-
光纤传感网络由于其耐腐蚀、抗电磁干扰、成本低、传输距离长等优点[1],被应用于各类大范围状态实时监测领域,例如油气管道、安防网络、电网安全等[2-4]。分布式光纤传感技术[5]利用待测区域中压力或振动对回波信号的干扰完成传感事件的识别,从而给出预警。由于光纤本身是传输媒介,故可以实现几十甚至几百公里的干扰事件类别分析。针对振动信号的光纤传感技术已在油气管道中得到广泛使用[6],但受限于其分类能力,其预警等级和预判的处理方法还受到一定的制约,所以,针对具体事件源的识别算法成为了近年来该领域的研究热点之一。
Sidelnikov等[7]研究了传感区域附近的异常扰动信号,由于其实验在没有太多干扰的环境中完成,所以测试精度较高,但对复杂入侵事件的种类及入侵程度无法量化分析。Tejedor等[8]将光纤传感网络应用于管道泄露,可获得管道沿途范围内高强度振动信号,从而识别可能的管道破坏活动。刘素杰等[9]提出利用不同干扰事件的信号周期与振幅不同的设计思路,对火车、机械施工和触摸光纤三种干扰事件进行对比分析,对比的参数主要是频谱分布,火车的频谱基频明显,约为126 Hz。机械施工呈时间间隔较大的离散分布关系,约在100~500 Hz之间。而触摸光纤的频谱连续性很强,赋值大于前两种。田苗等[10]采用基函数神经网络与模态分解相结合,对四种常见的入侵事件进行分析,平均识别率达85.75%。Xu等[11]采用支持向量机对测试数据的特征信息进行分析,从而对踩踏及敲击等入侵事件进行分析,平均识别率达93%以上。蔡海文等[12]采用瑞利散射的方式获取声波信号,该方法在声波信号提取时具有较好的信噪比。张旭苹等[13]研究了一种基于相位匹配的信号识别方法,其识别精度得到了大幅提升,但该方法易受环境干扰。
综上,光纤传感技术中识别种类与识别精度、测试环境复杂程度与识别概率之间存在矛盾关系,研究更合适的分类算法组合方式是提高系统性能重要手段。文中在分析各种识别算法的基础上,设计了基于深度神经网络的识别算法,将差分相关计算与深度学习相结合,实现提高信号提取精度与噪声抑制的目的。
-
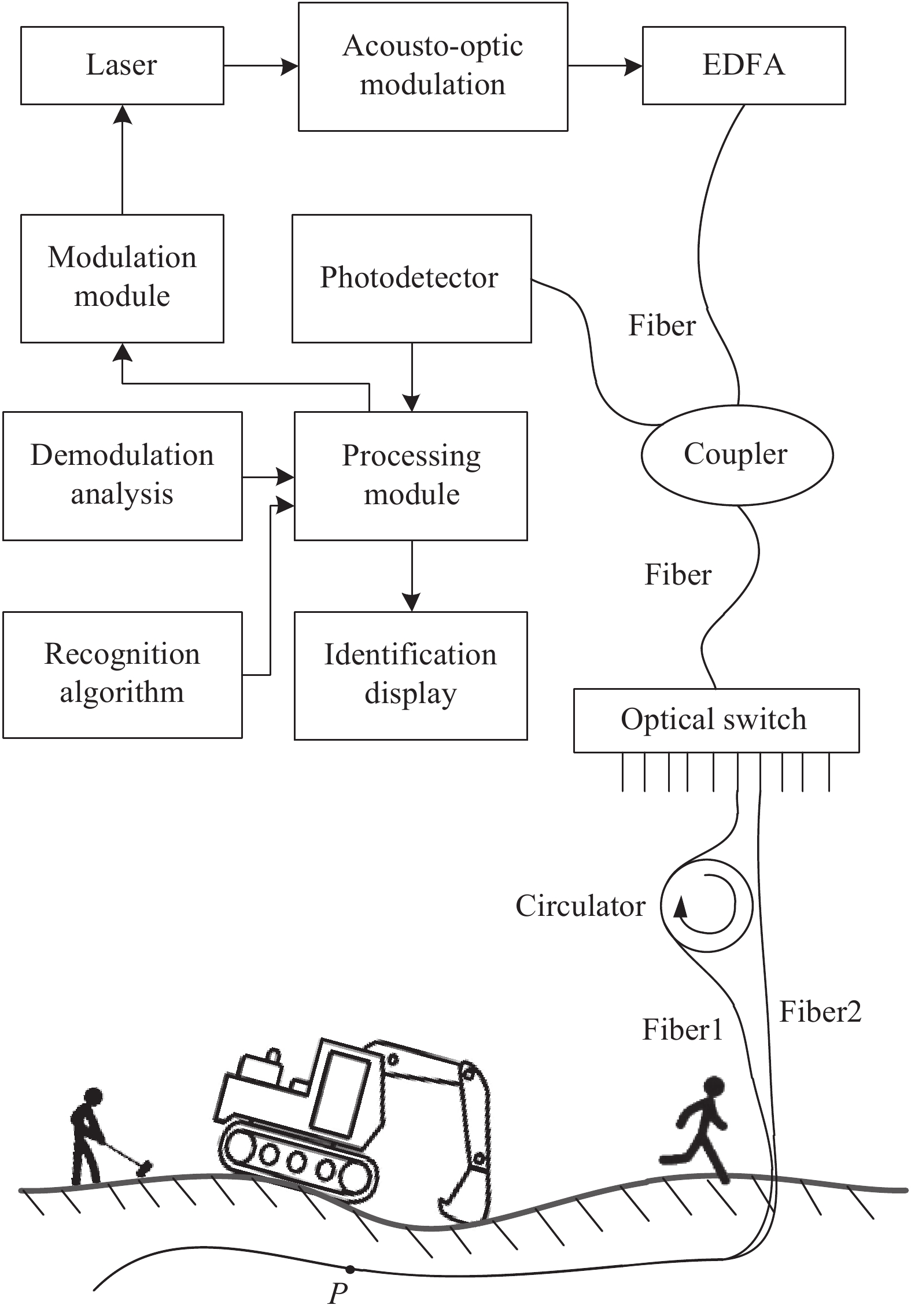
系统采用窄线宽调频激光器配合声光调制器完成对连续光的脉冲化,从而得到离散光脉冲信号。系统结构如图1所示。
回波信号采用掺铒光纤放大器对信号放大,由Relay OSW型光纤光开关完成不同光路切换(开关时间典型值为3 ms),回波信号分别采用光电探测器完成接收,系统对两组信号进行相关运算,实现对噪声的抑制及对有效信号的叠加,最终根据光谱分布特性完成信号类型与强度的分析。
处理模块控制调制模块产生连续激光信号,并根据测试需要设定波长扫描范围。激光器产生的激光信号通过声光调制器被离散化,形成光脉冲,光脉冲信号经过EDFA将信号光能量放大,然后通过光耦合器进入光开关,光开关用于对两根光纤传感通道进行切换输出,两根传感光纤分别采用了不同的封装包层形式,利用对不同类型振动信号的敏感程度不同实现差分对比,从而大幅提升单光纤传感的信噪比。为了保证测试光纤中信号的同步,采用环形器弥补光开关的时延问题。测试区域中将同时产生多种振动源事件,从而对不同事件进行分析。
-
由EDFA放大的脉冲激光信号作为初始脉冲信号,可以表示为:
式中:t为时间;c为光速;λ为示中光纤中传输的中心波长;E0为放大后的激光脉冲光强;φ0为初始相位。
当待测区域中P点位置(如图1所示)受到了外界的干扰,则其散射信号的相位产生偏移,则在P点位置对应的tp时刻上,测试所得光强信号为:
式中:Ep为P点上的激光脉冲光强值;φ0为初始相位;其他参数同上。设光开关的延迟为Tswitch,则采用光纤延长线的长度L=c·Tswitch,由此可以使光纤1的初始光信号与光纤2的初始光信号在到达测试位置上的时间同步,从而为差分同源振动事件提供参考信号[14]。由此可知,将原信号光强能量归一化后可以得到其相关系数:
式中:E1和E2分别表示光纤1和光纤2的激光回波信号强度。又因为初始信号被声光调制为脉冲信号,即可以采用离散信号表达方式,故其表示可写为:
式中:n表示采样点数;E1和E2分别表示光纤1与光纤2上在相应点位上的光强测试值。通常情况下,相关函数的时延会影响信号相关程度的计算,但在该系统硬件设计中由于采用了延时线与光开关配合使用,所以信号之间的时延可以忽略。对两个信号进行卷积分析有:
式中:τ为时间常数;R12为光纤1与光纤2之间的自相关值。由此可得到该信号的自相关函数与自能量谱密度为傅氏变换关系。所以,对两组函数做相关运算后,再通过傅里叶变换就能完成信号的提取。
-
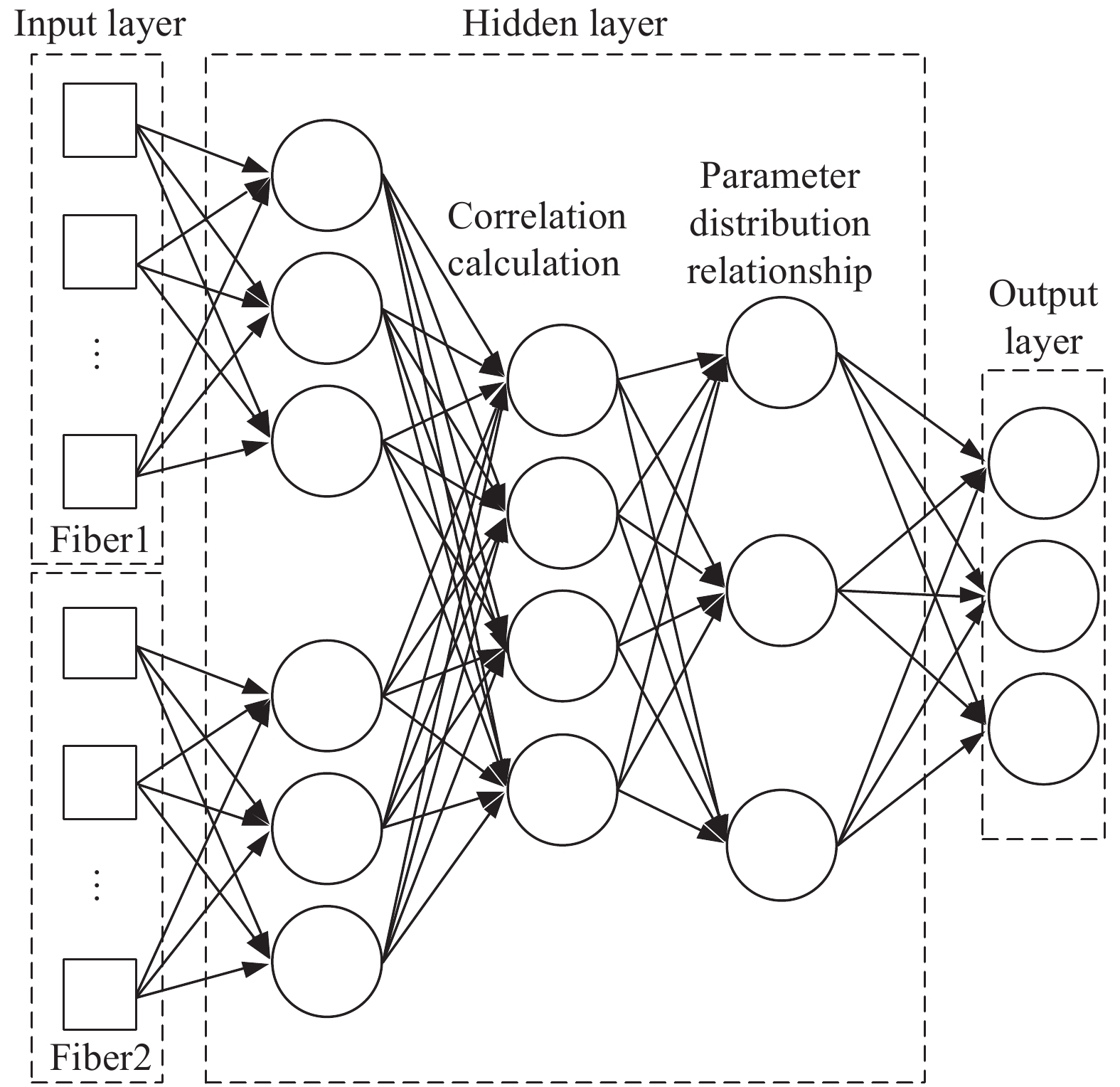
与传统的神经网络不同,虽然原始数据都是光纤传感的回波信号,但是同一点的测试数据是由两根光纤构成的,而两个光纤的感知系数不同,故输入数据需要分组,且隐藏层设置了相关运算,从而构成了深度神经网络结构,见图2。第一隐藏层由光纤1和光纤2的测试数据分别完成初级滤波与信号匹配;再进入第二隐藏层,即相关计算层,将双数组输入的信息进行相关处理;最终经过相关运算进行信号增强的数据进入隐藏层的第三层分类层,从而实现相关信号对入侵事件类型与程度的映射,完成最终的识别输出。
-
根据深度神经网络的结构设计,其程序流程如图3所示。
算法实现主要分为三个部分:第一,完成光纤1和光纤2的数据采集,并分别输入深度神经网络的第一层隐藏层,根据两条光纤不同封装方式的敏感系数进行匹配滤波,从而完成对初始数据的参数配置;第二,将经过预处理后的两组数据输入第二层隐藏层(相关计算层),完成两组数据的相关计算,依据相关计算得到的数据间的相关系数重新构建信号数组;第三,通过引入已知振动数据源(该数据源是预先采用已知事件的信号,通过网络学习得到的参数分布关系,该参数关系作为第三层隐藏层的控制条件嵌入在神经网络中),构建测试集,训练回波光谱分布数据与入侵事件类型的映射函数模型。
-
实验采用BOOSTIK-E15型窄线宽光纤激光器,波长调制范围1535~1575 nm,线宽1.0 kHz,初始功率2.0 W。声光调制器选用T-M040-0.5C8J-3-F2P型,EDFA选用GR-1312-CORE型光纤放大器,其输出功率典型值为20 dBm。测试位置为10 km远的露天场地,信号采集频率为2.0 MHz。
-
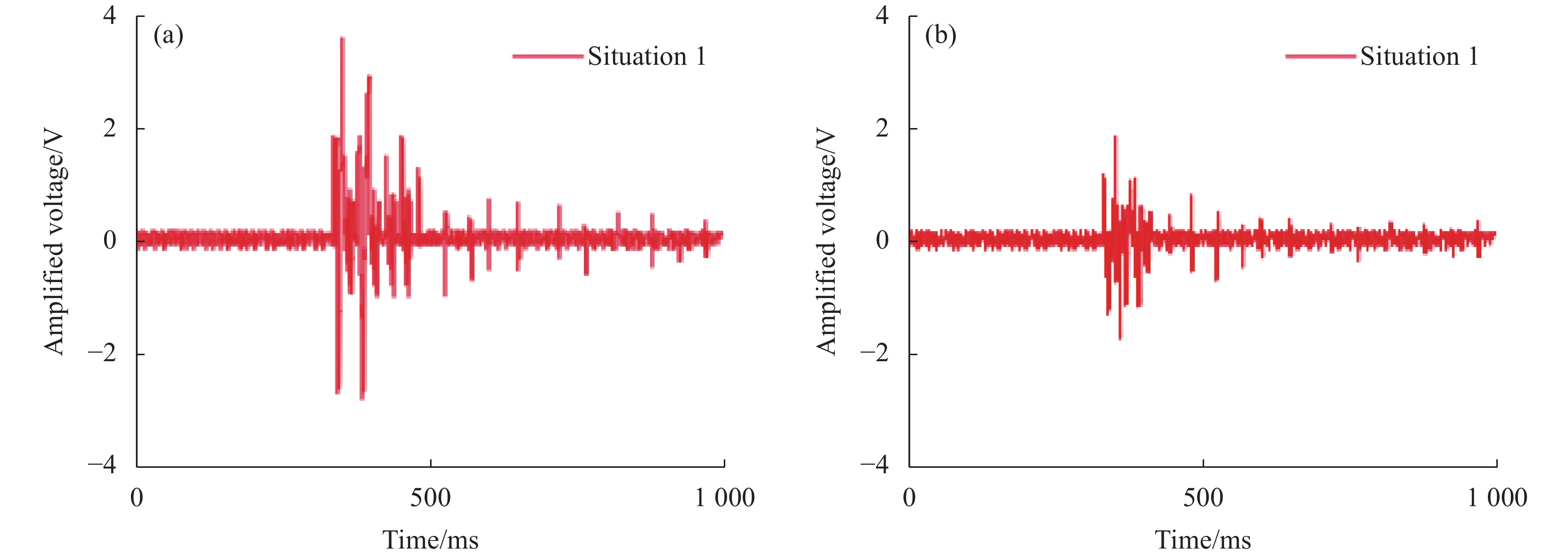
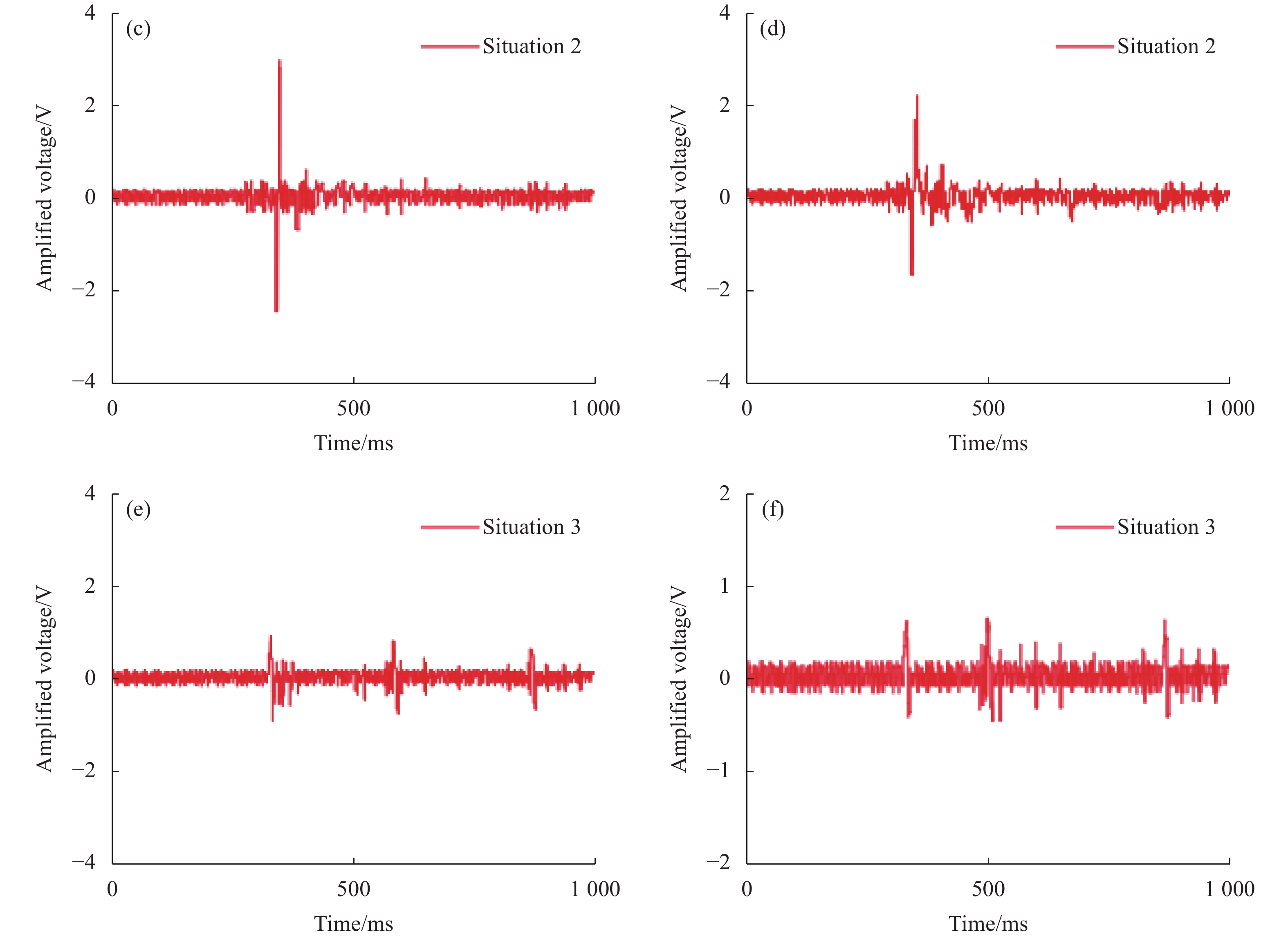
为了验证测试系统的灵敏度及算法的识别能力,分别对测试点P位置不同距离的机械挖掘(情况1)、人为敲击(情况2)、人匀速跑动(情况3)进行测试分析,则系统测试结果如图4所示。
图4(a)、(c)、(e)为光纤1的测试结果,放大电压最大值分别为3.47 V、2.81 V和0.91 V,图4(b)、(d)、(f)为光纤2的测试结果。放大电压最大值分别为1.81 V、2.11 V和0.65 V。由于光纤1和光纤2的封装材质不同,光纤1的测试数据响应振幅相对较明显,但其噪声幅值也较大,而光纤2的测试数据虽然总体振幅偏小,但是白噪声被弱化的效果比较明显。由此对两组数据进行相关计算可以进一步提高数据的信噪比。
6个测试曲线信号的脉宽范围分别是140~150 ms、80~90 ms、10~20 ms、115~125 ms、45~55 ms和15~25 ms。由此测试中均采用测试信号中个峰值位置附近的信号进行对比,这样可以增加信号识别的普适性。从谱形分布上可以看出,机械结构的响应变化延时较长。人为单次敲击的峰值线宽窄,旁瓣少。而跑步的振幅最小,但周期性响应比较明显。
-
对已获得的光纤回波信号进行分析,分别采用单光纤神经网络算法[15]、双光纤单层神经网络[16]和该算法中的双光纤深度神经网络算法。
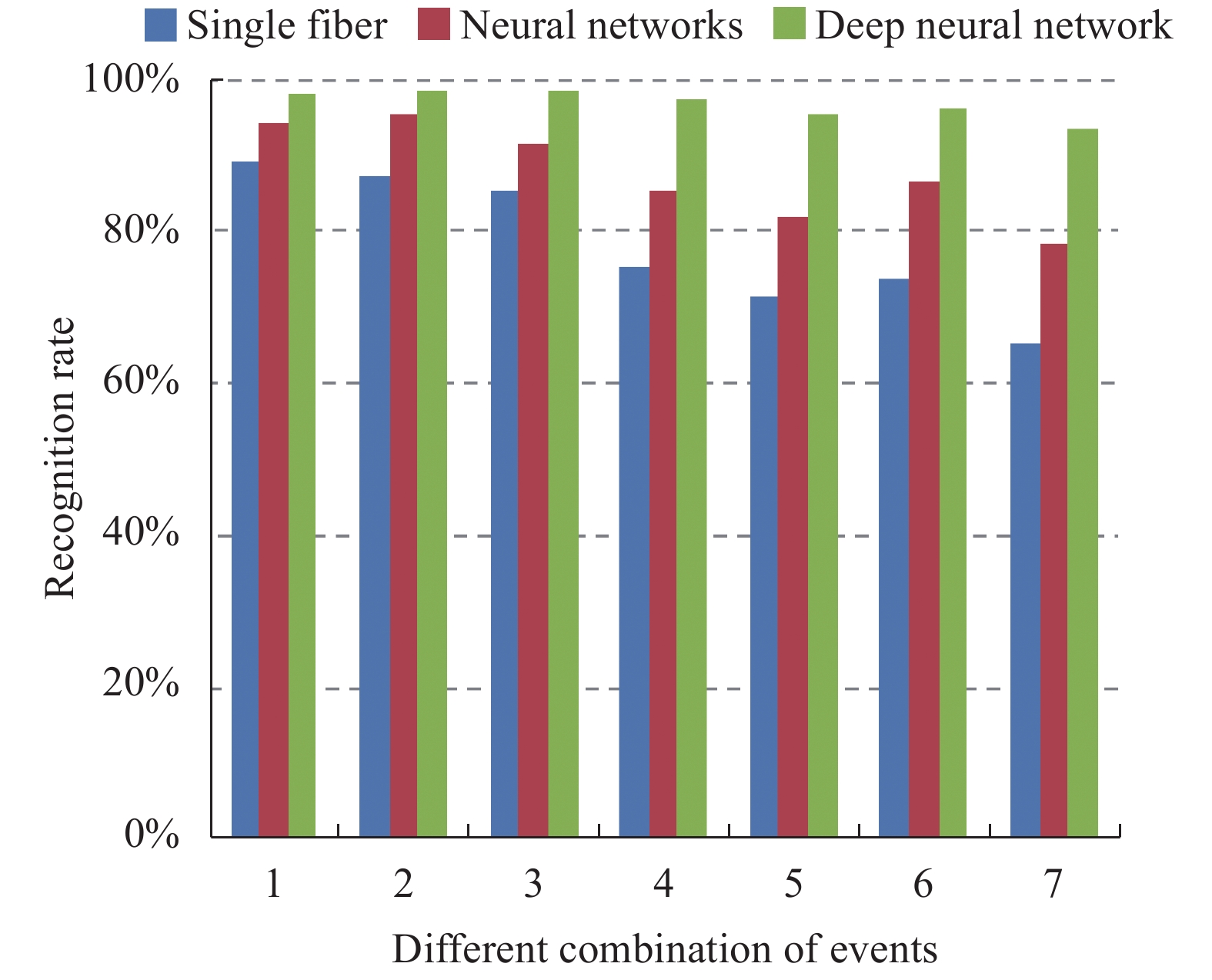
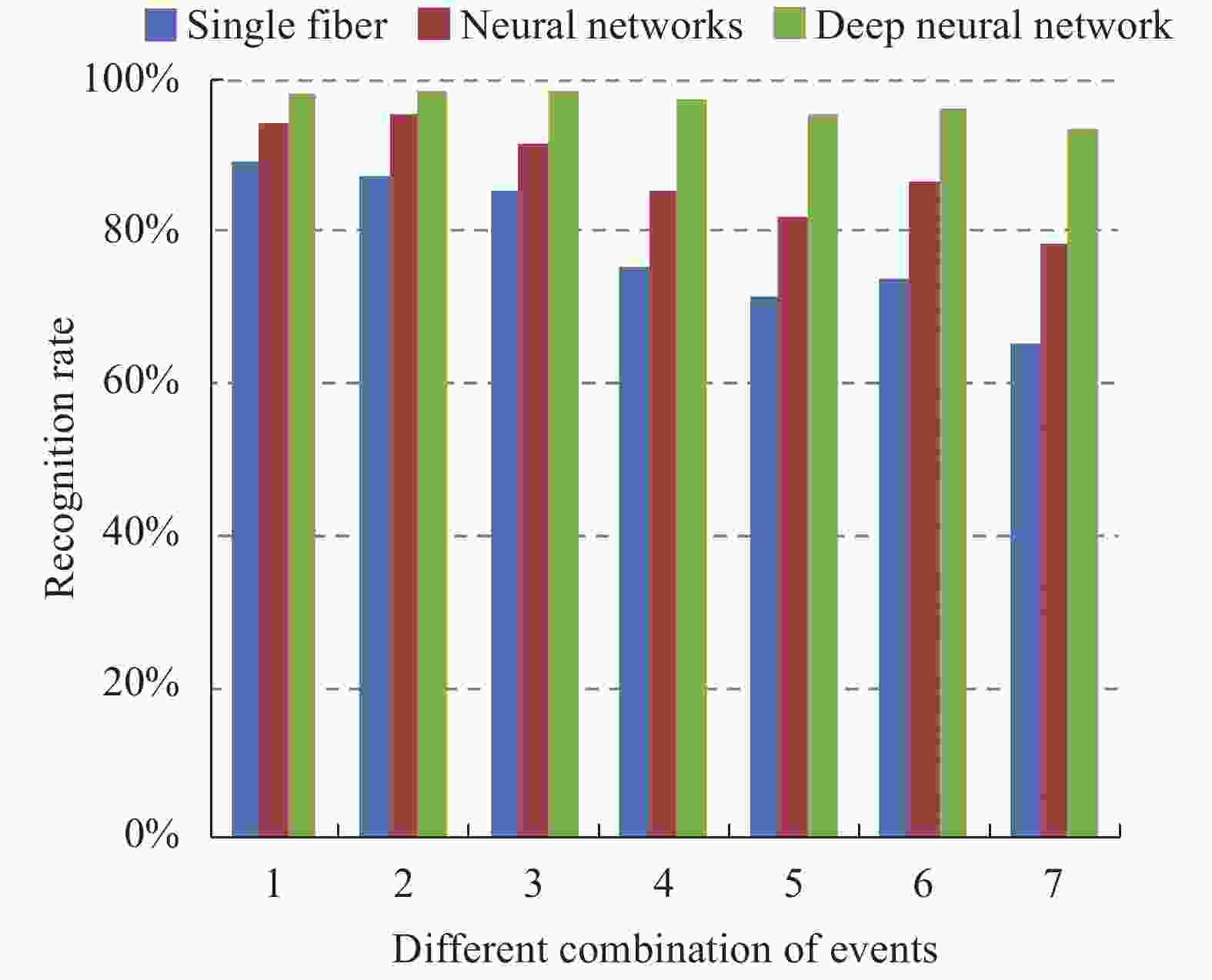
对实验中情况1、情况2和情况3三种事件进行组合分析,不同事件的组合形式共7种,分别对应:情况1、情况2、情况3、情况1和2、情况1和3、情况2和3、情况1和2和3。识别概率计算结果如图5所示。
如图5所示,前三个分类中由于是采用单独事件触发,所以三种方法的识别概率都比较高,均超过了95.0%。而联合两种以上事件同时触发后,前两种算法的识别概率明显降低,单光纤神经网络算法的识别率均值为73.4%,神经网络算法的识别率均值为84.5%,深度神经网络算法识别率均值为96.4%。而当同时识别三种事件时,前两种算法的识别概率仅为65.2%和78.3%,而采用深度神经网络算法的识别概率仍有93.5%。由此可见,该算法对混叠信号的提取与抑噪具有很好的作用。
-
文中设计了一种双光纤差分相关感知结构,并基于此完成了深度神经网络的构建。算法通过计算相关系数,设定滤波阈值等方式,抑制了基础噪声的干扰,提高了混叠信号的解调能力。实验对三种典型入侵事件进行测试,并且根据不同事件的组合发生验证了该算法的识别效果。实验结果显示,该算法在多种事件混叠时仍具有很好的识别概率,验证了算法的优越性。该算法可从一定程度上扩展光纤传感网络在信号识别领域的应用范围。
Optical fiber sensing recognition algorithm based on deep neural network
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210971
- Received Date: 2021-12-16
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-01-10
- Accepted Date: 2022-01-13
- Publish Date: 2022-09-28
-
Key words:
- optical fiber sensing /
- recognition algorithm /
- deep neural network /
- correlation coefficient
Abstract: In order to solve the problem of reducing the recognition probability caused by the aliasing of different types of event signals in the optical fiber sensing process, a dual optical fiber sensing structure using differential correlation calculation is built. On this basis, a signal recognition algorithm based on deep neural network is proposed. First, the echo signal of the dual fiber is used to calculate the correlation coefficient. Then, the threshold range is set by signal characteristics of different event types, so as to improve the signal-to-noise ratio through correlation calculation and threshold filtering. A deep neural network model with three hidden layers is designed, and the purpose of low-frequency noise suppression and signal aliasing demodulation is accomplished by separating the input layer and the related operation layer. The experiments separately test three common intrusion events. The recognition probability of combined events by different algorithms is analyzed. The results show that the echo spectrum shape of the three events has significant characteristics. The recognition probability of the three algorithms is more than 95% for a single trigger event, and the average recognition value of this algorithm is 98.5%. When two events are triggered at the same time, the average recognition probabilities of the three algorithms are 73.4%, 84.5%, and 96.4%, respectively. When three events are triggered at the same time, the average recognition probabilities of the three algorithms are 65.2%, 78.3%, and 93.5%, respectively. It can be seen that this algorithm has a better recognition effect when there is interference and aliasing of signals in optical fiber sensing.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: