HTML
-
光谱成像技术可以揭示自然物质光信息的波动本质,光谱图像具有精细的场景信息刻画能力,在气象观测、土地规划、医疗诊断、植被分类、军事侦察、资源勘测、地震监测、灾害预防等诸多领域具有重大的应用前景。
多光谱成像技术从成像时间维度上可以分为基于多次曝光的扫描方式和单次曝光的计算成像方法。传统的扫描方式一般只能获得静止的光谱图像,计算成像方法可以通过单次曝光,利用计算重构调制后的光谱数据获取动态场景下的多光谱数据,实现光谱成像由“静”到“动”的拓展[1]。关联成像技术作为一种新型的计算成像方法,主要通过参考光场对目标进行调制,利用光场的涨落和高阶关联获取目标图像信息,可以实现更高的信息获取效率[2]。压缩感知理论是一种全新的信号采集、编解码理论,将压缩感知理论应用于多光谱成像技术获得了广泛的研究[3-7]。目前,关联成像技术多采用主动光源,而采用太阳光作为光源则必须实时获取太阳光的涨落信息,在成像过程中具有很大的局限性[8]。将关联成像技术与压缩感知理论相结合,并应用于多光谱成像系统中,通过空间随机相位调制器实现对光谱维和空间二维的三维随机压缩采样,大大提高了系统的信息获取能力和效率[9]。
近年来,不少学者提出有关利用计算成像理论分析运动目标光谱成像的方案。美国杜克大学的Brady利用压缩感知原理进行编码光圈快照光谱成像(CASSI)[10],在欠定条件下重构光谱的三维数据立方体。此后又提出了直视型编码孔径快照式光谱成像仪(DV-CASSI)[11],该方案用CCD面阵探测器采集空间与光谱混叠的复合图像,再通过图像重构算法将采集的运动目标复合图像重构成三维数据立方体。2012年,中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所的龚文林等提出了基于参考臂探测器记录的光场强度分布平移补偿进而提高运动目标强度关联成像分辨率的方案[12],开展了强度关联成像领域中对于运动目标成像的研究,解决了目标与系统之间的相对运动引起的图像退化问题。2016年,该小组研究了目标与探测平面的相对运动对二阶强度相关成像分辨率的影响[13],分析了利用散斑图样的相位反演方法能够获得高分辨率成像。2018年,中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所的吴建荣等[14]利用系留气球装载多光谱关联成像原理样机,对试验目标和自然景物进行了单次曝光多光谱关联成像实验研究。
文中结合多光谱成像技术、关联成像技术以及压缩感知理论,提出了利用相位调制的方式通过单次曝光获取运动目标重构图像信息的方案。理论分析了成像原理和编码过程,通过实验研究揭示不同电子数均值探测信号与运动目标重构图像质量之间的关系,从而为多光谱视频成像及其应用提供一种新的研究思路。
-
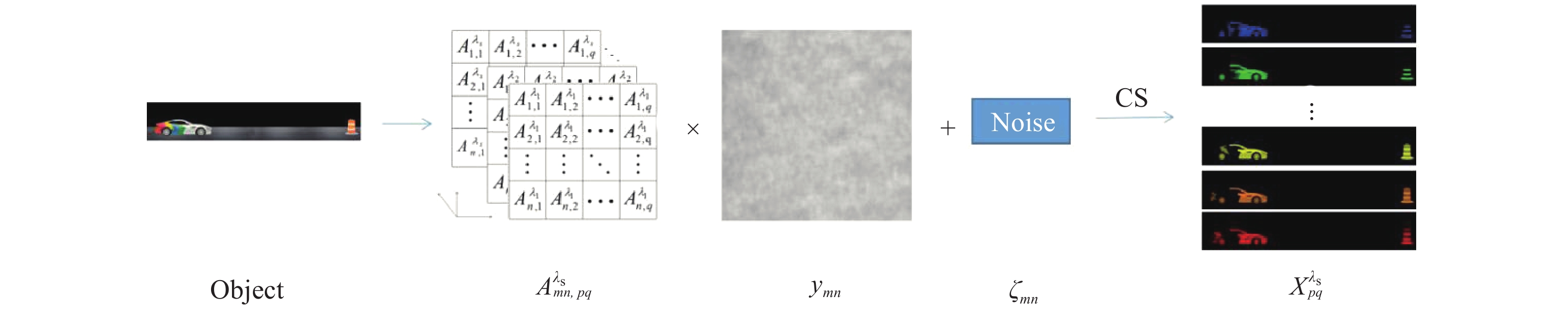
基于稀疏约束关联成像光谱相机(Ghost Imaging via Sparsity Constraints,GISC)的系统光路图如图1所示,目标物体置于焦距为
${f_1}$ 的透镜焦平面上,经焦距为${f_2}$ 的前置成像透镜成像到视场光阑所在的前置成像面上,在前置成像面上获得一幅宽波段图像。调制模块中的空间相位调制器将前置成像面上宽波段图像上每个点发出的光场进行随机相位调制,经调制后形成一幅散斑图样。中继成像透镜将调制后的散斑图放大成像于面阵光电探测器上。通过对散斑场的单次曝光探测,结合事先标定的测量矩阵和压缩感知等重构算法,利用计算机重构出目标的三维光谱图像[15]。在实际探测时,探测面获取的光强分布为:
式中:
${I_c}({r_t})$ 表示探测面上的光强分布;${I_b}({r_i},{\lambda _l})$ 表示多光谱物体的光强分布;${h_I}({r_t};{r_i},{\lambda _l})$ 表示物面上${r_i}$ 处位置波长为${\lambda _l}$ 的单色点光源发出的光在探测面上产生的光强分布。对前置成像面上视场范围进行如下的像素网格划分:1,1 1,2 $ \cdots $ 1,Q 2,1 2,2 $ \cdots $ 2,Q $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \ddots $ $ \vdots $ P,1 P,2 $ \cdots $ P,Q 对探测面进行像素网格划分(每个网格代表探测器上的一个像元):
1,1 1,2 $ \cdots $ 1,N 2,1 2,2 $ \cdots $ 2,N $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \ddots $ $ \vdots $ M,1 M,2 $ \cdots $ M,N 多光谱关联成像探测过程如下:
式中:
${X}_{pq}^{{\lambda }_{s}}\left(p=1,\cdots ,P;\;q=1,\cdots ,Q\right)$ 表示前置成像面上第p行q列像素在s个谱段中$s\left( {s = 1, \cdots ,S} \right)$ 重构的多光谱图像信息;${A}_{mn,pq}^{{\lambda }_{s}}\left(m=1,\cdots ,M; \;n=1,\cdots ,N\right)$ 表示成像系统标定点光源在物面上第p行q列像素上移动时,探测面CCD第m行n列像元得到的光强度值;$y_{mn}$ 表示成像时探测面上第m行n列探测信号的强度分布;$\varsigma $ 表示探测信号噪声。设探测面上的探测信号强度分布为:
根据GISC相机成像模型,目标物体的多光谱图像重构通过求解如下优化问题实现:
其中,A为前置成像面上各个像素发出的单色光经过空间相位调制器生成的散斑矩阵:
X为需要计算重构的多光谱图像信息按像素网格中先列后行顺序排列而成的列向量:
${\left\| {\left. {{\nabla _{i,j}}X} \right\|} \right._1}$ 为梯度范数,相当于提取图像的分段边缘,使变换后的图像更加稀疏;${\left\| {\left. X \right\|} \right._ * }$ 表示矩阵核范数,表明多光谱图像矩阵的低秩性;${\mu _1},{\mu _2} \geqslant 0$ 为各约束项的权重系数。文中采用TV-RANK压缩感知算法进行图像重构[16]。上述GISC成像过程示意图如图2所示。
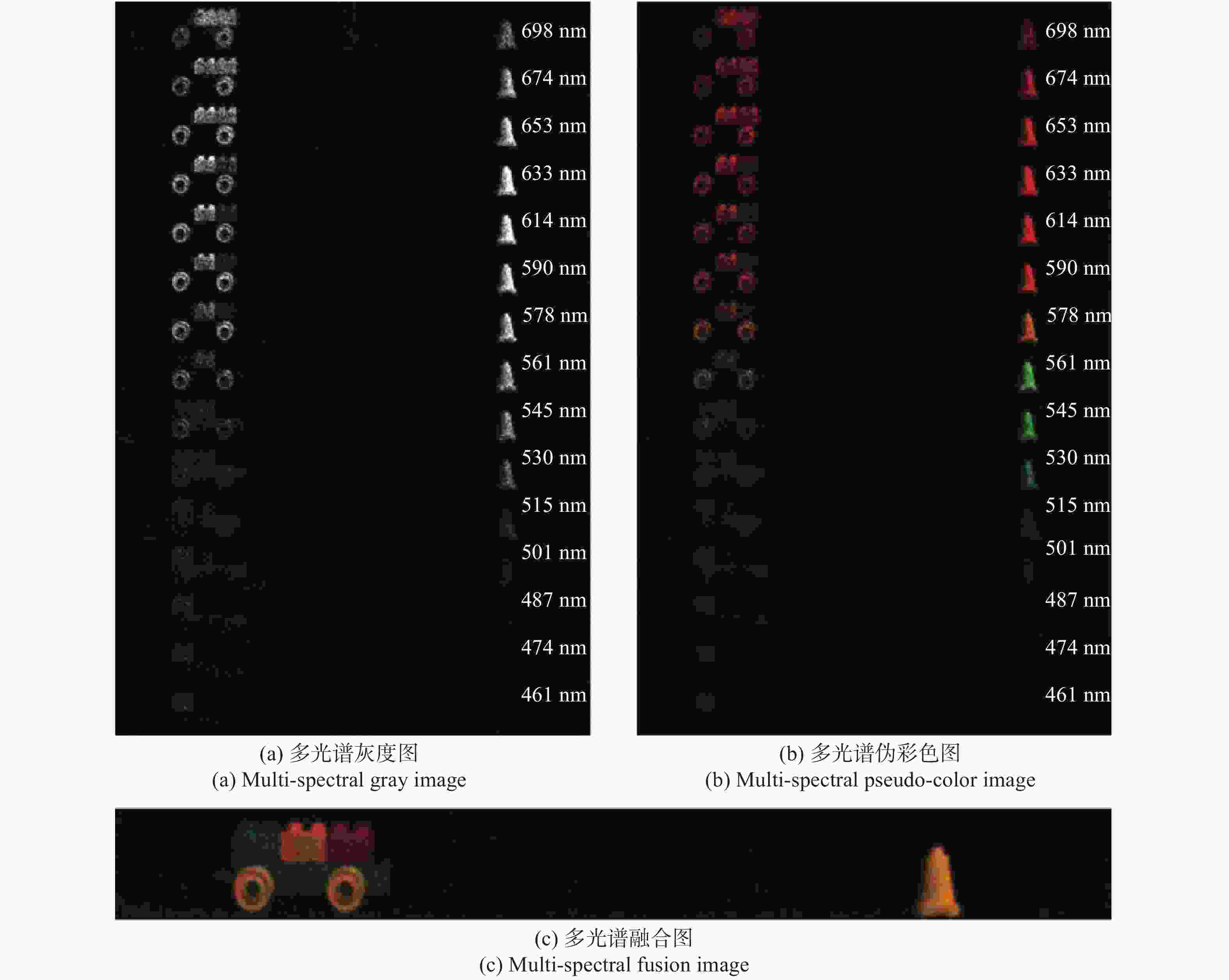
首先,通过单次曝光获取CCD探测信号,代入公式(4)得到重构的多光谱灰度图像,然后对不同光谱的重构图像进行伪彩色处理,最后通过图像融合算法将不同波长的多光谱图像合成一幅彩色图像。
-
基于运动目标的单次曝光多光谱关联成像外场实验装置如图3所示。原理样机成像系统由一个GISC相机和一个监视相机组成,固定在地面三脚架上。实验参数为:GISC相机光谱范围450~700 nm,15个光谱通道,光谱分辨率<20 nm,像元分辨率≥0.5 mrad。GISC相机和监视相机的曝光时间设置为40 ms。待测目标物体由长123 mm、高50 mm的彩色玩具车和长28 mm、高34 mm的黄色安全警示锥形桶组成,其中彩色玩具车作为运动目标物体,黄色安全警示锥形桶作为静止参考物体。利用步进精度为0.001 mm/s的SC100型步进电机以30 Hz的运行速度带动目标物体运动成像。采用日光作为照明光源,待测目标物体在距原理样机3.5 m处,成像视场宽范围60 mm×610 mm。
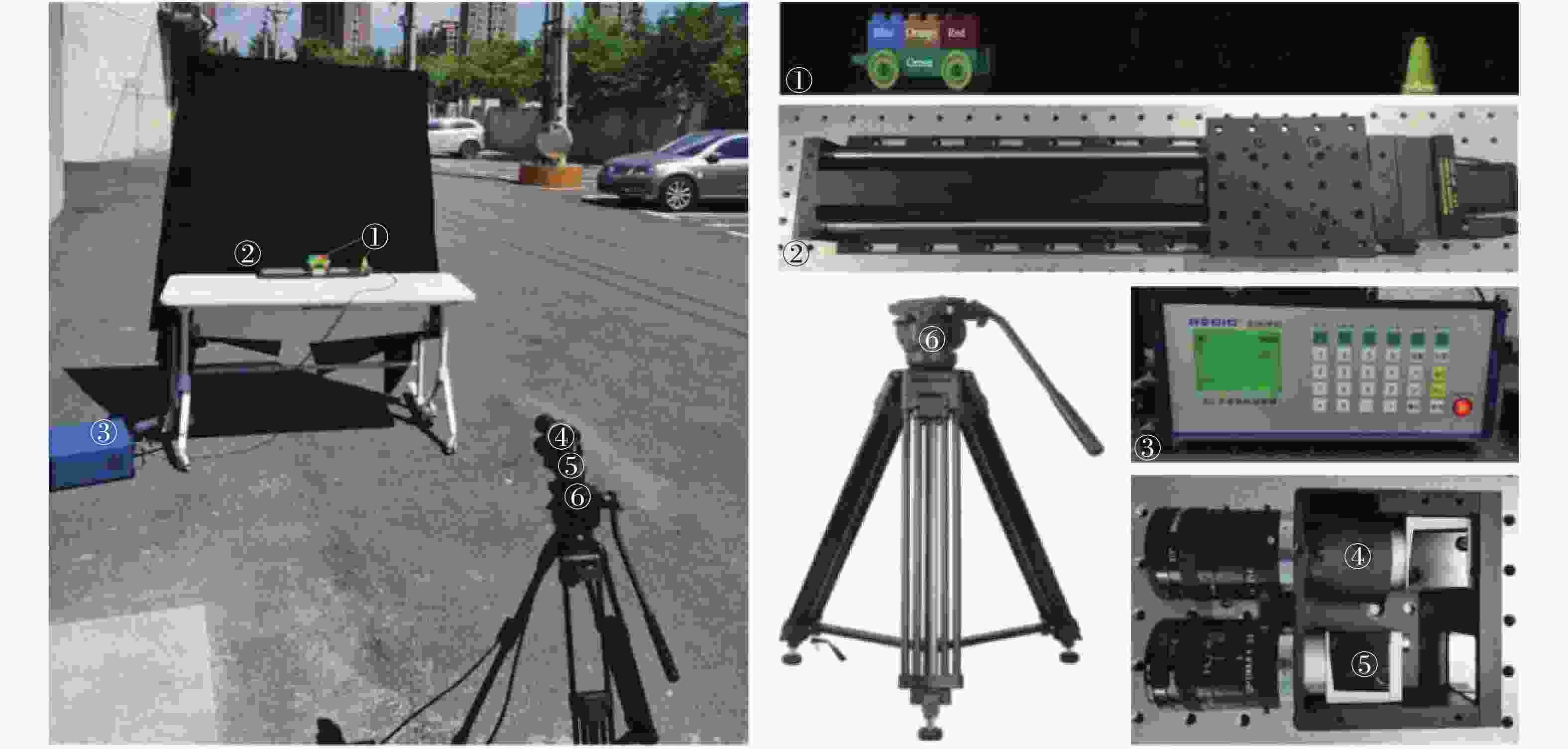

Figure 3. Diagram of the experimental setup in the field. ① Target object; ② SC100 stepping motor; ③ SC stepping motor controller; ④ GISC camera; ⑤ RGB camera; ⑥ KINGJOY VT-2500 tripod
单帧多光谱关联成像实验结果如图4所示。当CCD记录的电子数均值为1300 e−时,GISC相机通过单次曝光获取的CCD探测信号;利用事先标定好的测量矩阵和公式(4)得到重构的多光谱灰度图像如图4(a)所示,15个光谱通道波长分别为461、474、487、501、515、530、545、561、578、590、614、633、653、674、698 nm。对图4(a)的不同波长重构图像进行伪彩色处理,得到多光谱图像重构结果如图4(b)所示,最后合成的彩色融合图为图4(c)。与图3中①图待测目标物体相比较,得到了较高质量的目标物体形状和光谱信息重构结果。
为进一步考察GISC相机的探测信号值对多光谱图像重构质量的影响,将CCD记录的电子数均值参数设置为以100e−的间隔从200e−增加至1300e−,CCD探测信号实际结果如图5(a)所示,对应不同电子数均值的多光谱图像彩色融合图重构结果如图5(b)所示。对比图5(a)和图5(b)可以发现:当电子数均值为200e−时,重构图像质量较低,存在噪声较大;随着电子数均值逐渐增大,重构图像质量也相应不断提高,噪声随之减小;当电子数均值为1300e−时,可以获得较高质量的重构图像。
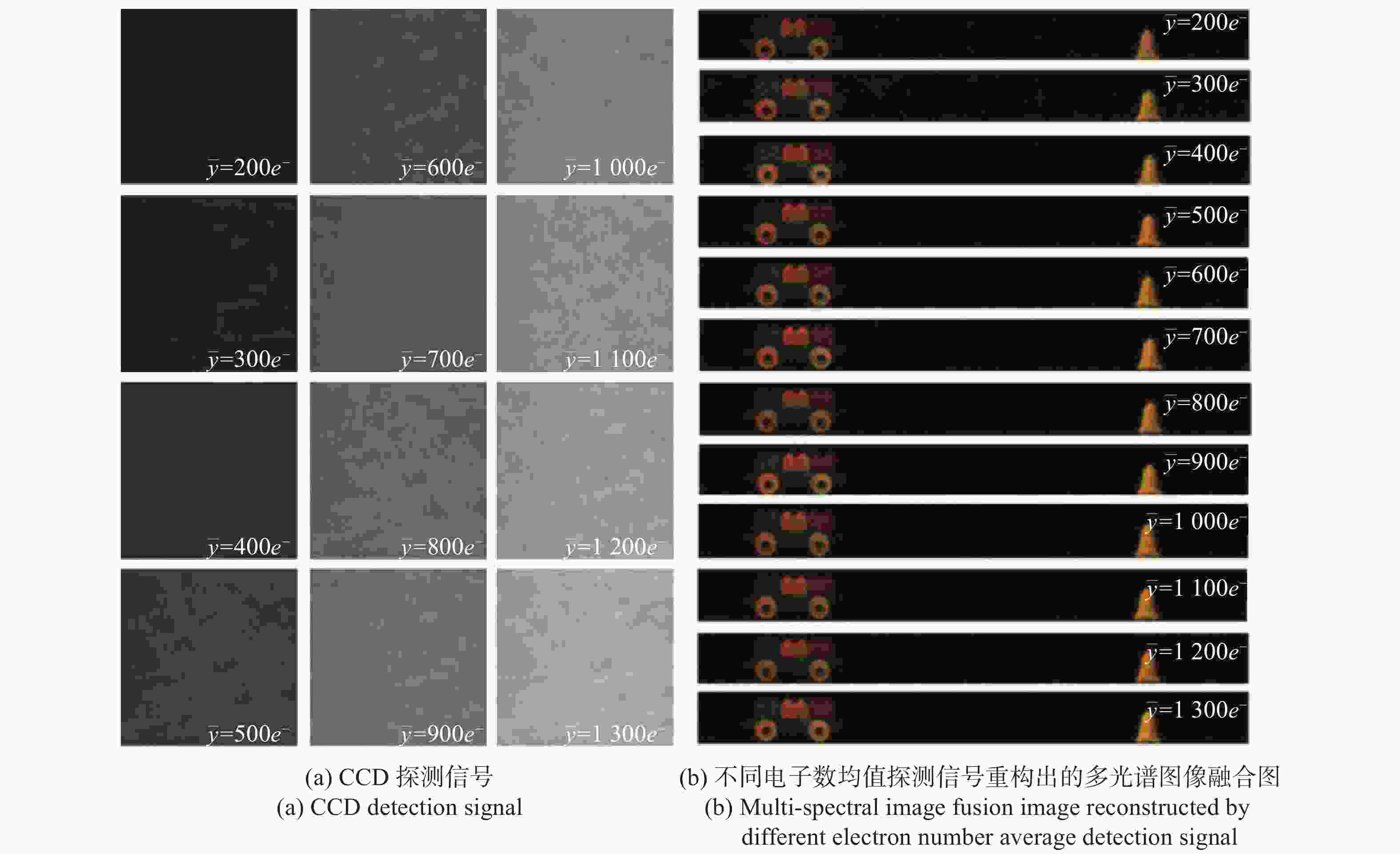
Figure 5. Experimental results of single-frame detection signal and reconstructed image with different electron number averages
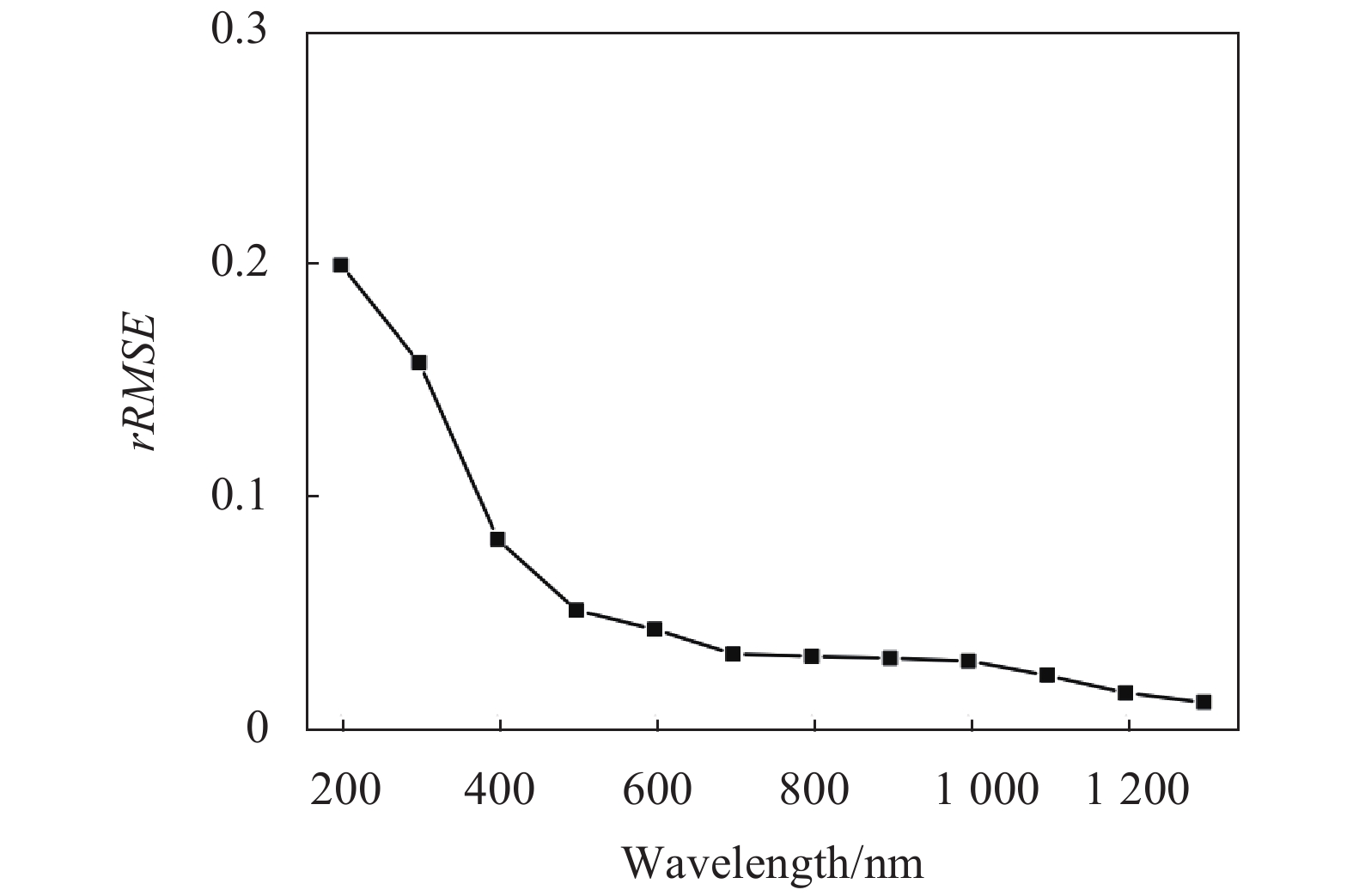
为进一步说明探测信号值对多光谱图像重构质量的影响,采用相对均方根误差(rRMSE)来评价图像重构质量,定义如下:
式中:M和N为CCD探测面上的行数和列数;
$x_{ref}^ * $ 为参考图像(实验中为电子数均值为1400 e−的单帧多光谱图像);${x^ * }$ 为重构图像。rRMSE值越小,重构图像质量越好。图6为
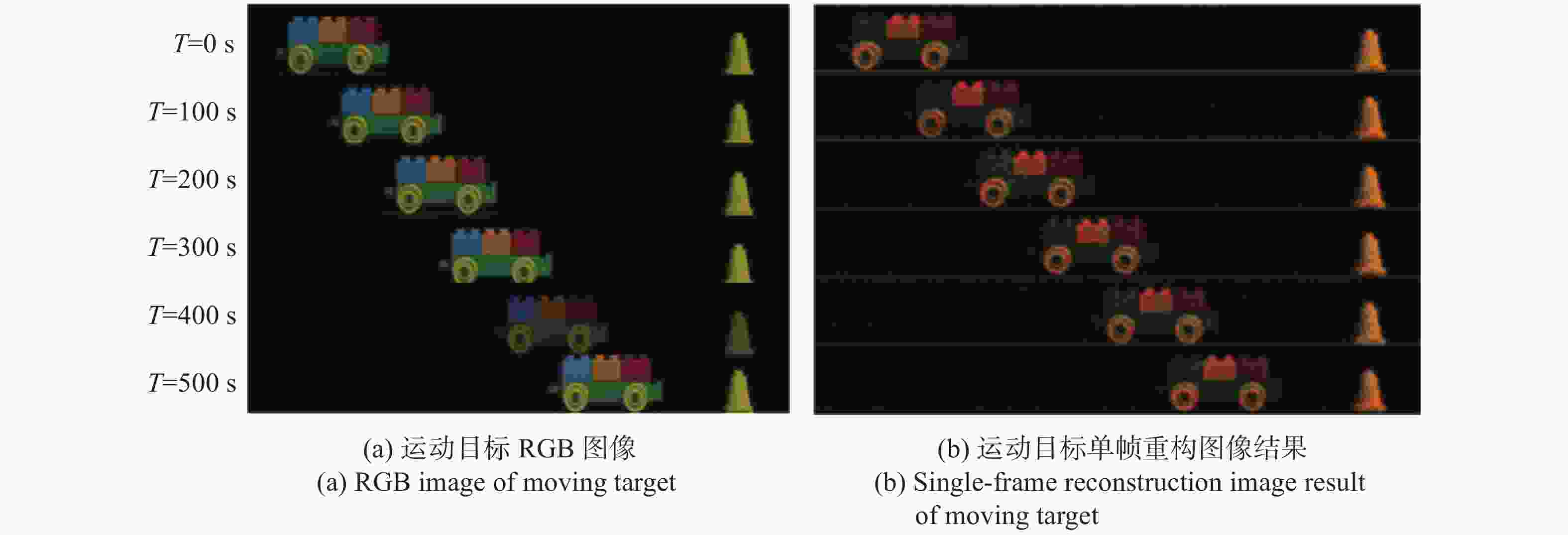
$rRMSE$ 随电子数均值变化关系曲线图。由图6可以看出,当电子数均值为200 e−时,重构图像的$rRMSE$ 值为0.1989,当电子数均值增加至1300 e−时,$rRMSE$ 值为0.0119,随着电子数均值的增加,$rRMSE$ 值单调下降,重构图像质量明显提高。下面分析运动目标的多光谱关联成像规律。利用步进电机以30 Hz的速度带动物体以0.6 mm/s的速度做连续匀速直线运动,多光谱关联成像重构结果如图7(b)所示。在初始位置,彩色玩具车与黄色安全警示锥形桶距离450 mm。当运动时间为100 s时,彩色玩具车向黄色安全警示锥形桶移动了60 mm;当运动时间增加到200 s时,彩色玩具车移动了120 mm,距离锥形桶330 mm;当运动时间为500 s时,彩色玩具车移动的总位移为300 mm,距离锥形桶150 mm。对比图7(a)与图7(b)可以发现:GISC相机拍摄的运动目标多光谱图像重构结果与监视相机在不同时刻所拍摄目标物体的RGB图像运动规律完全相同;但在相同位置处,RGB相机只能拍摄3个光谱通道,而由图4可知GISC相机能够获得15个光谱通道,可以从待测运动目标重构图像中提取更加丰富的光谱特征。
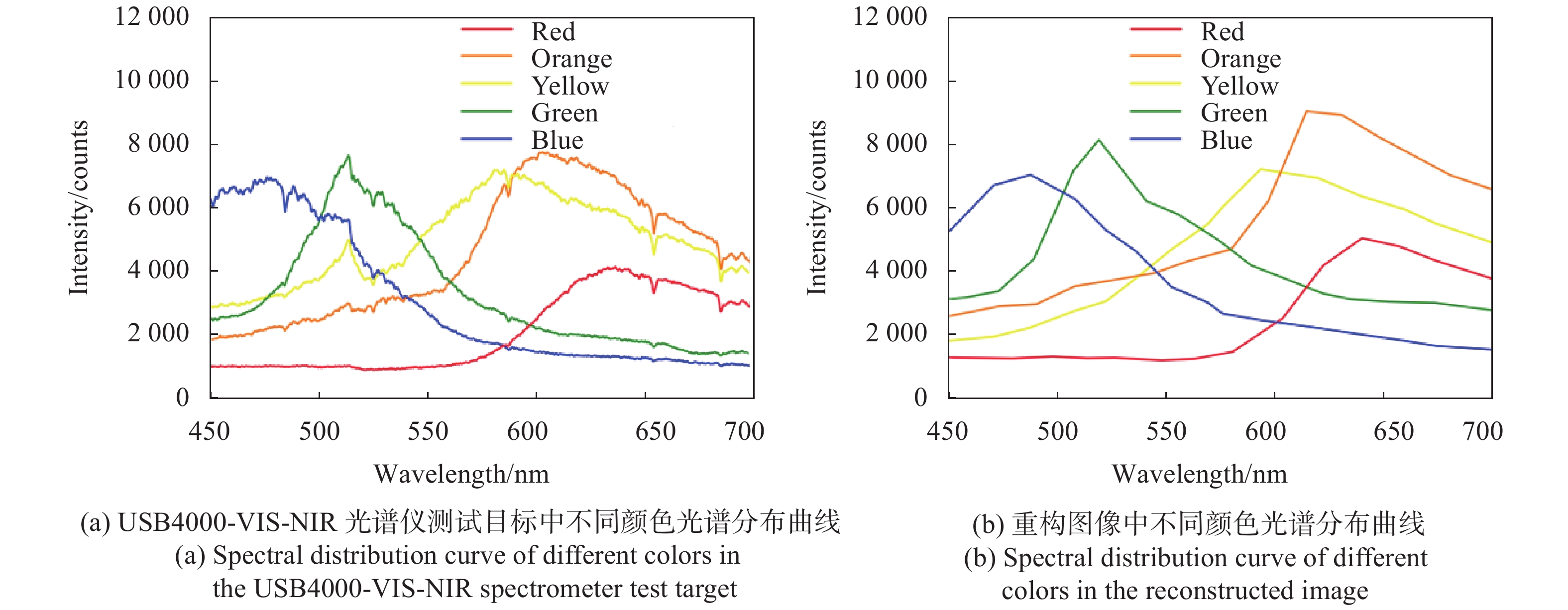
为了进一步说明实验的可行性,采用USB4000-VIS-NIR光谱仪对目标物体中450~700 nm不同颜色的光谱分布进行了测试,并与GISC相机拍摄的重构图像实测光谱曲线进行对比分析,如图8所示。采用商用光谱仪测试目标物体中蓝色、绿色、黄色、橙色和红色部分光谱曲线的波峰分别位于481、513、587、608、638 nm,实测重构图像中对应部分光谱曲线的波峰位于490、519、593、614、640 nm。实验结果与商用光谱仪测试结果误差小于10 nm,主要是由于实验标定系统产生的误差。
-
针对传统多光谱相机对运动目标探测灵敏度低、采样次数多、光能损失严重等问题,将多光谱成像技术、关联成像技术以及压缩感知理论相结合,在成像光路中引入空间随机相位调制器,提出了基于运动目标的单次曝光多光谱关联成像方案,系统具有能量利用率高、信息获取效率快、单次曝光即可获取三维“数据立方体”信息等优点。理论分析了GISC相机对运动目标成像的原理和编码过程,并在外场环境下完成了运动目标的单次曝光多光谱关联成像实验。结果表明,多光谱关联重构图像质量随着电子数均值的增加而提高,可实现与监视相机RGB图像相同规律的运动物体图像重构,具有更加丰富的光谱特征。商用光谱仪测试结果验证了多光谱重构图像具有较高的光谱复原精度。
致 谢 感谢中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所吴建荣的有益讨论。



































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: