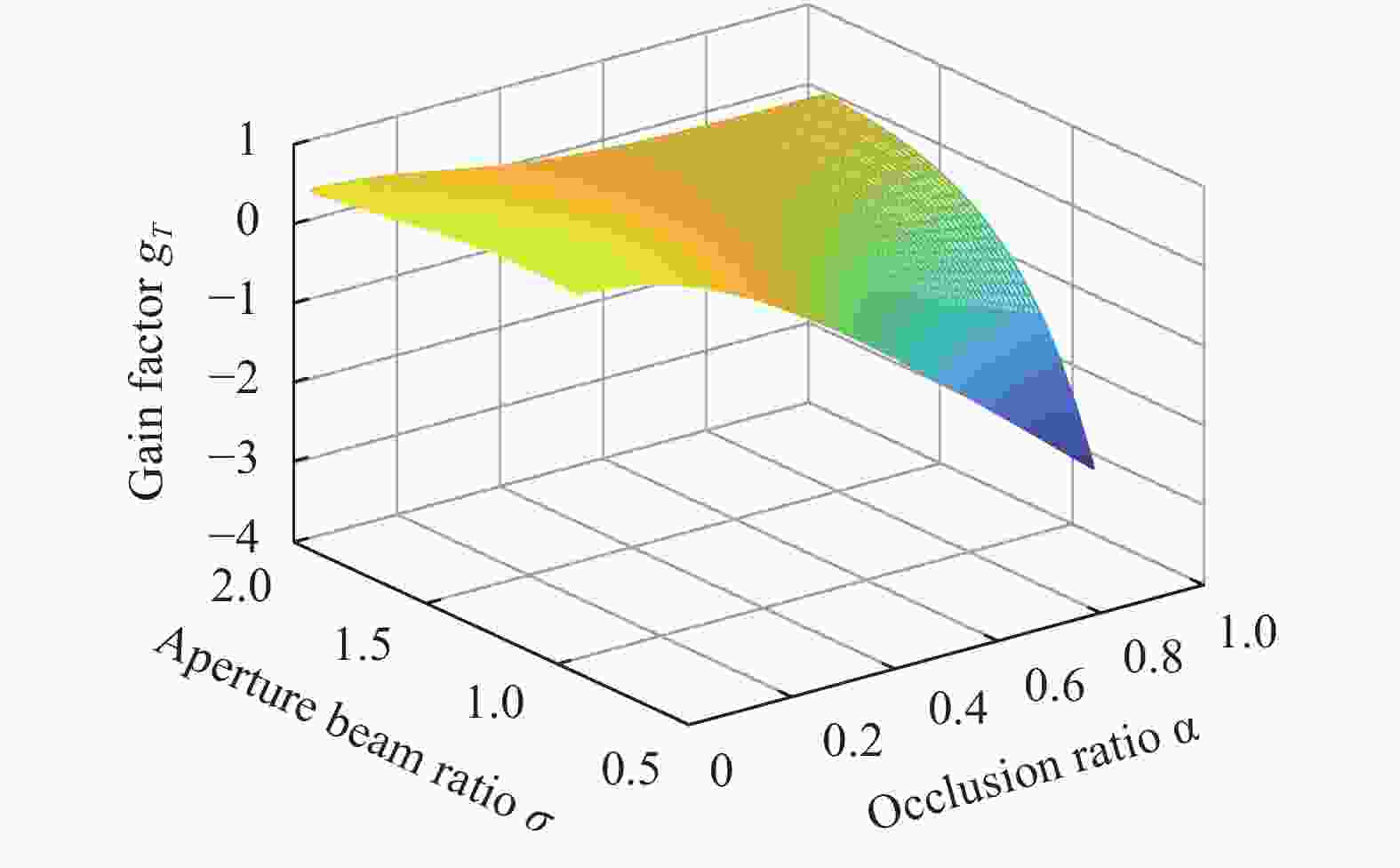
${g_T}$ 为天线增益因子;$\sigma $ 为孔径光束比(即主镜内孔径$c$ 与激光光束束腰之比)。为了提高光学天线的轴向增益,再根据二阶微扰理论就可以得到最优遮挡比与孔径光束比之间的关系:从图2以及考虑信噪比来看,最优遮挡比应该选择在孔径光束比为1(即主镜内孔径和光束大小相等)的附近,即遮挡比
$\alpha = 0.336\;463$ 或$0.707\;107$ 附近。但由仿真图3分析可见遮挡比的增加,会使得增益下降。根据以上分析,遮挡比的减小又不利于像差的校正,如果遮挡比太小也会引起反射能量太小,如果遮挡比很大同样会造成信噪比的减弱,故遮挡比选择为:$\alpha = 0.336\;463$ 。具体设计光学系统时,应综合各种因素,一般遮挡比选择在$0.3 \leqslant \alpha \leqslant 0.5$ 之间[12]。 -
合理的光学结构有助于在校正像差的同时,兼顾体积、质量、性价比等问题。共口径光学系统在设计之初一般会规定体积大小、系统长度和系统焦距等参数。笔者取系统焦距
$f = 1\;500\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,两镜间隔$d = $ $ 300\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,遮挡比$\alpha = 0.34$ 。由公式(1)、(2)、(5)得${R_1} = $ $ - 909.090\;909\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,${R_2} = - 443.478\;261\;{\rm{mm}}$ ,$\;\beta = - 3.3$ 。对以上讨论的几种类型光学系统的非球面系数${k_1}$ 、${k_2}$ 进行计算,计算结果如表1所示。Type of optical system Cassegrain Dall-kirkham Pressmann-Camichel Ritchey-chretien Aspheric coefficient (k1) −1.000 000 −0.597 652 0.000 000 −0.905 390 Aspheric coefficient (k2) −3.495 274 0.000 000 5.191 917 −4.317 169 Table 1. Aspheric coefficients of mirrors for various optical systems
对上述几种光学系统进行计算优化,得到优化后得光学结构参数,如表2所示。经过光学软件得优化结果与计算结果对比,可以发现两种求解方式光学参数一致,说明笔者的计算结果和软件优化结果一致,上述计算方法精准便捷。
Type of optical system Cassegrain Dall-kirkham Pressmann-Camichel Ritchey-chretien R1/mm −909.090 910 −909.090 903 −938.599 510 −909.090 909 R2/mm −443.478 261 −443.478 276 −455.281 951 −443.756 312 d 299.999 999 299.999 992 312.880 016 299.903 103 k1 −1.000 000 −0.597 777 0 −1.092 489 k2 −3.495 274 0 5.602 234 −4.298 315 β −3.300 000 −3.300 000 −3.196 251 −3.300 000 α 0.340 703 0.339 795 0.331 827 0.341 195 Table 2. Optimization results of optical structure parameters
-
文中从薄透镜三级像差理论出发,给出了各种像差和系统焦距
$f$ 、主次镜间距$d$ 、遮挡比$\alpha $ 之间的关系式,又基于微扰理论,给出了光学天线的最优遮挡比,确定了卡塞格林式光学天线初始结构的计算方法,此计算方法既考虑了光学系统设计的体积要求又兼顾了光学天线的光学收发效率。简要分析计算了四类卡塞格林式光学天线的光学参数,不但给出了四类卡塞格林式光学天线的光学结构参数计算公式,并且结合实际使用对不同的适用场合进行说明及优缺点对比。通过四种典型光学天线的实例计算结果和最优结果比对,表明此方法是一种方便快捷精准求解卡塞格林式光学天线结构的方法,在工程上具实际指导意义。
Initial structure solution of Cassegrain type transceiver optical antenna for laser communication and imaging
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210173
- Received Date: 2021-03-12
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-04-20
- Publish Date: 2022-04-07
-
Key words:
- laser communication /
- occlusion ratio /
- Cassegrain antenna /
- solving method of initial structure
Abstract: In the laser communication and imaging system, whether the Cassegrain type optical antenna is used as a laser signal transceiver or an optical imaging device, the existence of aberrations will inevitably influence its signal intensity and imaging quality. By analyzing optical antenna of the third-order aberration theory and the perturbation theory, according to the relationship between the antenna gain factor and the occlusion ratio, a convenient and fast method for solving the Cassegrain type optical antenna structure was proposed. This method can not only consider the efficiency of the optical antenna, but also meet the requirements of the volume size and aberration of the optical system design. Especially in the case that only knowing the focal length of the optical system, the distance between the primary and secondary mirrors, the occlusion ratio, the structural parameters of the optical antenna can be calculated quickly. Not only gives the calculation formulas of the optical structure parameters for four types Cassegrain optical antennas, but also explains the advantages and disadvantages in the different application. According to comparing the calculation results of four typical optical antennas with the optimal results, the results show that this method is a convenient, fast and accurate method to solve the Cassegrain type optical antenna structure, and has practical significance in engineering.







































































 DownLoad:
DownLoad:

