HTML
-
激光是进行无线输能的一种方式,具有方向性好、传输距离远、能量密度高等优点,在应急抢险输电、空间能源网络和能源互联网等领域有广泛的应用前景,近年来发展迅速[1-5]。光电池具有非线性的输出特性,而激光无线能量传输(Laser Wireless Power Transmission,LWPT)系统中光电池的光强和温度极易变化,造成光电池不能稳定工作在功率匹配状态,这往往会导致整个系统的能源大量损失[6-7],因此开发针对LWPT的最大功率跟踪系统(Maximum Power Point Tracking,MPPT)非常重要。
MPPT在太阳能领域广泛应用[8],但太阳能电池的MPPT系统不能直接用于LWPT。主要是因为太阳能MPPT系统对算法收敛速度要求不高,但由于大气湍流和跟瞄系统误差的原因,LWPT系统的光强和温度通常快速变化,对MPPT的算法收敛速度提出了很高的要求。因此研发针对激光输能领域的最大功率跟踪系统是目前急需解决的实际问题。
目前在LWPT领域的MPPT研究一般使用太阳能电池模型进行仿真,无法体现激光照射的实际情况,例如无法设置特定的激光波长,这是LWPT与太阳能的最大区别[9]。在硬件开发上,一般也使用太阳能MPPT控制芯片,不利于开发针对LWPT的算法和电路[10]。所以根据实际情况建立参数更灵活、分析能力更强大、输出结果更丰富的仿真系统,对LWPT系统的开发和应用有重要意义。
笔者研究设计和构建了一种针对激光无线能量传输的MPPT集成仿真系统,基于对光电池的建模,可以计算六结GaAs光电池在不同波长、光功率和温度条件下的输出特性。将光电池与MPPT系统模块耦合,可以实现功率匹配、功率失配以及MPPT调制后的多种输出参数。基于此仿真系统,对六结GaAs光电池在不同波长、光功率和温度条件下的物理规律进行研究,并研究了不同条件下功率失配时光电池的工作情况。基于光电池特性的研究结果,利用仿真系统设计MPPT电路,选用时间扰动算法实现MPPT仿真。整个仿真系统可以用于研究光电池的在不同条件下的输出特性和开发MPPT系统的电路及算法,对于激光无线能量传输的相关研究和应用有重要作用。
-
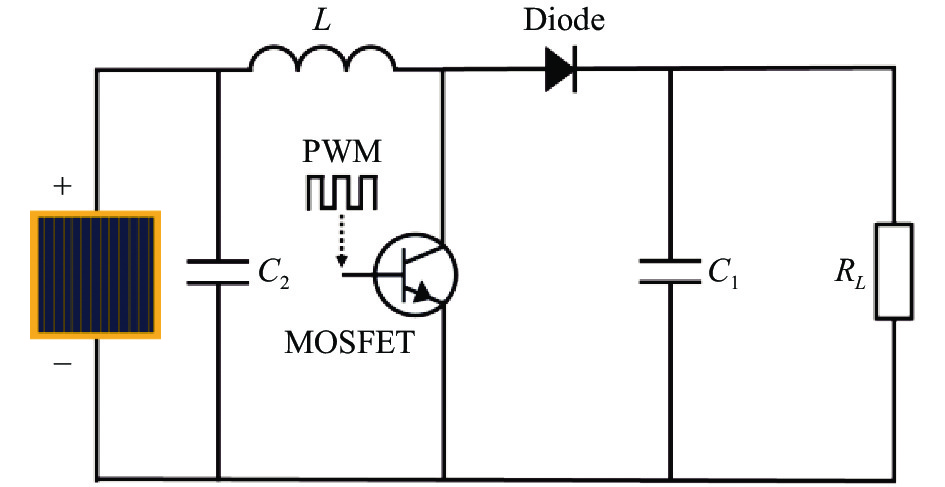
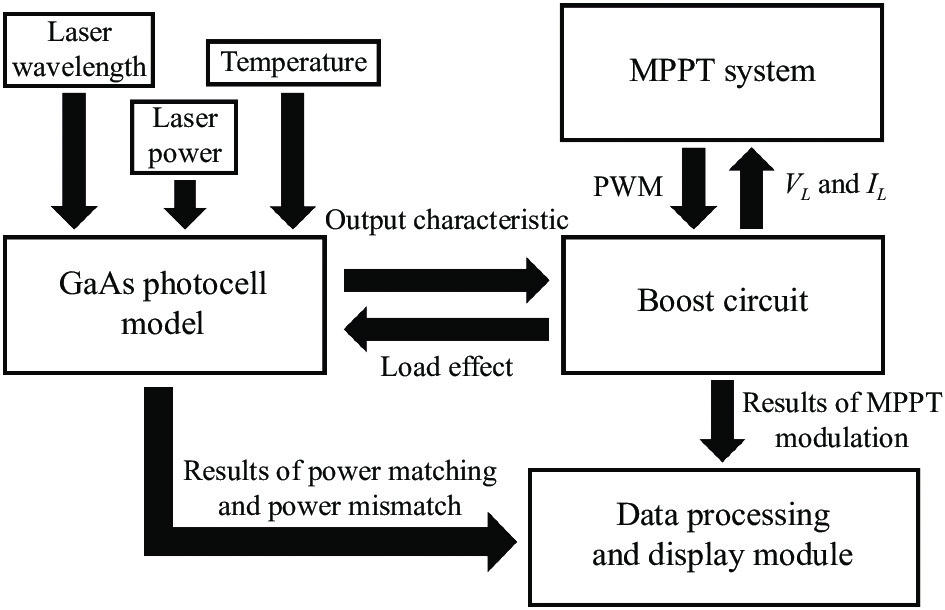
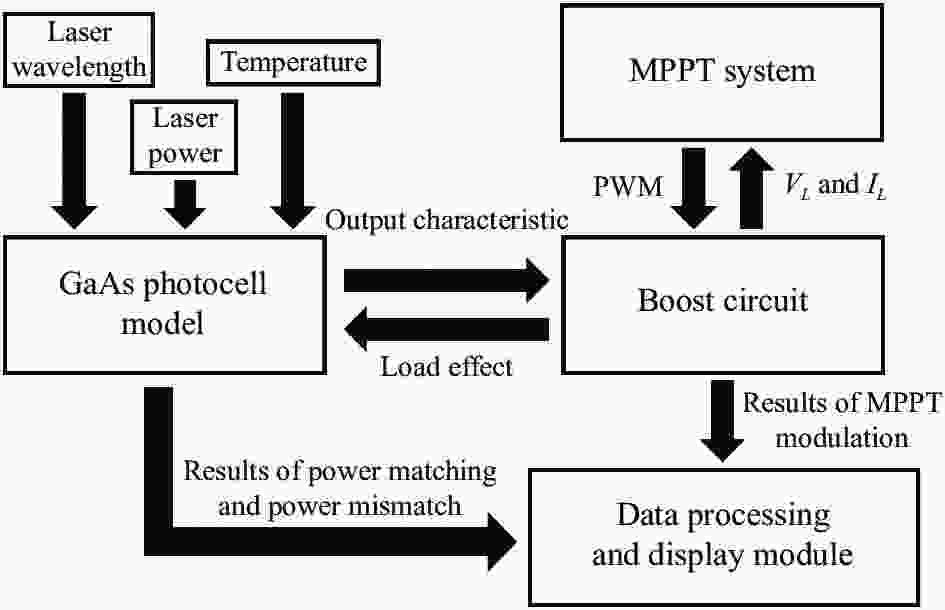
利用MATLAB/Simulink搭建的MPPT集成仿真系统如图1所示。该模型分为四部分,包括:光电池模型、MPPT系统、升压(Boost)主电路和数据处理显示模块。光电池选用六结GaAs光电池,根据数值计算理论建立光电池模型。MPPT系统相当于主控芯片,采集光电池模型和Boost电路中负载电阻的输出特性,再根据MPPT算法,输出占空比变化的PWM信号,调制Boost电路工作状态。Boost主电路对光电池进行脉宽调制(PWM),实现功率匹配和最大功率输出。数据处理显示模块处理并显示MPPT系统设计中关注的电路运行参数,系统中的各个模块将在后文详细论述。
-
如果采用软件自带的PV模型,无法体现不同激光波长和不同光电池材料之间的关系,模型还需要体现激光输能中快速变化的光功率和温度条件。
模型引入负载电阻对光电池输出的影响,可以得到光电池在功率失配下的输出特性。经过MPPT系统调制过后,光电池由功率失配重新变为功率匹配状态。所以,在光电池模型内部再建立一个MPPT系统对光电池输出特性影响的模块,可以得到光电池在经过MPPT算法调制后的输出参数,再与功率匹配和失配的输出参数进行实时对比,用于判断算法和电路的正确性。
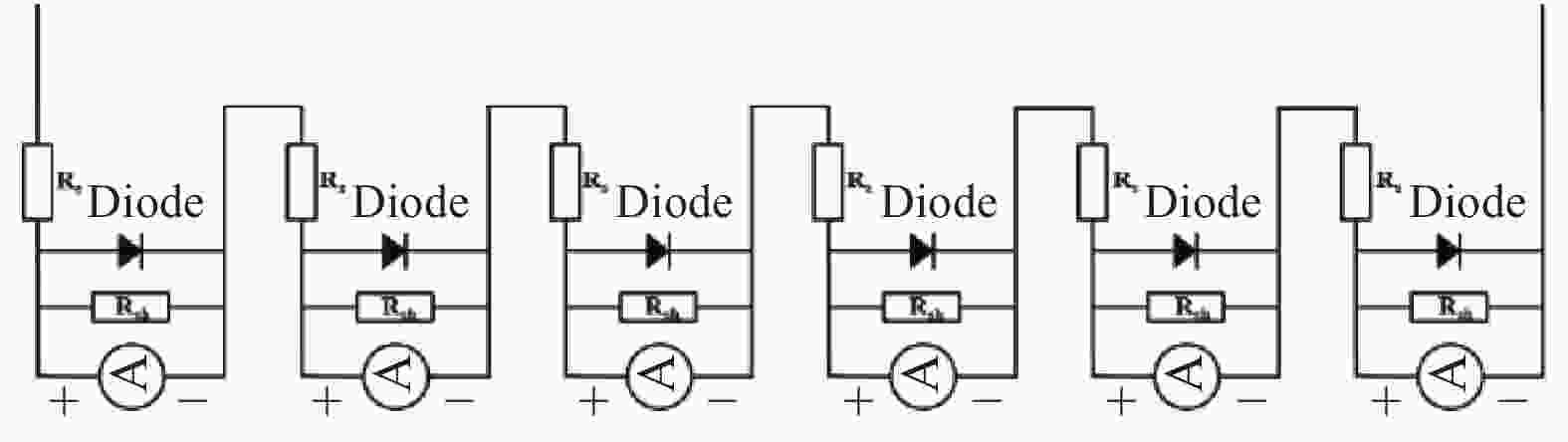
文中选用光敏面面积为16 cm2的六结GaAs光电池进行建模。如图2所示,六结光电池等效于六块单结光电池串联,因此首先需要对单结的光电池进行建模,再利用串并联关系得到六结GaAs光电池模型[11]。
光电池存在公式(1)这样的伏安特性关系:
式中:I为光电池输出电流;Isc为短路电流;e为单位电荷;V为光电池输出电压;Voc为截止电压;k为玻耳兹曼常数;T为光电池温度[12]。
因此要想求解公式(1),就需要得到不同波长、光功率和温度下的Isc和Voc。短路电流与内量子效率IQE有关[7]:
式中:R为反射率;Plaser为入射光功率密度;S为光照面积;λ为入射波长。当不同激光波长照射光电池时,由于禁带宽度对不同波长光子吸收的能力不同,内量子效率会发生变化。简化后不同波长下的内量子效率近似值如公式(3)所示[13]:
式中:αλ为GaAs在波长λ时的吸收系数;Lb为载流子扩散长度。由此可以计算得到不同波长下的内量子效率,实现不同波长时光电池输出特性的仿真。但内量子效率同样受温度的影响[12]:
式中:IQE(T)为不同温度下的内量子效率;IQE(λ)为T=300 K时,波长为λ时的内量子效率;σT为温度修正因子;T0为初始温度,此时能够耦合温度对内量子效率的影响。由公式(2)~(4)可以得到不同波长、功率和温度下的短路电流。
式中:Is为反向饱和电流;Voc(T0)为温度为300 K时的截止电压;v∆t为截止电压温度系数。不同温度下的反向饱和电流可以表示为[12]:
式中:Ir为常温下反向饱和电流;n为GaAs光电池的理想二极管因子;Eg为禁带宽度,其随温度变化表示为[12]:
式中:EgT为不同温度下的禁带宽度;Eg为T=0 K时的禁带宽度;式中温度取值范围满足0<T<103,a和b都是常数。由此可以建立耦合了波长、光功率和温度影响的GaAs光电池模型。上述所有参数由表1所示。
Parameter Value Unit e 1.602×10−19 C k 1.380 65×10−23 J/K Lb 10 μm Eg 1.519 eV Ir 4.25×10−18 A v∆t 1.6×10−3 V/K σT 8×10−4 1/K a 5.405×10−4 - b 204 - n 1 - Table 1. Photocell model parameters
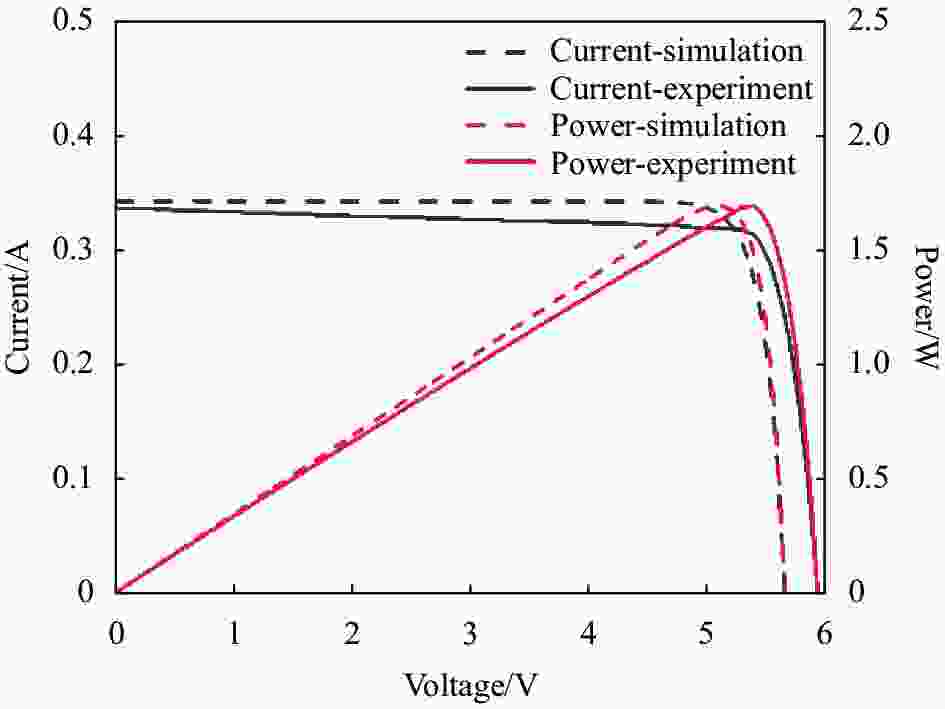
上述为单结GaAs光电池模型,再由串并联电路原理建立光敏面面积为16 cm2的六结GaAs光电池模型。图3为该光电池在温度为300 K时,以波长为808 nm,光功率4 W激光照射下的仿真和实验测得的I-V曲线和P-V曲线。光电池的输出电流和电压受掺杂元素种类、掺杂浓度以及厚度等因素的影响,存在一定的误差。且实际的光电池内部会存在寄生电阻,与光电池的结构和生产工艺有关,所以输出电压会存在一定误差。该模型基本能正确表示实际条件下光电池的输出特性。P-V曲线的最大值为功率匹配时的最大输出功率,对应的电阻为最大功率匹配电阻RLmax。
光电池模型可以同时得出三组输出结果:功率匹配下的输出特性、功率失配下的输出特性以及MPPT调制后的输出特性。再结合Boost电路中的负载电阻输出特性,一共得到四组输出结果。该系统可以对激光无线能量传输系统中,MPPT算法和电路设计的正确性进行实时判断,满足开发用于激光输能的快速响应MPPT系统的需求。
-
MPPT系统主要实现运行最大功率跟踪的算法和输出PWM信号的功能,系统需要采集负载输出的电压VL和电流IL。此模型可以灵活地更改MPPT算法,且由于文中使用单块六结光电池,不存在串联导致的多峰效应,所以选择时间扰动算法(Perturband Observation,P&O)。P&O算法通过判断光电池输出的电压和功率在P-V曲线上的位置,计算PWM信号占空比是增大还是减小,从而实现MPPT控制,时间扰动法算法调制判断方法。算法进行判断的依据由下列公式确定[15]:
式中:I(k)、V(k)和P(k)分别表示第k次采集光电池的输出电流、电压和功率;∆V(k)和∆P(k)分别表示第k次和第k−1次的差值。对上述结果进行比较判断,得出算法下一步V(k+1)的调制方向[15]:
(1) ∆P(k)>0,∆V(k)>0 时,V(k+1)=V(k)+dV;
(2) ∆P(k)>0,∆V(k)<0 时,V(k+1)=V(k)-dV;
(3) ∆P(k)<0,∆V(k)>0 时,V(k+1)=V(k)-dV;
(4) ∆P(k)<0,∆V(k)<0 时,V(k+1)=V(k)+dV。
式中:dV表示每次调制时电压V的变化量。
-
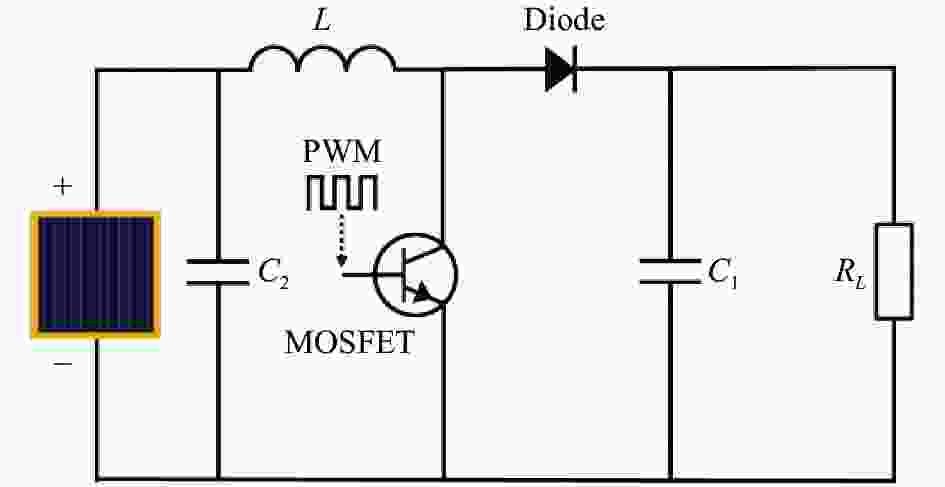
如图4所示是Boost电路拓扑结构,Boost电路是一种DC-DC升压电路,主要包含升压电感、升压电容、MOSFET和二极管。将PWM信号接入MOSFET的栅极,控制其导通和截止,从而实现Boost电路的两种工作状态[16]。在PWM调制时,电路中的升压电感L实现充电和放电,相当于在光电池和负载之间串联一个正向电流源,实现升压。电容C1和光电池并联,在MOSFET导通时,给负载提供电压。电容C2是滤波电容。
Boost电路的调制能力和效果主要由L和C1决定,二者分别满足下式[15]:
式中:Uin为光电池输入电压;D表示PWM信号的占空比;fs为开关管工作频率,同时也是PWM信号的频率;∆I0为纹波电流,通常取20%~40%;∆U0为纹波电压。这样根据具体的芯片参数和输出特性要求可以得出电路元器件的参数。同时电路中光电池输出电压和负载电压满足公式(11)[15]:
该模型可以灵活更改L和C1的参数,对于MPPT系统设计有重要的参考价值。
-
对于文中的激光无线能量传输的MPPT集成仿真系统,同时有四组信号输出:功率匹配和功率失配时光电池输出特性、MPPT调制后光电池和负载输出特性。四组信号再分为电流、电压、输出功率和转换效率,实现各种工作状态的对比。经过后处理,将所有结果进行显示,判断MPPT系统的工作效果。
-
为了研究激光输能系统中,六结GaAs光电池在不同条件下的工作状况,以及为了确定MPPT系统的设计标准,先对不同的波长、光功率以及温度条件下光电池的输出特性进行仿真。
假设标准工作条件为:入射波长λ=808 nm,入射光功率密度Plaser=250 mW/cm2,照射面积S=16 cm2,总的入射光功率为Pin=4 W,温度T0=300 K。为了研究光电池在不同条件下的输出特性,以及最大功率匹配点的变化规律,分别将光电池接收的激光波长、光功率以及温度在2.2 s的时间内快速变化。仿真时只改变单个条件,其余均为假设的标准工作条件。2.2 s内波长变化范围为700~900 nm,间隔为20 nm;光功率变化范围为3~5 W,间隔为0.2 W;温度变化范围为280~380 K,间隔为10 K。后续将对不同条件下的输出特性进行分析。
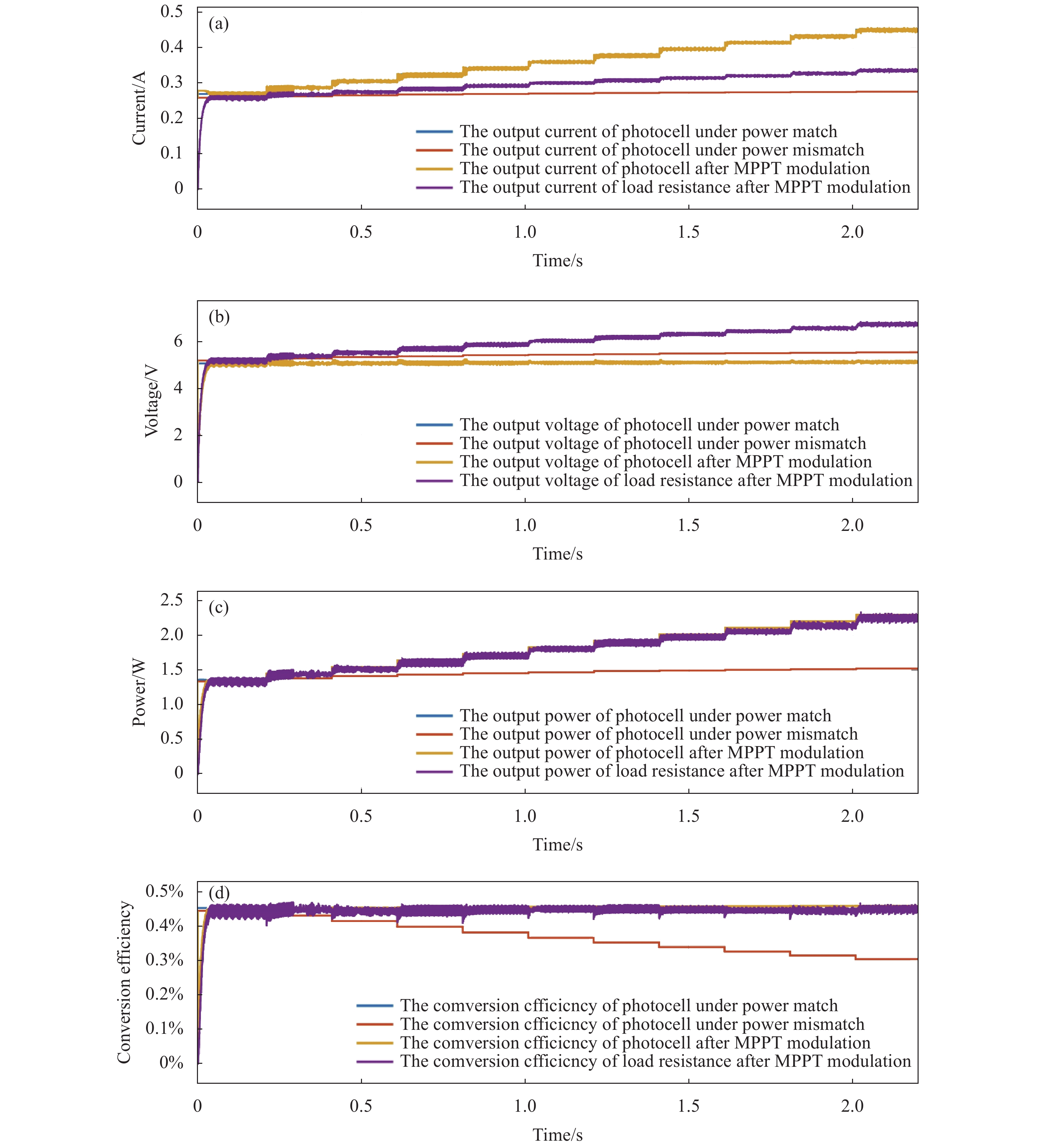
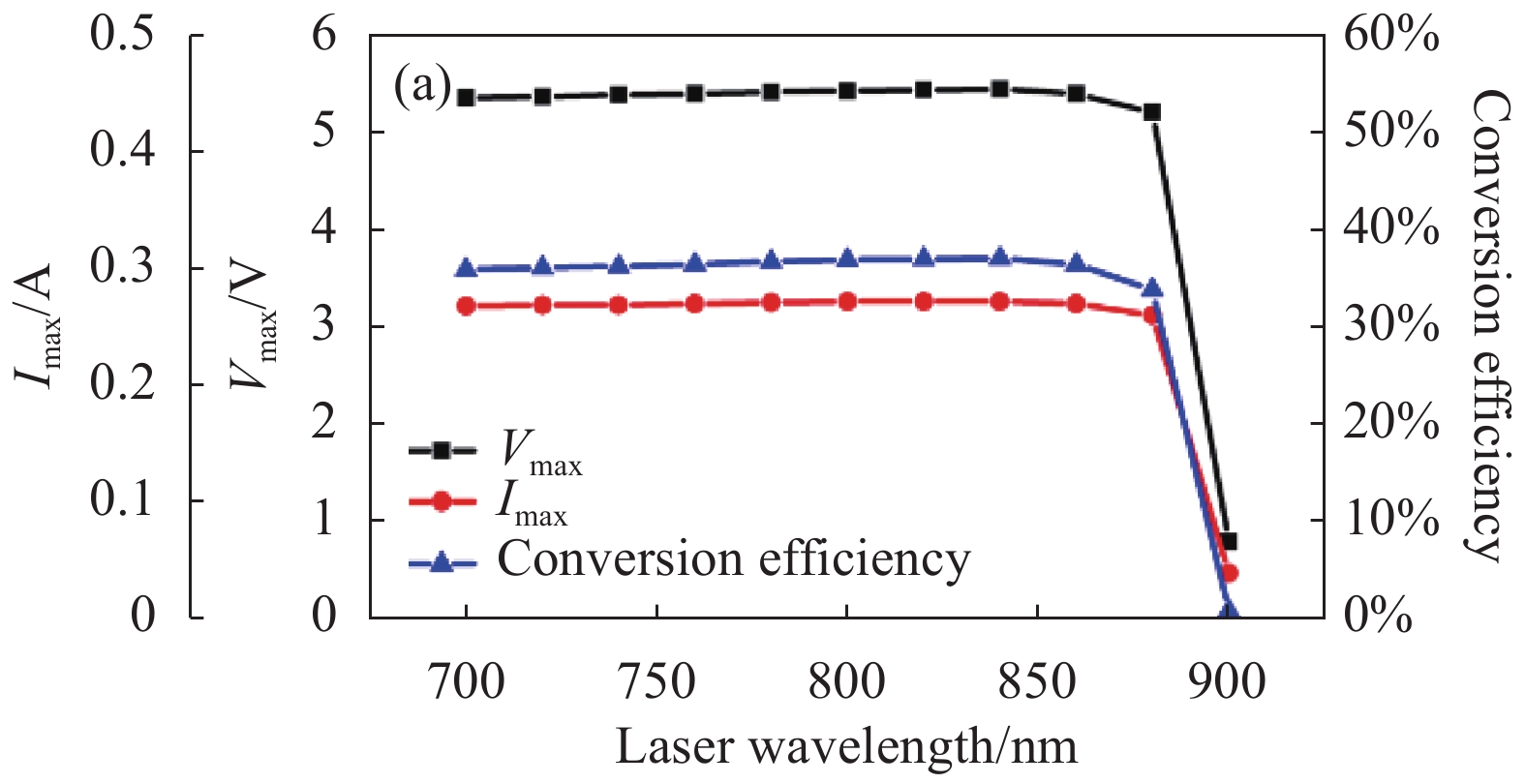
如图5为只改变光功率的仿真结果,集成仿真系统同时输出了四组结果:功率匹配时光电池的输出特性、功率失配时光电池的输出特性、MPPT调制后光电池的输出特性和MPPT调制后负载电阻的输出特性。对光电池在不同条件下电压、电流、电阻以及转换效率进行分析,研究其物理规律和MPPT工作效果。
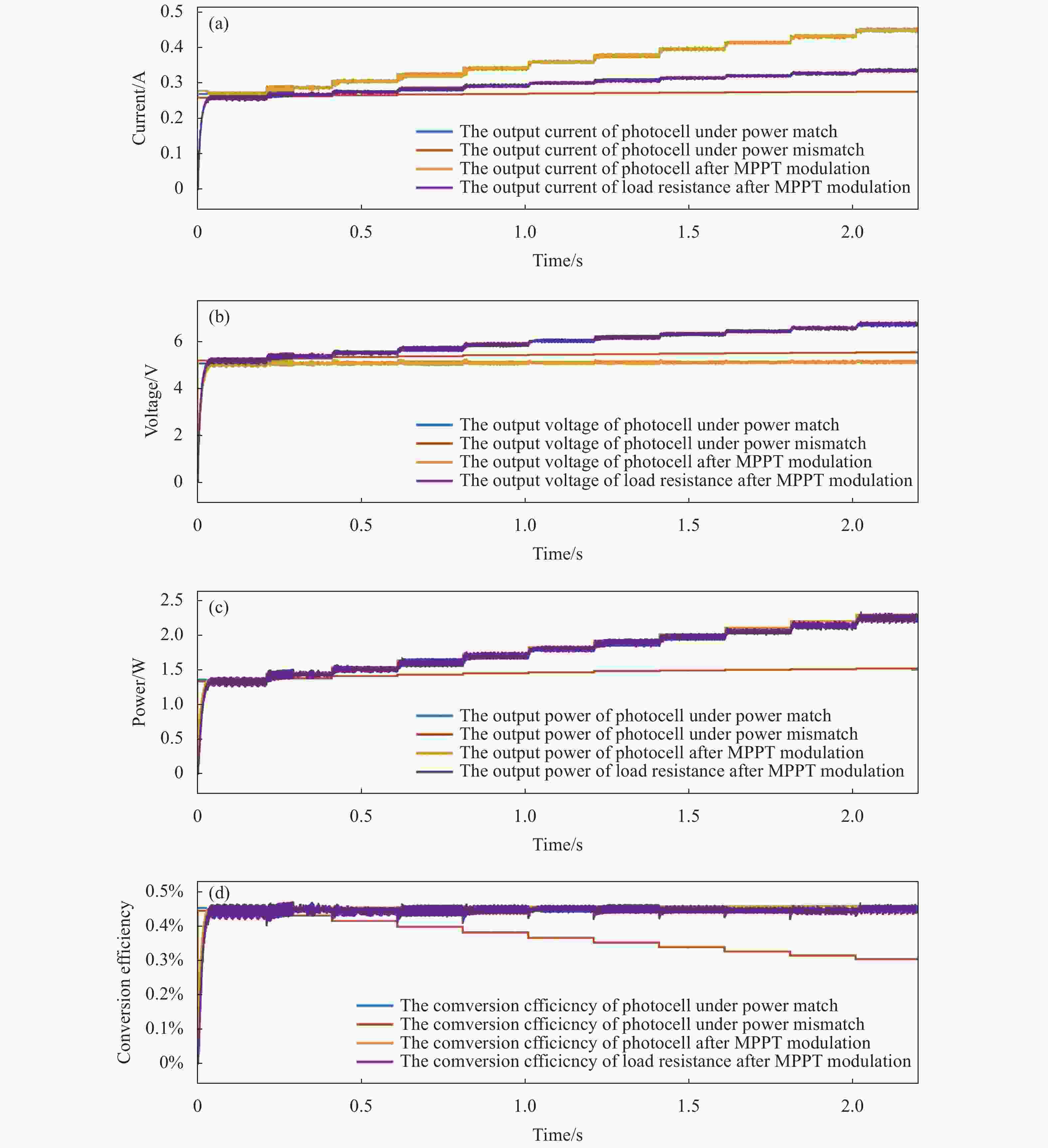
Figure 5. Results of MPPT integrated simulation system under only changing the laser power. (a) Output voltage; (b) Output current; (c) Output power; (d) Conversion efficiency
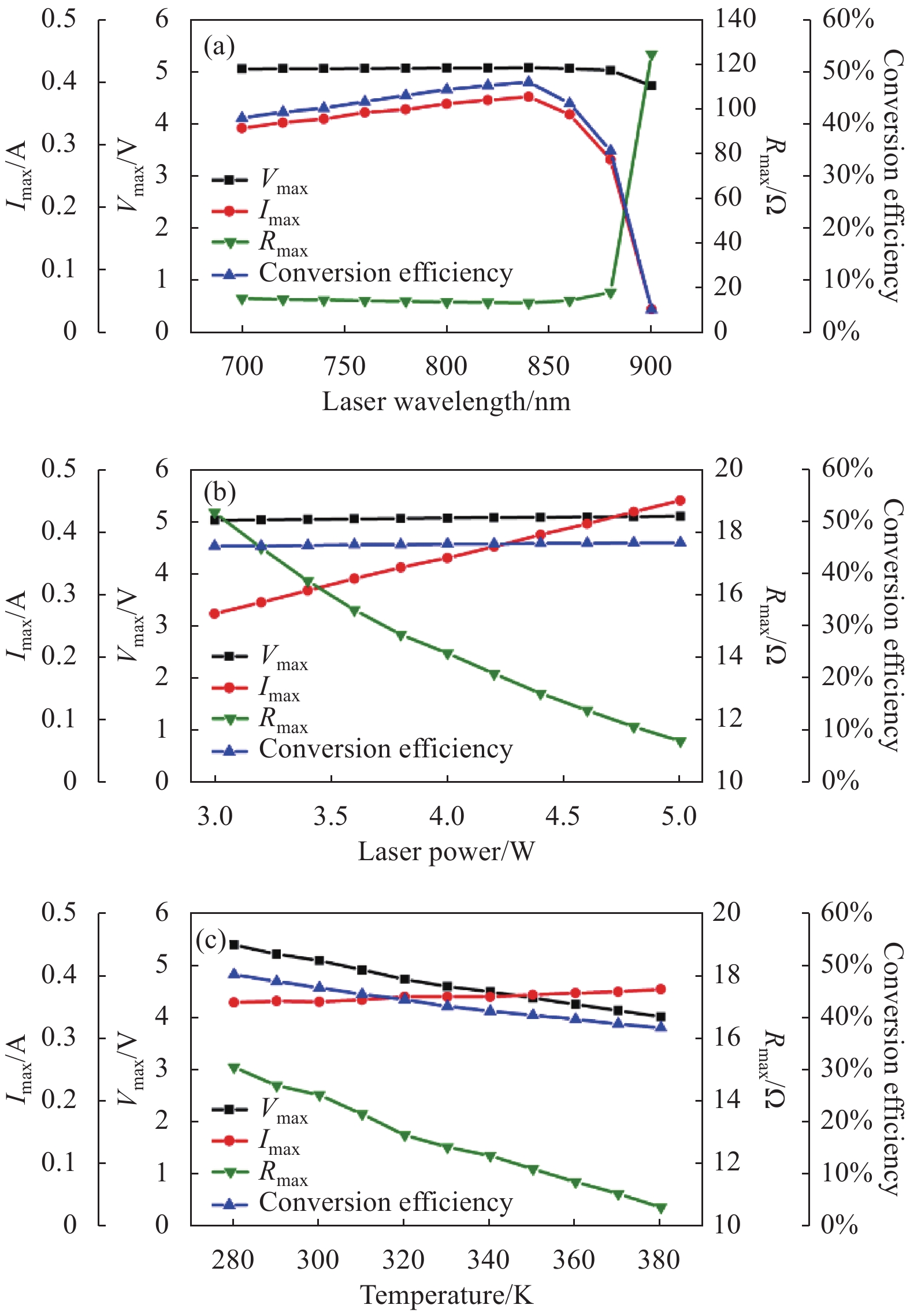
首先对功率匹配的情况进行分析。如图6(a)所示,2.2 s内波长从700~900 nm,光电池转换效率逐渐增大至50%左右的最大值,然后开始迅速下降,同时,波长接近900 nm时,最佳匹配电阻也迅速增大。因为GaAs光电池对波长大于850 nm的激光吸收率急剧下降,并在900 nm左右截止,所以波长对转换效率的影响主要是体现在由于光子能量的变化,从而导致光电池产生的载流子数量变化,最终体现为输出电流的上升和下降。由图6(b)所示,2.2 s内光功率从3~5 W,光电池转换效率基本恒定在45%。Vmax略微上升,Imax与光功率呈线性增大的关系,Rmax逐渐从18 Ω减小至11 Ω,所以光功率增大主要是增大输出电流和减小最大功率匹配电阻。如图6(c)所示,2.2 s内温度从280~380 K,转换效率呈下降趋势,从50%~39%左右。分析可知,主要是由于温度上升,GaAs光电池的禁带宽度降低,导致Vmax下降,但同时可以激发更多的光生载流子。总体而言,电压下降占主导,使得整个转换效率降低。同时随着温度的增大,Rmax从15 Ω减小至11 Ω。
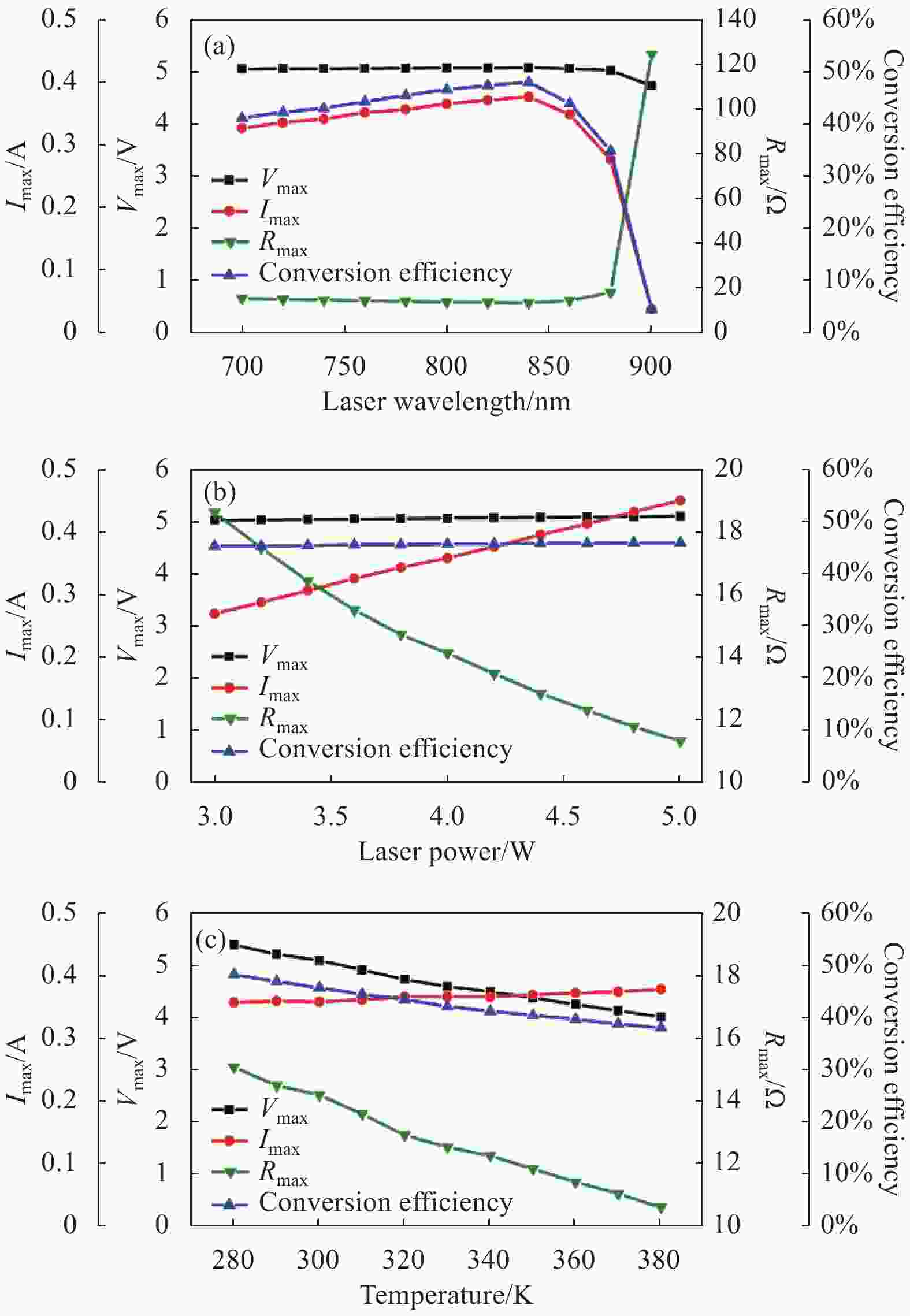
Figure 6. Output characteristics of photocell with power matching. (a) Only changing the wavelength in the range of 700-900 nm; (b) Only changing the laser power in the range of 3-5 W; (c) Only changing the temperature in the range of 280-380 K
由上述结果分析可知,光电池的最大功率匹配电阻是随波长、光功率以及温度变化的,所以需要研究不同情况下功率失配时的输出特性。上文的结果中,除了波长接近900 nm的情况下时功率匹配电阻突然增大,其余电阻均在20 Ω以内。由Boost电路设计原理可知,负载电阻RL要略大于光电池的最佳匹配电阻,才可以实现升压。因此假设RL=20 Ω且恒定不变,研究功率失配时光电池输出特性。
如图7(a)所示,对比图6的相同条件下功率匹配时的仿真结果。由于负载电阻大于最大功率匹配电阻,转换效率从40%以上下降至35%左右。
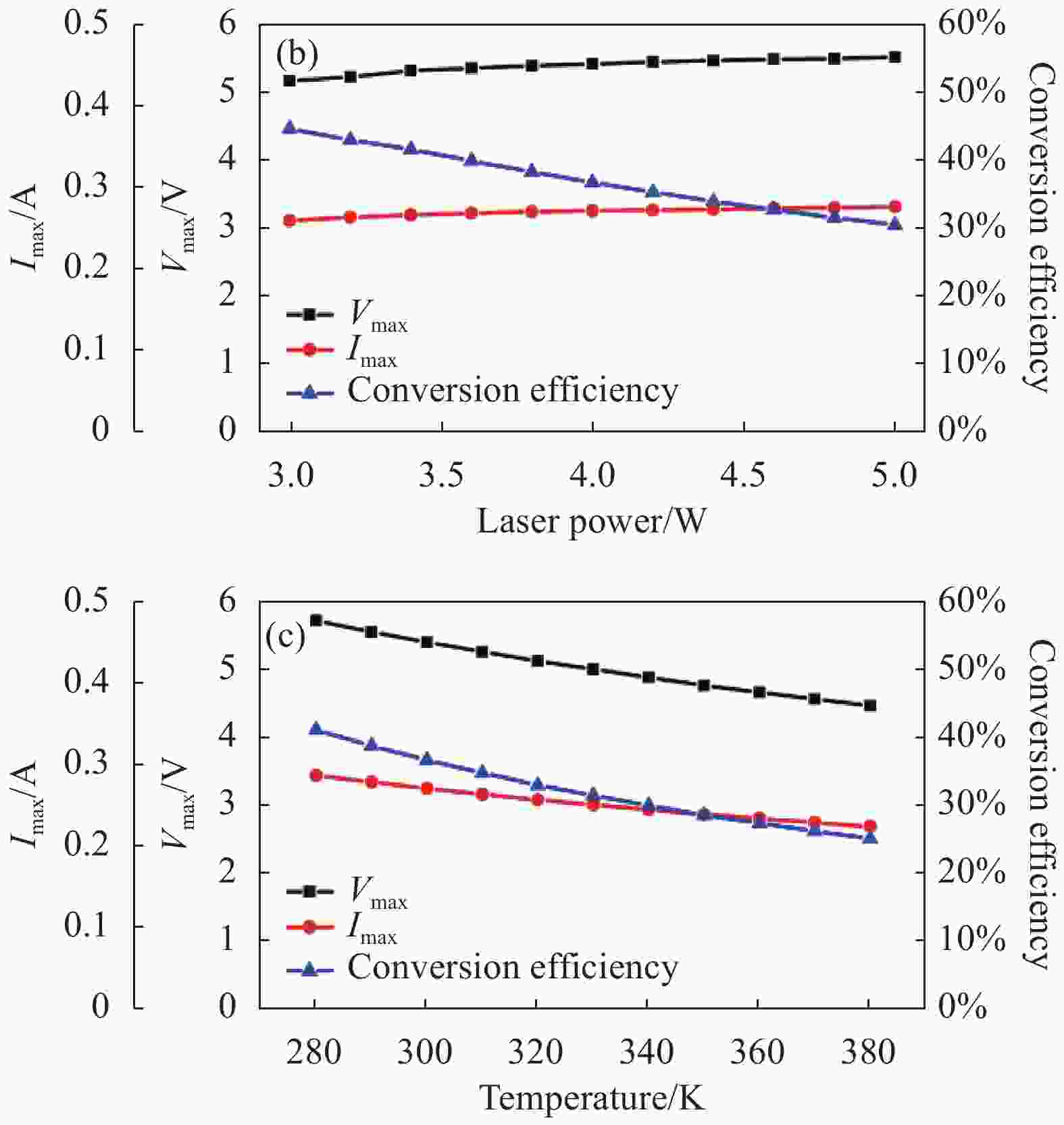
Figure 7. Output characteristics of photocell with power mismatching. (a) Only changing the wavelength; (b) Only changing the laser power; (c) Only changing the temperature
主要原因是负载电阻和光电池的伏安特性曲线的交点在最大功率点的右侧,电流急剧降低,输出功率减小。同样如图7(b)和图(c),由于功率失配的原因,转换效率下降到30%左右甚至更低,所以在LWPT的实际应用中,由于工作条件的变化,如果不使用MPPT系统,光电池产生的能量被大量浪费,将会对整个系统的转换效率产生严重的影响。
-
根据光电池在不同条件下的输出特性,由公式(9)和(10),设计Boost电路的各项参数如表2所示。
Parameter Value Unit L 350 μF C1 30 μH C2 100 μH RL 20 Ω Table 2. Boost main circuit parameters
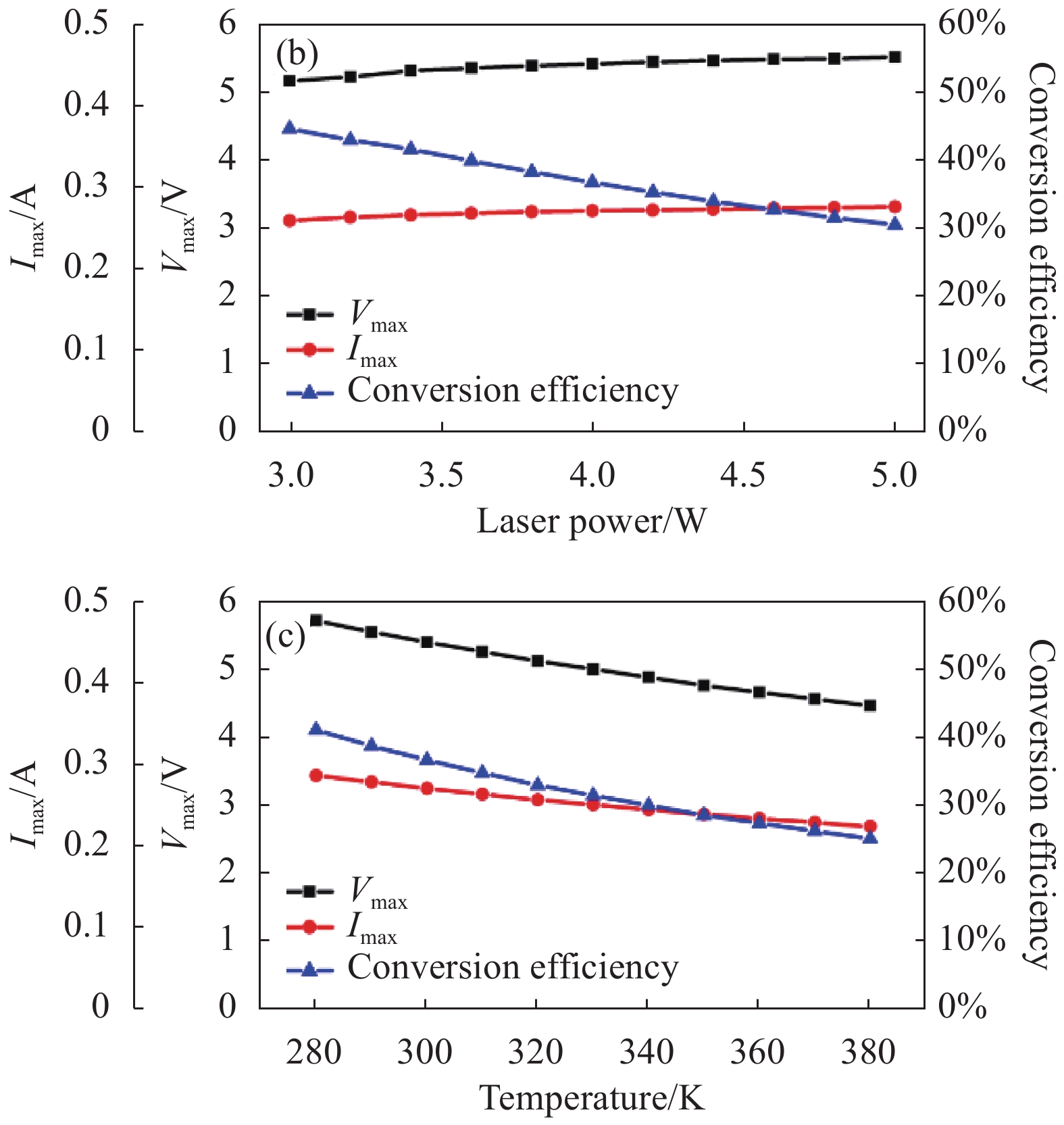
如图6所示,激光波长、光功率和温度同样在2.2 s的时间内变化,得出如图8所示MPPT系统调制后光电池的输出特性。除了图8(a)中,由于波长将近900 nm时,最大功率匹配电阻迅速增大至120 Ω,导致MPPT电路调制失效,其余的条件下的Vmax、Imax以及转换效率均和功率匹配的结果基本相同。
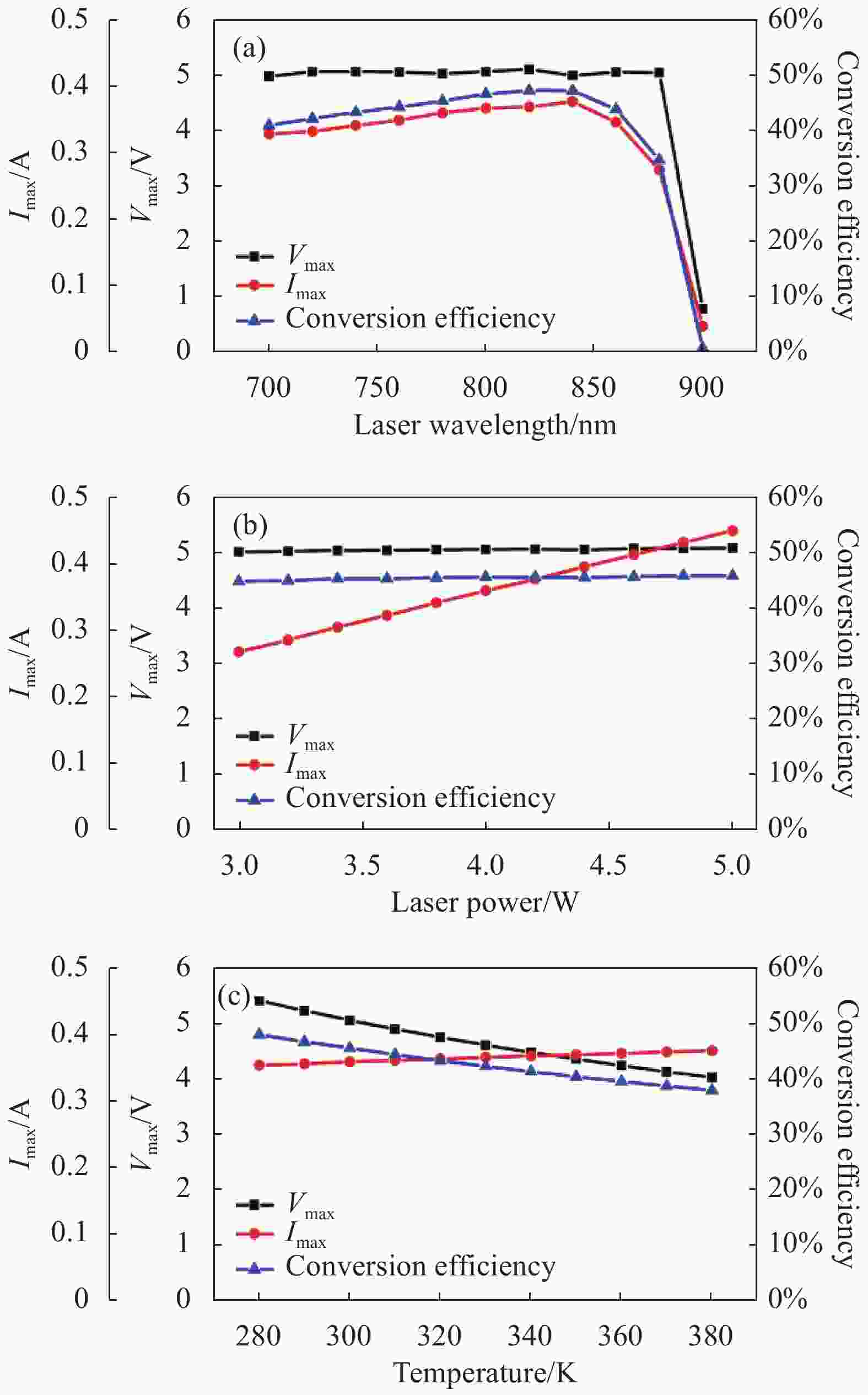
Figure 8. Output characteristics of MPPT modulated photocell. (a) Only changing the wavelength; (b) Only changing the optical power;(c) Only changing the temperature
所以,经过MPPT调制后,光电池工作参数和功率匹配时保持一致。对于负载电阻,由于升压电路的作用,负载电阻电压升高,电流降低,最终负载电阻的输出功率也达到光电池的最大输出功率,成功实现MPPT调制。采用上述算法和电路设计得到功率匹配时光电池的输出功率Pmatch以及MPPT调制后的输出功率PMPPT。将上述结果进行比较:
可以得出光电池的能量利用率ηeff可达99.93%。
-
基于六结GaAs光电池,文中开发了针对LWPT的MPPT集成仿真系统。利用该系统研究了不同激光波长、光功率和温度对六结GaAs光电池输出特性的影响。光电池在波长850 nm时达到最大转换效率50%,随着波长的增大,对激光的吸收率下降,转换效率迅速降低。光功率对转换效率影响很小,但最大功率匹配电阻RLmax
从18 Ω下降到11 Ω。温度升高,转换效率从48%下降至38%,RLmax从15 Ω下降至10 Ω,所以波长、光功率和温度均对功率匹配有重大的影响。然后研究了光电池在波长、光功率和温度变化时,功率失配条件下的输出特性。根据Boost电路原理,设置负载电阻为20 Ω,由于负载电阻不变,光电池时刻处于功率失配的工作状态,转换效率都下降15%以上,严重影响LWPT系统的应用。最后基于对六结GaAs光电池特性的研究,设计MPPT系统电路参数,使用时间扰动算法,进行MPPT调制,使不同条件下的光电池均工作在最大功率点。在MPPT系统的调制范围内,光电池的能量利用率达到功率匹配时的99.93%,证明了该仿真系统的可行性。 相较国内外其他针对激光无线能量传输的最大功率跟踪的仿真系统,该模型更能体现激光实际照射条件下的光电池输出特性,并且可以同时实现光电池在功率匹配、功率失配和MPPT调制后的输出特性对比。对上述结果的分析利于MPPT系统的算法和电路的设计、改进和优化,对于激光无线能量传输的应用提供有力参考价值。










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: