-
激光作为最亮的光、最快的刀、最准的尺,每一次新的激光光源出现都大大加速了相关科学技术的发展。脱胎于超快脉冲激光器,光学频率梳这一光源的出现[1],在过去20年中极大地改变了精密测量的方式[2]。所谓光学频率梳(简称光梳),就是在频谱上表现为严格等间距的激光序列,呈梳齿状,故而得名。其每根梳齿的频率由光梳的重复频率(简称重频)和载波包络偏移频率(简称偏频)决定。这两个频率既可以锁定到稳定的微波源,也可以锁定到原子能级或光学谐振腔上。利用稳频光梳,对光学频率的测量就可以转化为对微波拍频信号的测量,从而实现测量精度的飞跃。
作为世界上精度最高的频率标准,光梳已被广泛应用于时间标准、精细光谱、激光雷达等众多领域,在基础科学研究、产业应用和军事国防上都具有重大需求。 2005年,德国马克斯普朗克研究所的T. Hansch和美国国家标准计量局的J. Hall就因其在光梳以及精密测量领域的贡献共同获得了诺贝尔物理学奖[3-4]。
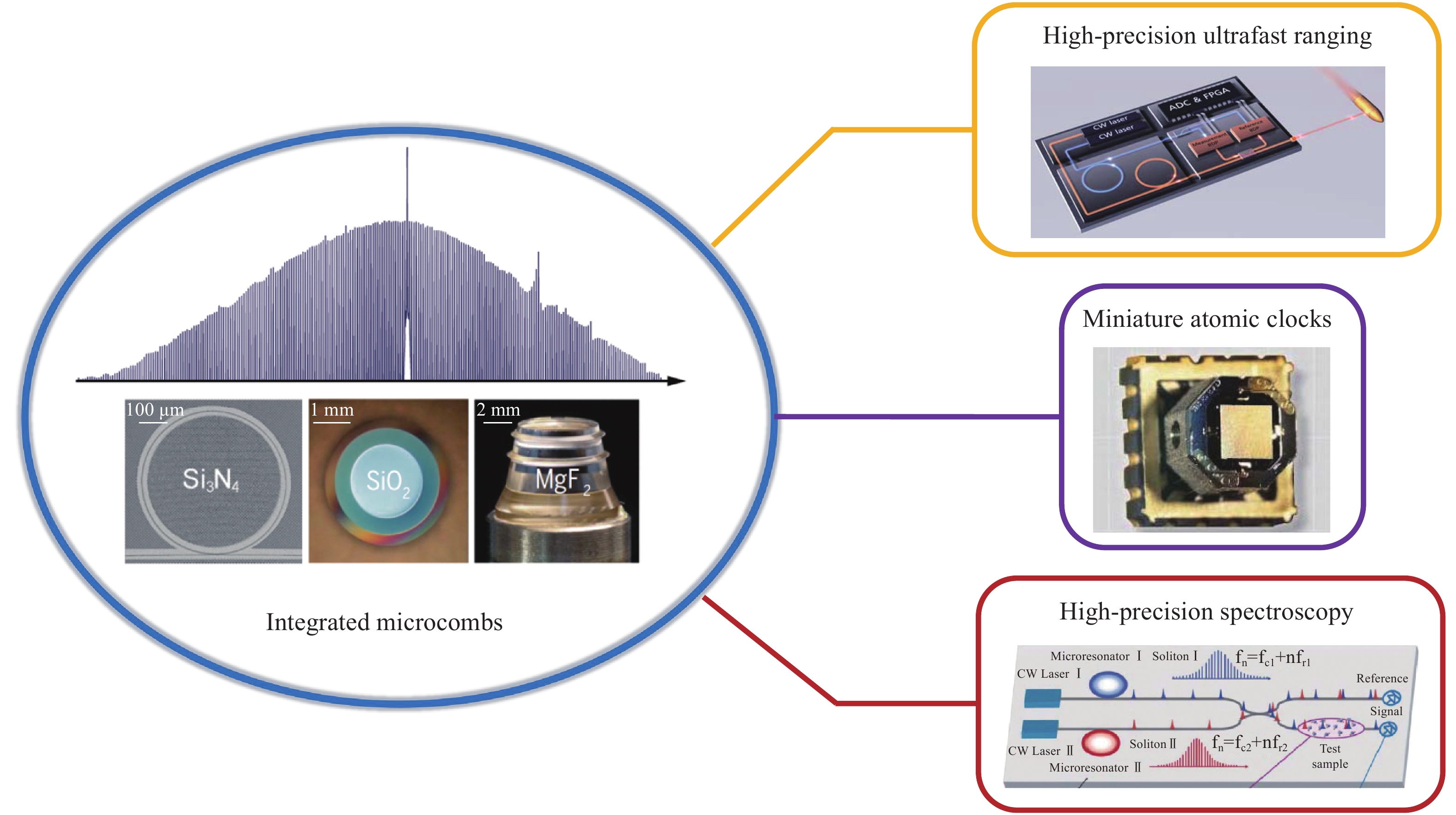
传统的光梳平台包括锁模固体激光器和掺铒光纤光梳,这些桌面级光梳相位噪声低、系统成熟,但在体积、能耗和造价等方面具有很大的局限性,且对工作环境十分敏感,目前主要适用于实验室范围内,极大地限制了精密测量的应用场景。近年来,一种基于集成光学微腔的孤子光梳出现有望彻底打破这种局限性[5-6]。这种微腔光梳不依赖于增益介质,而是利用腔体材料的非线性效应产生锁模的边带。如图1所示,在连续光泵浦下,当微腔色散与克尔效应自发平衡时,腔内就会产生包络不随路径干扰的时域光孤子,在频域上就对应于锁模的、频率严格等间距的孤子光梳[7]。由于光学微腔具有超高的品质因子和极强的场增强效应,光梳的工作阈值可低至毫瓦量级,而且每根梳齿具有很窄的线宽,因此完全适用于传统光梳所涉及的精密测量应用。文中将综述近年来这种集成微腔光梳在精密测量应用中取得的成果,并对其未来的发展趋势展开讨论。
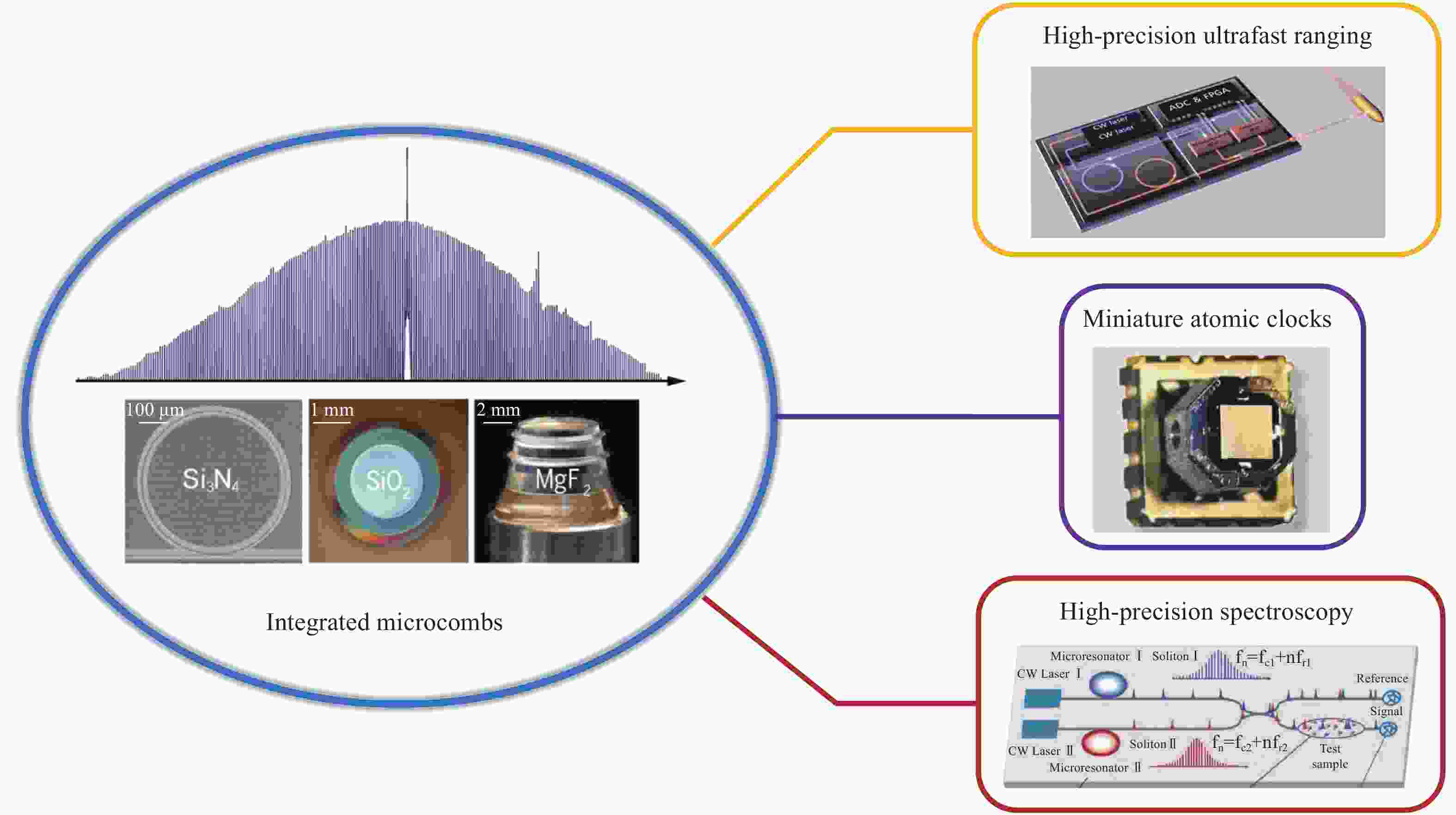
Figure 1. Integrated microresonator-based optical frequency combs in precision measurement[7](from top to bottom): High-precision ultrafast ranging, miniature atomic clocks and high-precision spectroscopy
-
在原子中电子的能级跃迁是原子的固有共振频率, 几乎不受外界影响, 同时原子具有的稳定性和普遍性, 使得原子共振频率成为绝佳的时间频率标准。1967年第13届国际计量大会将时间单位“秒”改由铯原子基态能级的微波共振跃迁频率来定义, 并延续至今。而原子钟,即是以原子共振频率作为参考,产生精准时间信号的装置。
目前,最精准的原子钟是以原子在光学波段的共振频率作为时间频率基准,即光学原子钟(简称“光钟”),其准确度已经达到了 10−19量级。光梳是光钟的核心组成部分,它使得光频段的原子跃迁谱线可以通过电子学仪器精密测量,实现原子钟的锁定。而利用集成微腔光梳代替传统锁模光梳可大大降低光钟的能耗与体积,有望为光钟走出实验室惠及人们生活的方方面面起到重要推动作用。
2014年,美国标准计量局首先作出了尝试,构建了第一台基于微腔的光学原子钟[8]。他们将单频泵浦激光经电光调制后输入硅基片上微腔,通过微腔内的非线性光学效应展宽产生光梳。随后将微腔光梳的两根梳齿分别锁定在Rb原子的两个能级上。最后输出了33 GHz的光钟信号,1 s内的不确定度为5 × 10−9,主要精度受限于Rb原子参考源。 2019年,美国标准计量局用单频连续激光直接泵浦集成氮化硅微腔,实现了倍频程展宽的微腔孤子光梳产生[9]。光梳的倍频程展宽为测量偏频提供了前提条件,实验上,研究人员通过f-2f自参考技术测量并锁定了偏频,同时也将光梳的一根梳齿锁定在了超稳激光光学参考上。这种自参考锁定技术的引入以及优越的光学参考源性能,大大提升了微腔光钟的稳定性,实现了0.01 mHz精度的THz信号输出。同年,为了解决THz信号难以电学探测,而GHz重频光梳难以倍频程展宽的矛盾,美国标准计量局在另一个工作中采用了THz重频倍频程光梳与另一套GHz重频光梳相互锁定的方法,同时实现了光梳的自参考锁定和微波频段的光钟信号输出。此外,为了进一步减小光钟系统的体积和复杂性,该工作采用了微型化的Rb原子气室作为光学参考。最终实现了22 GHz, 频率稳定度10−13的光钟信号输出[10]。
基于集成微腔光梳的微型光钟,由于具有能耗、体积上的先天优势,在全球定位导航卫星、广义相对论验证、暗物质探测等空间应用中有望发挥巨大作用。而提高微型化原子系统的精度、实现电学可探测重频的倍频程展宽集成光梳、提高光梳系统的长期稳定性等将是未来集成光钟的主要发展方向。
-
高精度的距离测量对人类的生产生活、科学研究具有举足轻重的作用,从生活中的车载激光雷达、工业测绘、微纳加工、生物医疗到国防军事上的导弹定位、航天器对准无不需要高精度的距离测量装置。而这些应用场景不仅对精度有着较高要求,也同时需要满足较快的采集速度以及较高的便携性。
得益于集成微腔光梳的超小体积、超低功耗以及高重复频率等优势,在高精度超快距离测量领域具有巨大的应用前景和优势,目前已有多个国际研究团队将集成微腔光梳应用于距离测量领域。2018年加州理工学院的Vahala课题组在单个微腔中产生了相向传播的、重复频率略有差别的两套光梳(双光梳),采用飞行时间的技术方案,在500 ms的积分时间内测距精度达到200 nm,其模糊距离为16 mm[11]。同年,瑞士洛桑联邦理工学院的Kippenberg课题组在两个分立的氮化硅微环腔中分别产生了100 GHz的孤子光频梳,两个光频梳的重频差为96.5 MHz,使测距系统的采样时间缩短到10.4 ns;基于双光梳干涉法,在13 μs的平均时间内,测距不确定度低至12 nm;并实现了对速度为160 m/s转盘表面轮廓和瞬时速度为150 m/s的飞行子弹的高精度超快测量[12]。2020年,Kippenberg课题组通过快速调谐泵浦激光的频率,实现了30路并行的相干激光测距系统,实现了对三维目标的距离和运动速度的同步测量,其测量帧率相对于现有的相干测量系统有两个数量级的提升[13]。此外,基于色散干涉法,天津大学和中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所联合团队与美国加州大学洛杉矶分校分别实现了纳米级精度的距离测量[14-15]。
集成微腔孤子光频梳作为一种先进的新型光源,通过结合飞行时间法、双光梳采样法、色散干涉法等路径已在精密距离测量中取得巨大进展,其超高的频率稳定性保证了测距的精度,而小型化、低功耗和低成本的优势,未来将在精密测距装置集成化、产业化的趋势中起到重要的作用。
-
光梳一直以来是光谱学研究中一种备受关注的光源,因为它们能提供:(1)宽的光谱覆盖范围,有利于同时检测多分子种类;(2)高空间相干性,即允许更长的测量路径和更高的灵敏度;(3)极高的频率分辨率和精度。而集成微腔光梳相对于传统光梳还具有高重复频率、有望实现便携探测装置等优势,自诞生以来这一小型化光源被迅速、广泛地应用于精密光谱测量研究中。
2016年,加州理工学院的Vahala课题组首次将集成微腔光梳应用于精密光谱学测量中[16]。利用微腔中相向传播重频略有差别的两套光梳构成双光梳。结合微腔光梳的高重频和双光梳电学采样技术,实现了对氰化氢气体吸收谱的超快精密测量,测量时间仅为386 ns。2017年,哥伦比亚大学的Gaeta组通过扫描梳齿频率的方法(扫描范围达到16 GHz),实现了中红外波段乙炔吸收光谱的宽谱测量[17]。2019年,Vahala课题组利用两套光梳构建了一个集成游标卡尺光谱仪,联合了扫频连续波激光器,实现了对窄吸收谱气体的精密测量[18]。2020年,美国国家标准计量局通过对微腔光梳进行精细的重复频率和载波包络偏频同时控制,实现了直接的亚多普勒和超精细原子光谱测量[19]。
集成微腔光梳由于体积小、可集成等特性,未来有望实现便携式气体检测仪,在户外环境检测等方面有望发挥巨大作用,同时微腔光梳的高重复频率也将大大提高光谱测量速度。而单根梳齿功率低、梳齿间隔大导致分辨率较低等问题将是未来主要面对的挑战。
-
由于保持测量的高精度通常需要复杂的支持系统和高昂的维护费用,精密测量技术一直以来被人们看作计量实验室里的专属技术。而近些年来,随着集成光梳的出现,精密测量系统已经逐渐小型化,未来有望形成产品,满足市场对超快测距系统、微型精密光谱仪等仪器的迫切需求。在基础科学研究方面,不久的将来,基于微腔光梳构建可移动光学原子钟将促进相距遥远的计量实验室之间的时钟比较,对支持秒的光学重新定义起到重要作用。除了时钟比对之外,基于便携式光梳的星载光钟系统具有低振动和无地球引力势等优势,可能有一天能够在10−20精度下实现高精度测地学和基础物理定律的测试。而目前集成微腔光梳在提高能量转化效率、产率和降低系统复杂性上仍然面临挑战,所以探索提高集成光梳效率的新机制、进一步优化集成微腔的制备工艺、光梳光源的鲁棒性将是未来的主要发展方向。
Applications of integrated microresonator-based optical frequency combs in precision measurement (Invited)
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210560
- Received Date: 2021-07-15
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-08-20
- Available Online: 2021-12-03
- Publish Date: 2021-11-30
-
Key words:
- precision measurement /
- integrated microresonator-based optical frequency comb /
- optical atomic clock /
- optical soliton
Abstract: Precision measurement is a cornerstone of modern physics, and the development of laser sources directly promotes the progress of science and technology. In the early 21st century, the invention of the optical frequency comb created the optical atomic clock, the most accurate time/frequency standard device, a lot of precision measurement applications have been implemented, including absolute optical frequency measurement, fundamental physical constants measurement, precision distance measurement and molecular spectroscopy measurement. However, the early comb systems were complex and expensive, and worked in large laboratories, which restricted their application scenarios. In recent years, an integrated microresonator-based optical frequency comb (microcomb) has attracted great attention from the scientific and industrial communities because of its advantages such as compact size, low power consumption and excellent scalability. Different from traditional optical frequency combs, which rely on gain media or saturable absorbers to realize the mode locking, this kind of integrated microcomb benefits from the enhanced nonlinear effect of high-quality factor microcavity to realize the excitation and mode locking of the frequency comb. This new mechanism greatly reduces the volume and cost of optical frequency combs, which has great advantages in civilian-based precision measurement applications. The progress of integrated microresonator-based optical frequency combs in precision measurement applications is introduced, which mainly focuses on miniature optical atomic clock, ultra-fast precision distance measurement and high-precision spectroscopy in this paper. Finally, the opportunities and challenges in the future application of integrated microresonator-based optical frequency combs in precision measurement are summarized and prospected.









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: