HTML
-
随着红外传感元器件和红外成像技术的发展,高分辨率红外图像在军事和民用领域得到广泛运用[1-5]。在民用领域,红外夜视仪、夜间交通管控系统等设施设备发挥了重要作用。在军事领域,基于红外成像的导弹末制导系统具有精度高、针对性强等特点。红外图像目标识别技术可依托观测图像获取感兴趣目标的所属类别,为情报解译提供支撑。红外目标识别方法一般区分特征提取和分类决策两个阶段。根据现有文献,红外目标识别方法中涉及的特征包括几何外形、局部纹理、像素分布特性等[6-9]。分类过程中,根据提取得到的特征进行分类器的选择或设计,典型代表包括支持向量机(SVM)[10]、稀疏表示分类(SRC)[11]等。深度学习理论的出现和发展为信号处理、图像分析提供了重要手段。特别地,在图像识别领域,以卷积神经网络(CNN)为代表的深度学习模型成为炙手可热的工具,并验证了其有效性。参考文献[12-14]就针对红外图像目标识别问题设计了深度网络模型并进行了应用。特别地,参考文献[14]以某卷积神经网络为基础对红外图像进行特征提取,将各个卷积层输出的特征图进行处理,获取相应的深度特征矢量。最后,采用联合稀疏表示模型对多层次深度特征进行联合决策。相比传统直接应用深度模型进行端到端分类的方法相比,多层次深度特征的联合运用进一步提高了识别性能,反映了方法的有效性。
文中提出基于筛选深度特征的红外图像目标识别方法,主要是对参考文献[14]中联合深度特征方法进行两个方面的改进优化。一方面,采用ResNet替换参考文献[14]中的卷积神经网络。根据现有文献报道,ResNet通过引入残差学习算法可显著提高深度网络的稳健性[15-16]。相比一般的卷积神经网络,ResNet输出的多层次深度特征具有更强的鉴别力。另一方面,对于ResNet各个卷积层输出的深度特征矢量,基于斯皮尔曼等级相关系数[17-18]评价它们与原始图像的相关性,进而合适的门限选取若干相关性较高的深度特征矢量。最终,基于联合稀疏表示模型[14,19]对选取的多层次深度特征矢量进行表征分类,获取决策结果。与参考文献[14]中利用全部深度特征矢量的算法相比,文中通过有效的特征筛选可以提出部分冗余甚至负面信息,从而提高分类的精度和效率。因此,通过充分运用ResNet学习得到的深度特征,文中方法可以进一步提高红外图像识别性能。实验中,采用公开的中波红外目标图像数据集(MWIR)对设计方法进行测试和分析,分别在原始样本、噪声样本和遮挡样本三类情形下与部分现有方法进行对比。实验结果反映了提出方法的有效性和稳健性。
-
ResNet作为一种代表性的卷积神经网络,在图像分割、分类识别等领域得到了广泛应用和验证[15-16]。与一般的卷积神经网络相比,ResNet能够随着网络层数的增加,获得更佳丰富的深度特征,同时可避免梯度消失问题。假设
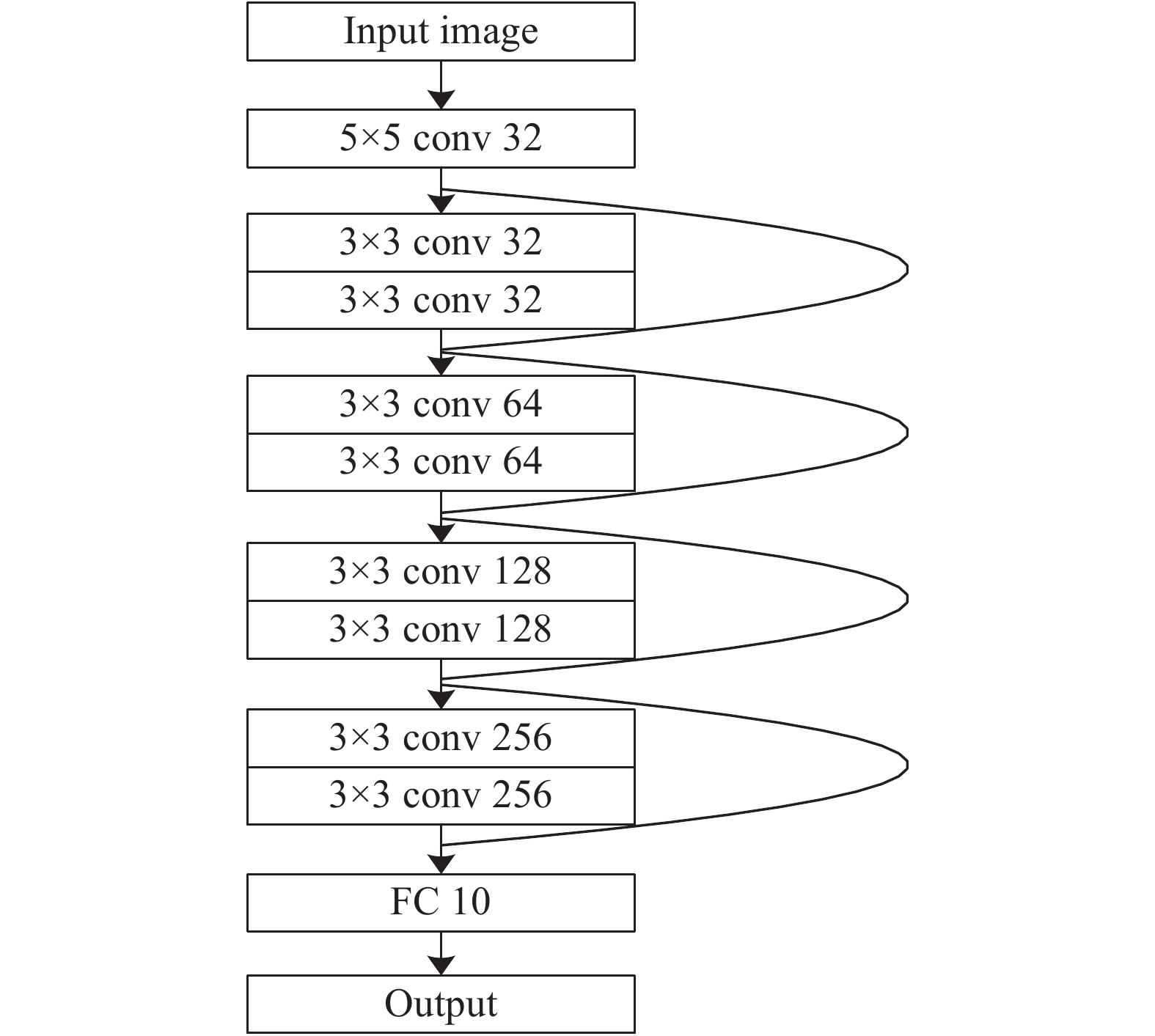
$H\left( x \right)$ 为最佳映射,利用堆叠的非线性层得到新映射$F\left( x \right) = H\left( x \right) - x$ ,从而计算新的最佳映射$F\left( x \right) = H\left( x \right){\rm{ + }}x$ ,提高网络的整体学习性能和分类能力。文中将ResNet引入红外图像目标识别,主要用于学习多层次的深度特征。图1显示了文中设计的针对10类目标分类问题的ResNet整体结构,共包含12层,在每个卷积层均可以输出特征图,通过矢量化操作获得相应的深度特征矢量。与一般的卷积神经网络结构相比,ResNet能够将输入与后续非相邻层直接相连,从而最大程度保持了图像中的有效信息。此外,ResNet降低了网络学习的整体难度,有利于提高网络学习效率。基于图1可获得红外目标图像多层次深度特征。这些深度特征可从不同方面描述目标特性,联合运用它们可为后续的分类识别提供有效支撑。
-
基于ResNet学习得到的多层次深度特征对于描述红外图像中的目标特征具有互补性,联合运用这些信息有利于提高识别性能。然而,实际过程中并不是所有层次的深度特征对于正确识别都有贡献,其中不乏冗余分量,不仅会降低识别效率还可以降低识别精度。为此,有必要对多层次深度特征矢量进行可靠筛选,筛选保留的深度特征用于后续的分类过程。
文中采用斯皮尔曼等级相关系数作为深度特征筛选的基础相似度度量准则。斯皮尔曼等级相关稀疏用于评价两个变量之间的统计相关性[17-18],有不依赖样本分布的优点。设定
$P$ 和$Q$ 为两个$n$ 维的变量,${P_i}$ 、${Q_i}$ 分别为两者的第$i(1 \leqslant i \leqslant n)$ 个元素。按照升序或降序对$P$ 和$Q$ 的进行重新排列,得到新的变量序列$p$ 、$q$ 。其中,${p_i}$ 表示${P_i}$ 在$P$ 中的排序,${q_i}$ 表示${Q_i}$ 在$Q$ 中的排序。然后,计算差分集合$d = {p_i} - {q_i},1 \leqslant i \leqslant n$ 。在此基础上,$P$ 和$Q$ 的斯皮尔曼等级相关系数按照下式计算:根据上述过程,斯皮尔曼等级相关系数可用于快速计算不同深度特征矢量与原始红外图像之间的相关性。在此基础上,设置适当门限
$T$ ,对于相关性高于门限的深度特征矢量予以保留。反之,相关性小于门限的深度特征矢量则予以剔除,不再进入后续的分类过程。
-
联合稀疏表示模型是处理多个关联稀疏表示问题的有效工具,通过利用内在关联提高求解精度,为信号重构,图像识别等应用提供支撑[14, 19]。对于测试样本
$y$ ,假设其经过筛选后得到的$K$ 个ResNet深度特征矢量为为:$\left[ {{y^{(1)}}{\rm{ }}{y^{(2)}}{\rm{ }} \cdots {\rm{ }}{y^{(K)}}} \right]$ 。它们的联合稀疏表示模型构建如下:式中:
${A^{(k)}}$ 表示对应第k个深度特征的全局字典,记为所有训练样本获取的第k个深度特征的矩阵合集;${\alpha ^{(k)}}$ 为稀疏系数矢量;$\;\beta = \left[ {{\alpha ^{(1)}}{\rm{ }}{\alpha ^{(2)}}{\rm{ }} \cdots {\rm{ }}{\alpha ^{(K)}}} \right]$ 则为系数矩阵。公式(2)给出了联合稀疏表示的最基本形式,但并未考虑不同成分之间的联系。为此,实际应用的联合稀疏表示模型增加了相关性约束,新的目标函数如下式所示:
式中:
$\lambda $ 正则化系数。${\ell _{\rm{1}}}/{\ell _2}$ 范数对稀疏矩阵的约束使得不同深度特征对应的系数矢量倾向于相近的分布特点,即它们之间的相关性。对公式(3)进行求解,可获取稀疏系数矩阵,即不同深度特征对应的稀疏系数矢量。在此基础上,按照类别对测试样本的深度特征进行联合重构,计算重构误差之和,用于最终的类别决策,如下式所示:
式中:
$A_i^{(k)}$ 为第i个训练类别对应第k个深度特征的局部字典;$\alpha _i^{(k)}$ 为对应的系数矢量。 -
根据上述分析,文中设计如图2所示的识别流程。首先,根据所有训练样本对图1所示的ResNet进行训练,获得可靠的网络参数。对于测试样本,在ResNet的各个卷积层构建相应的深度特征矢量。在该计算书,利用斯皮尔曼等级相关系数进行深度特征的筛选,获取若干个深度特征矢量。与此同时,所有训练样本按照测试样本选取的深度特征进行对应抽取,并相应构建全局字典。最终,测试样本选取的深度特征通过联合稀疏表示模型进行分析和重构,根据最小重构误差的准则判定其所属的目标类别。
3.1. 联合稀疏表示
3.2. 识别流程
-
实验基于中波红外目标数据集(MWIR)实施。该数据集在合作条件下对10类地面车辆目标(Pickup、SUV、BTR70、BRDM2、BMP2、T72、ZSU23-4、2S3、MTLB、D20)进行了全方位高分辨率红外图像采集,相关数据集的介绍可参见参考文献[13]。红外观测图像可以反映出不同目标的外形特点与热源分布特征,从而达到区分不同目标的目标。根据参考文献[14],文中对任一类目标选用120幅图像作为训练样本,另外100幅不同的图像作为测试样本。
从现有文献选取若干方法进行对比分析,包含参考文献[10]中基于SVM的方法,参考文献[11]中基于SRC的方法;参考文献[13]中采用CNN的方法以及参考文献[14]中联合深度特征的方法(记为JSR-Deep)。其中CNN方法仅仅采用一般的CNN网络实现端到端的特征学习与分类。为全面测试提出方法的性能,后续实验分别在原始测试样本、模拟噪声测试样本以及模拟遮挡测试样本上开展,通过上述三类场景的测试与对比,可对提出方法的有效性和稳健性进行较为综合的评估。
-
首先基于原始测试样本进行实验。如前文所述,原始测试样本与训练样本一样采集自合作条件,两者之间存在较高的相似度,因此识别难度相对较低。采用提出方法对各类目标的100个测试样本进行识别,正确识别样本数目分别为98、98、98、100、100、100、99、97、98、98 (对应4.1节描述的目标类别顺序),据此可得各类目标的正确识别率。为综合评估方法性能,文中定义平均识别率为
${P_{{\rm{av}}}}{\rm{ = }}{N_{\rm{c}}}/{N_{\rm{T}}}$ ,其中${N_{\rm{c}}}$ 为正确识别样本数,${N_{\rm{T}}}$ 为测试样本总数。在此条件下,分别计算文中方法和四类对比方法的平均识别率,如表1所示。对比可知,文中方法在当前条件下的平均识别率为98.4%,高于对比方法,体现其更强的有效性。与CNN方法相比,文中通过引入鉴别力更强的ResNet进一步提升了分类能力。与JSR-Deep方法相比,文中通过优化网络结构以及进行必要的深度特征筛选保证了特征的可靠性,进一步促进了识别性能的提升。Method Average recognition rate Proposed 98.4% SVM 94.5% SRC 95.1% CNN 96.6% JSR-Deep 97.8% Table 1. Comparison of reuslts from different methods on the orginal test samples
-
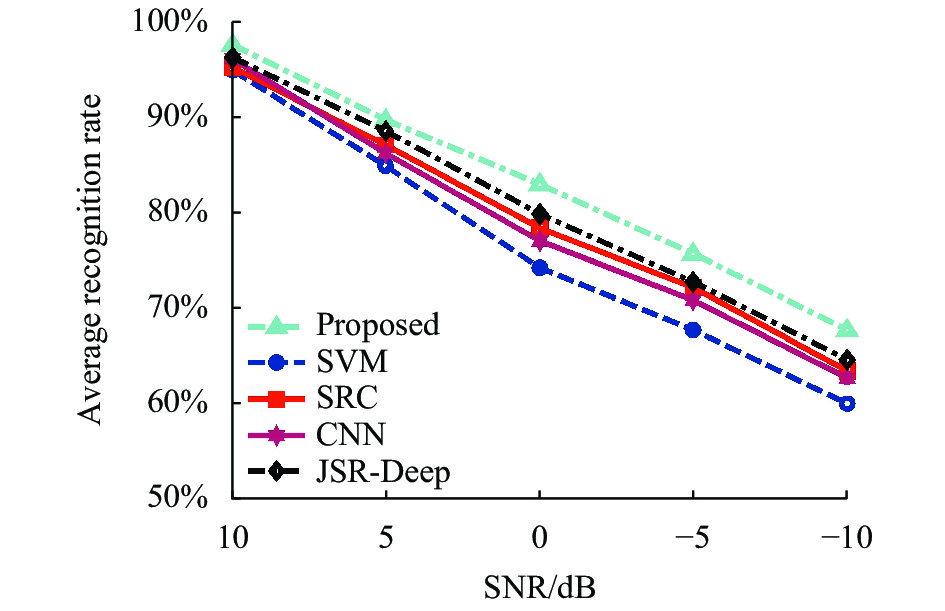
噪声发生在红外图像采集和后续处理的各个环节,因此实际过程中非合作条件下的红外图像往往受到较为严重的噪声干扰。相比合作条件下的高信噪比(SNR)红外图像,噪声干扰下的样本中,目标特性变得模糊,从而加剧了识别难度。文中在原始样本的基础上,按照设定信噪比的原则对其进行加性噪声添加,构造信噪比分别为10 dB、5 dB、0 dB、−5 dB和−10 dB条件下的噪声测试集。在此基础上,分别采用提出方法和对比方法对五个不同噪声测试集进行分类,统计结果如图3所示。文中方法在各个噪声水平下均取得最高的平均识别率,体现其最优的噪声稳健性。CNN方法在噪声干扰条件下性能下降最为剧烈,反映了深度学习模型对于噪声等异常条件存在一定的不适应性。JSR-Deep通过对多层次深度特征的联合表征,一定程度降低了噪声的影响,提升了识别稳健性。文中方法则是通过结合ResNet优势,同时进行剔除不必要的特征,确保了最终对于噪声样本的识别性能。
-
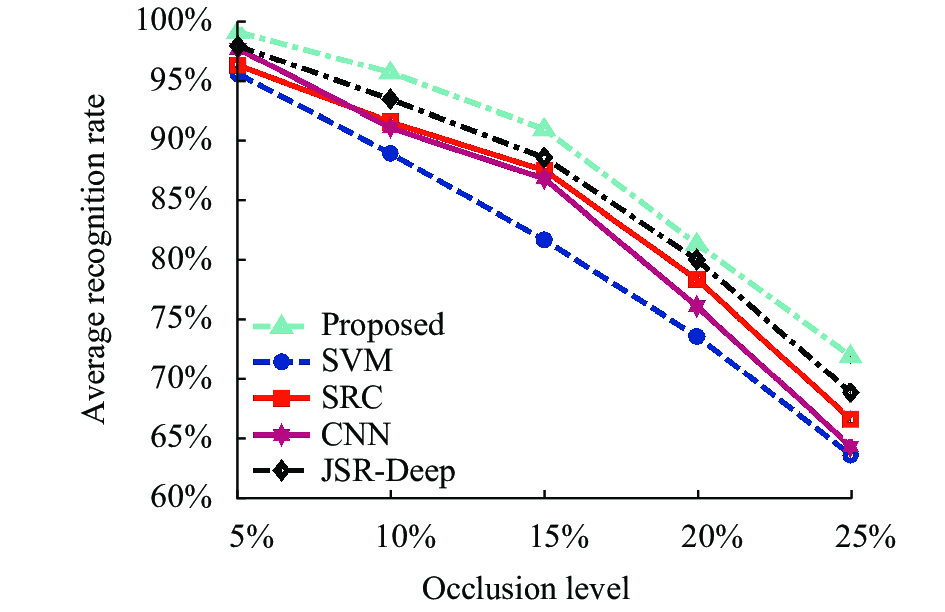
与噪声干扰的情形类似,在非合作条件下获取的红外目标图像也可以存在遮挡的情况,导致目标局部特性不能体现在获取的图像内。为测试提出方法在遮挡条件下的性能,文中首选对原始测试样本中的目标部分区域进行模拟遮挡。遮挡水平采用被遮挡目标区域占目标全部区域的比例进行衡量。据此,该实验构造了遮挡比例分别为5%、10%、15%、20%和25%条件下的测试集,进而对提出方法和对比方法进行测试,获得如图4所示的统计结果。由此可以看出,提出方法在遮挡条件下相对可保持更强的稳健性。CNN方法的结果与噪声干扰类似,性能下降最为剧烈。其余方法的性能趋势也与噪声干扰基本相同。文中方法综合了ResNet多层次深度特征的优势,通过进行了必要的特征筛选,确保影响正确识别的不良因素得以剔除,因此可进一步提高方法对于遮挡样本的识别稳健性。
4.1. 数据集介绍
4.2. 结果与讨论
4.2.1. 原始测试样本
4.2.2. 模拟噪声样本
4.2.3. 模拟遮挡样本
-
文中提出基于筛选深度特征的红外图像目标识别方法。在特征提取阶段,采用ResNet学习红外图像的多层次深度特征。同时,基于斯皮尔曼等级相关系数筛选其中的部分深度特征,剔除不必要的冗余成分。在分类阶段,采用联合稀疏表示对筛选得到的深度特征进行分析,获取最终的决策结果。因此,方法可结合ResNet多层次深度特征的优势,提高最终识别性能。实验在中波红外目标数据集上开展,分别对原始测试样本、模拟噪声样本和模拟遮挡样本进行分类,结果验证了方法的有效性和稳健性。

















































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: