-
基于事件的传感器[1](也称事件相机)是受生物视网膜的启发的新型仿生视觉设备,可有效捕获高速运动物体,具有功耗低、时间分辨率高、数据传输带宽小等突出优势。常见的事件相机有动态视觉传感器(Dynamic Vision Sensor,DVS)、异步时间图像传感器(Asynchronous Time Based Image Sensor,ATIS)、动态有源像素视觉传感器(Dynamic and Active Pixel Vision Sensor,DAVIS)[2]、以及最新发展起来的高分辨率相机CeleX-V(1280×800)[3]和DVS-Gen4(1280×960)[4]。与固定帧速率生成强度图像的传统相机不同,事件相机的各像素独立异步地感受光照强度的变化。当某一像素的对数光强度变化在某个时间超过阈值时将输出一个事件,该事件包含像素位置(i,j)、时间戳t和极性p(正或负)三个信息。由于其独特的工作模式,即使在具有挑战性的高速场景和高动态范围环境中也可以提供高质量的视觉信息,事件相机的出现为视觉应用提供了新的发展领域。
随着硬件性能的不断提高和算法研究的不断深入,事件相机在目标跟踪、图像去模糊、机器人实时交互以及航空航天领域的应用优势日益突出。此外,事件摄像机的高时间分辨率、高动态范围、小数据量是传统摄像机无法比拟的,因此对事件像机的研究具有重要的现实意义。由于开关泄漏电流、电荷注入效应、阈值波动等[5]原因,即使像素感知的亮度没有变化或变化未达到阈值,事件相机也可能错误地输出事件。此外,由于外部环境干扰,相机输出中存在一些无法反映目标的信息的孤立事件。以上两种情况产生的事件统称为噪声,与其相对的事件称为有效事件。噪声的存在会影响图像质量,占用不必要的带宽,对算法开发和后端应用带来巨大的困难。
经过过去几十年的发展,诸如空域像素特征去噪算法、变换域去噪算法等[6]针对传统图像的去噪算法已经发展成熟。通过积累一段时间的事件生成帧图像,就可以利用传统去噪算法进行事件相机去噪,但该方法忽略了事件的时空性和高时间分辨率特性,去噪效率低且效果差。此外,目前基于事件流的去噪方法主要为噪声滤波器、阈值去噪[7]等,通过设置简单的时间阈值、距离阈值、密度阈值等进行去噪,尚且没有统一的评估指标来评估降噪效果的优劣。因此,迫切需要一种新型的基于事件流的去噪算法和去噪效果评价指标。
文中使用改进马尔可夫随机场模型[8]对事件流进行降噪。根据有效事件之间的强相关性构建有效事件X和输出事件Y之间的联合概率分布P(X,Y),并通过设置合理的势函数将概率最大化问题转变为能量最小问题。此外,通过使用改进的迭代条件模式算法[9](Iterated Conditional Modes,ICM)优化能量函数寻求局部最优解,得到去噪后的事件流。采用仿真事件流数据和真实事件流数据进行验证,实验结果均证明了提出的去噪算法的有效性。
-
马尔可夫网模型是一种概率无向图模型,由节点和边组成,用于描述变量之间的无向交互影响。其中节点代表变量(事件),边表示近邻变量之间交互影响的概率(事件之间的相关性)。
在一段时间内产生的事件中,以其中某一事件
${x_{i,j,t}}$ 为中心(中心事件),将其他事件$x_{_{i,j,t}}'$ 映射到以其为中心的时空极坐标系。映射关系如公式(1)所示:参数之间关系分别表示为:
式中:
${\rm{\theta }}$ 为时空极坐标的极角,取值范围为$[{0^ \circ },{90^ \circ }]$ ;$||\Delta i + \Delta j|{|_1}$ 表示两个事件在平面上的曼哈顿距离,反映事件在空间上的相关性;${\rm{\alpha}} $ 为归一化系数;$\;{\rm{\rho}} $ 为时空极坐标的极径;$||\Delta t|{|_1}$ 反映两事件在时间上的相关性;β为衰减系数,取值小于0。$\Delta t$ 越小,对应的$\Delta {\rm{\rho }}$ 越大,反映事件在时间上的相关性。式中:
$\Delta x$ 和$\Delta y$ 分别表示两个事件在两个地址方向的像素差值;M和N分别表示两个地址方向上的像素最大值,即相机的分辨率大小;$\Delta {t_{\min }}$ 表示中心事件和其余事件的最小时间间隔;$\Delta {t_{\rm{max}}}$ 表示最大时间间隔。事件相机的时间分辨率可达到微秒级甚至纳秒级,因此有效事件的相关性体现在同一像素的时间连贯性上。此外,由于相机的运动成像性,物体的运动或者相机的转动导致事件相关性不仅仅表现为同一像素上事件的时间连续性,也体现在邻近像素在时间上的连续性。根据曼哈顿距离和时间衰减特性构建的时空极坐标系能反映事件之间的相关性。通过极坐标时空邻域描述这种相关性,则极坐标时空邻域Ω可表示为:
式中:
$f({\rm{\rho}} ,{\rm{\theta}} )$ 为密度函数。${{\rm{\rho}} _1}$ 和${{\rm{\theta}} _1}$ 可表示为:式中:m、n分别为
${\rm{\theta }}({\rm{\rho}} )$ 和$\;{\rm{\rho}} ({\rm{\theta}} )$ 极坐标系中散点图拟合的正比例函数斜率,该斜率对应角度一般小于10°,通过两个斜率得到极坐标时空邻域的边界范围,如图1(a)所示。将每个事件与极坐标系的时空邻域内事件相连,并以此循环每个事件,同时将事件的观测值yi,j,t连接对应事件xi,j,t,即可构建完整的马尔可夫网模型,模型示意图如图1(b)所示。
事件相机输出数据Y中分为两部分:一部分是有效事件X,另一部分是噪声N。求联合概率分布P(X,Y)最大时X的值即可过滤噪声。根据Hammersley-Clifford定理[10],马尔可夫网模型的联合概率分布可表示为随机变量在最大团上势函数的乘积:
式中:C为模型的最大团;
$\varPhi ({X_Q},{Y_Q})$ 为Q上的势函数,对团Q上的变量关系进行建模;Z为归一化因子,确保P(X,Y)为正确定义的概率。其表达式为:为了满足非负性,指数函数通常来定义势函数,即:
其中,
$E({X_Q},{Y_Q})$ 为定义在变量(XQ,YQ)上的实值函数,采用形式为:式中:
${\alpha _{uv}}$ 和${\;\beta _v}$ 为参数。第一项考虑到两个节点之间的相互关系,第二项考虑观测值的直接影响。${\alpha _{uv}}$ 为两事件的曼哈顿距离归一化系数,取值范围为[0,1],两事件越相关,能量值越小,${\;\beta _v}$ 的值为−1/m,m为中心事件邻域中事件数量。根据公式可知中心事件和邻域内状态相同事件越多,时空距离越小,两个事件相关性越大,即能量函数越小。 -
根据最大后验查询(MAP)[11],在给定先验信息Y=y的情况下找到X中变量最可能的赋值:
上述公式的意义为概率最大时求x最可能的赋值。将求最大概率问题转换为求最小能量问题,即寻找能量最小时X的取值:
每个事件xi,j,t的状态有两种:+1和−1,其中+1表示该事件为有效事件,−1表示该事件为噪声。ICM算法是一种优化算法,用于获取马尔可夫随机场联合概率分布(能量函数)局部最大(最小)配置。其主要思想是:初始化事件状态为+1,计算能量函数值E1;反转事件状态为 −1,再一次计算能量函数值E2,对比两次计算能量函数值的大小,判定事件的真实状态。算法流程图如图2所示。
为了优化去噪效果,同时优化算法运行时间,文中对ICM算法进行了改进。将事件流分割成事件流单元,迭代算法在细胞单元中进行。通过增加ICM算法迭代次数k,使得解更接近于全局最优解。
-
衡量降噪效果优劣的评价指标需要具有科学性和综合性。通过视觉直观定性的评价降噪效果好坏在一定程度上具有说服力,但缺少定量指标进行支撑。文中提出降噪精度Pprecision和真实事件损失率Ploss[12]两个概念来描述降噪效果的好坏。
在未知事件状态的情况下,通常假设算法过滤掉的事件为噪声事件,降噪精度指噪声占总事件的比例:
式中:Nnoise为噪声事件数量;Ntotal为事件总数量。该值越大,去噪效果越好。
在已知事件状态的情况下,通常用真实事件率Ptrue来代替降噪精度:
式中:Ndenoised_true代表去噪后事件中真实事件数量;Ndenoised代表去噪后事件的数量。该比值越大,反映降噪精度越高,效果越好。
降噪不可避免地会导致真实事件的损失,为反映真实事件的损失情况,可以定义真实事件损失率Ploss:
式中:Ntrue代表相机输出事件Y中有效事件数量。Ploss值越大,反映降噪算法对于真实事件的损失越少,降噪效果越好。
-
为了验证方法的有效性和降噪指标的合理性,分别用仿真数据和真实场景数据进行对比实验分析。此外,为对比降噪效果,将Inivation公司开发的DV软件中开发的Dvsnoisefilter模块和文中算法对比,该滤波器主要参数如表1所示。
Parameter Value Background activity support min 1 Background activity support max 8 Background activity time/μs 2 000 Refractory period time/μs 100 Table 1. Main parameters of Dvsnoisefilter
-
事件相机仿真器[13]是模拟事件相机生成数据的软件,使用该仿真器将一段高帧视频转化为模拟事件流数据。高帧视频是在相机固定情况下拍摄单个行人获得的,如图3(a)所示。由于相机处于固定状态,场景运动目标单一且简单,仿真得到的事件流可看作无噪声事件流数据,图3(b)为仿真事件3D可视化效果,图3(c)为2D可视化效果。
Khodamoradi团队[14]证实了事件相机的噪声事件,也称背景活动(Background Activity,BA)[15],可用泊松分布来描述:
式中:t为时间间隔;n为该时间段内的BA事件数;λ为每个像素点产生BA的平均速率。
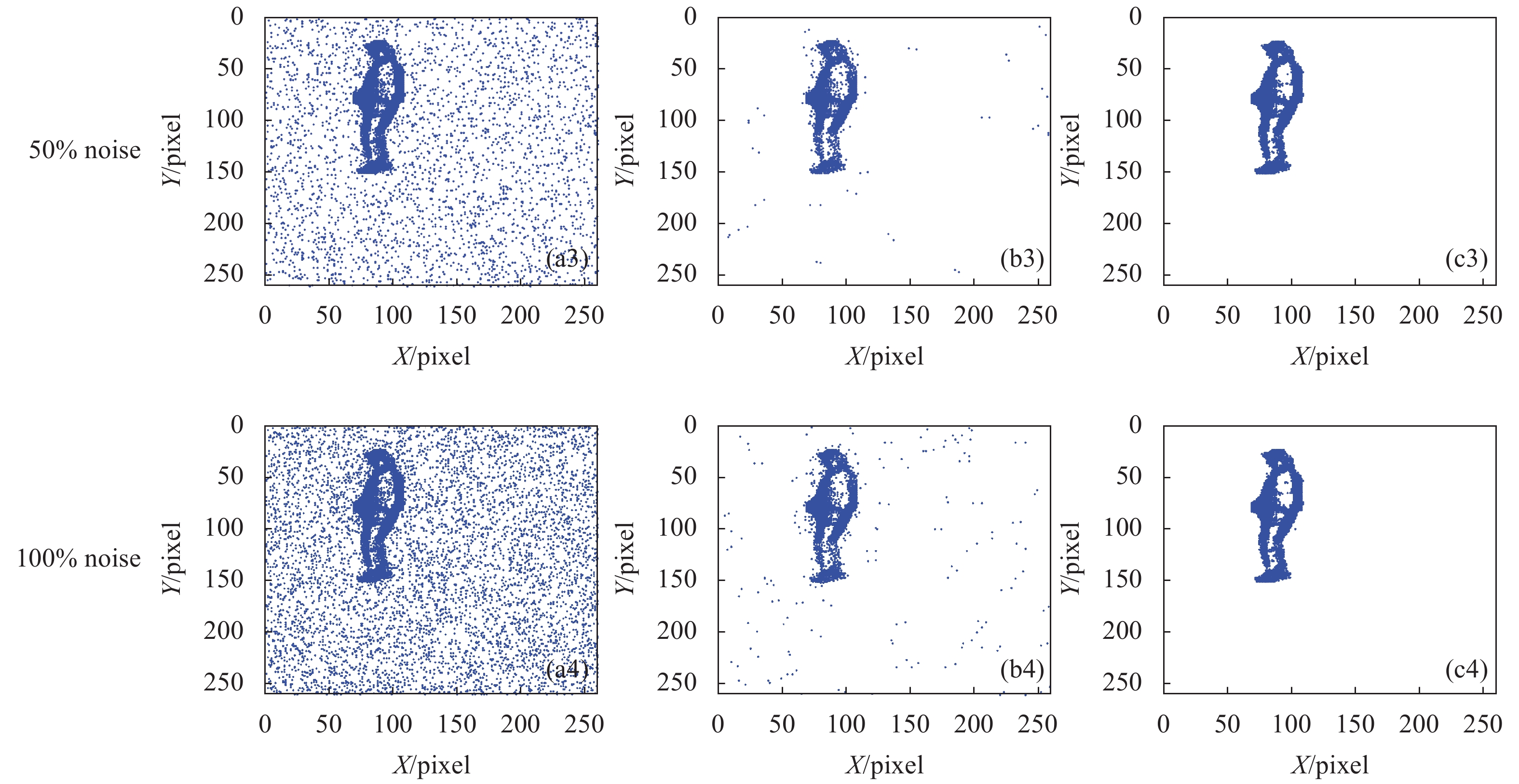
为了验证算法的效果,首先在仿真事件流数据中分别加入一定比例(10%、20%、50%和100%)、符合泊松分布的噪声事件,图4(a)为加入噪声后的可视化效果图。其次,分别用滤波法和文中算法对上述加入噪声后的数据集进行去噪,如图4(b)和图4(c)所示。最后,通过对比去噪前后二维可视化效果图定性分析去噪效果。此外,为了对去噪算法定量分析,统计并对比了滤波法和文中算法真实事件率和事件信噪比。实验结果如图3~图5和表2~表3所示。
Method Real events rate, Ptrue 10% 20% 50% 100% Initial state 90.90% 83.33% 66.67% 50.00% Filtering 98.03% 97.31% 96.54% 89.01% Proposed 98.66% 98.21% 97.59% 93.89% Table 2. Statistics table of true event rate under different noise
结果表明,随着噪声比率的增加,滤波法降噪后目标周围出现越来越多的噪声事件未被过滤掉,出现这种情况和阈值大小设置有关系,而文中算法只是人内部和周围极少噪声事件被当作有效。另外随着噪声比率增加,真实事件率和事件信噪比都有所下降,但是文中算法下降较小,尤其是在噪声较大的情况下,文中算法相对于滤波法的优势更明显,从而也证明了文中算法的有效性。
-
在该实验中,真实场景数据来源事件相机DAVIS346,其空间分辨率为346×260,动态范围120 dB,延迟20 μs,芯片功率10~170 mW。
为了验证算法的有效性,使用DAVIS346捕获的室内的场景事件流数据作为验证数据集。该场景背景复杂,包含桌子、饮水机、柜子、台灯等物体,帧图像如图6(a)所示。真实数据3D、2D可视化图像如图6(b)和图6(c)所示,从可视化效果图中可以看出相机拍摄数据中存在大量的噪声。
使用滤波法和文中算法对采集的数据进行降噪,降噪后3D和2D可视化效果如图7所示,其中图7(a)和图7(b)为滤波法降噪效果,图7(c)和图7(d)为文中算法降噪效果。从可视化效果上分析,文中算法更好地去除了目标边缘处的噪声,使边缘轮廓更加清晰,明显更优于滤波方法。此外,滤波法降噪后剩余35524个事件,文中算法降噪后剩余32982个事件,降噪精度高于滤波法,见表4。文中算法直接对事件流数据降噪,利用相机高时间分辨率的特点设计的去噪算法可有效去除噪声,去噪后数据可直接应用于后续的事件流处理算法中。
Method Loss rate of real events, Ploss 10% 20% 50% 100% Filtering 1.87% 2.69% 3.84% 4.25% Proposed 1.75% 2.51% 3.44% 3.80% Table 3. Statistics table of true event loss rate under different noise
Number Pprecision Method 50000 - Filtering 35524 28.95% Proposed 32982 34.04% Table 4. Statistics of noise reduction accuracy of real events by different algorithms
-
文中介绍了一种直接对原始数据流降噪的算法。针对真实事件之间具有相关性这一先验信息,构建概率无向图模型来描述事件之间的关系。利用最大后验查询的思想,将求随机联合分布最大问题转换为求能量最小问题,并采用改进ICM算法优化配置。降噪精度和真实事件率两个评价指标用于定量分析去噪效果。此外,为了更好地反映降噪性能,将滤波法与文中算法进行对比,通过仿真数据和真实数据进行验证,证明了文中算法的有效性。后续工作将对算法结构进行优化,以降低运行时间,实现实时去噪。未来将进一步进行基于事件相机的高分辨图像重建以及三维重构等视觉应用研究。
Denoising algorithm based on improved Markov random field for event camera
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210294
- Received Date: 2021-05-05
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-06-21
- Available Online: 2021-10-20
- Publish Date: 2021-10-20
-
Key words:
- event camera /
- denoising algorithm /
- probability undirected graph model /
- conditional iteration mode
Abstract: To solve the problem of the large amount of noise in the event stream output by the event camera, an event stream denoising algorithm based on the probability undirected graph model was introduced. Due to the imaging principle of the camera, the change of the target had certain regularity and correlation in time and space. By mapping the event to the polar coordinate space-time neighborhood, the local correlation of the event was established to build a complete probability graph model. In addition, the improved conditional iterative mode algorithm was used to optimize the iterative solution of model. The experimental results of simulated data generated by the event camera simulator and the real data recorded by DAVIS346 show that the proposed algorithm can effectively remove noise events. Finally, the comparison with the filtering algorithm proves that the algorithm is superior to the filtering algorithm.











































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: