-
超表面是一类利用一系列人工制备的亚波长微结构进行有序排布从而与光场发生明显相互作用的平面光学器件[1]。通过选取金属[2]、电介质[3]、二维材料[4]等不同的构成材料进而将其裁剪成不同的几何结构,可以实现不同的电磁局域模式,如电磁多极谐振[5]、法诺共振[6]、波导模式[7]等。这些电磁模式的存在直接影响了电磁场在近场、倏逝场、远场区的不同光场维度如偏振、相位、空域分布等的物理特性,为光场的近场调控、波前调控、近场远场耦合调控提供了新的方式[8-9],同时也为光学器件的微型化、高性能化和集成化发展提供了广阔的前景。
微结构光场调控特性的基础是电磁谐振。由于微结构的几何形貌、入射光场的偏振、波长和结构光特性与电磁谐振关系密切,因此与非谐振光场调控技术比较,微结构光场调控技术天然具有多维度光场调控的特性[9-11],这对于新型光子学技术的发展具有重要意义。例如通过偏振和相位的联合调控可以实现偏振编码的全息技术[12],利用振幅和相位的联合调控可以实现无固有噪声的信息光场传输及多路技术[13]。如何有效利用不同的光场调控维度,实现超表面信息光场新技术是目前超表面研究的热点之一。文中利用两个近距耦合的非晶硅微结构的结构不对称性,实现了双频带、双偏振通道的反射式超表面。利用微结构的胞内旋转产生的几何相位实现了异常反射光的波前调控,并利用微结构在不同偏振、不同入射波长的反射率不同的特性实现了多功能的正负灰度成像超表面。
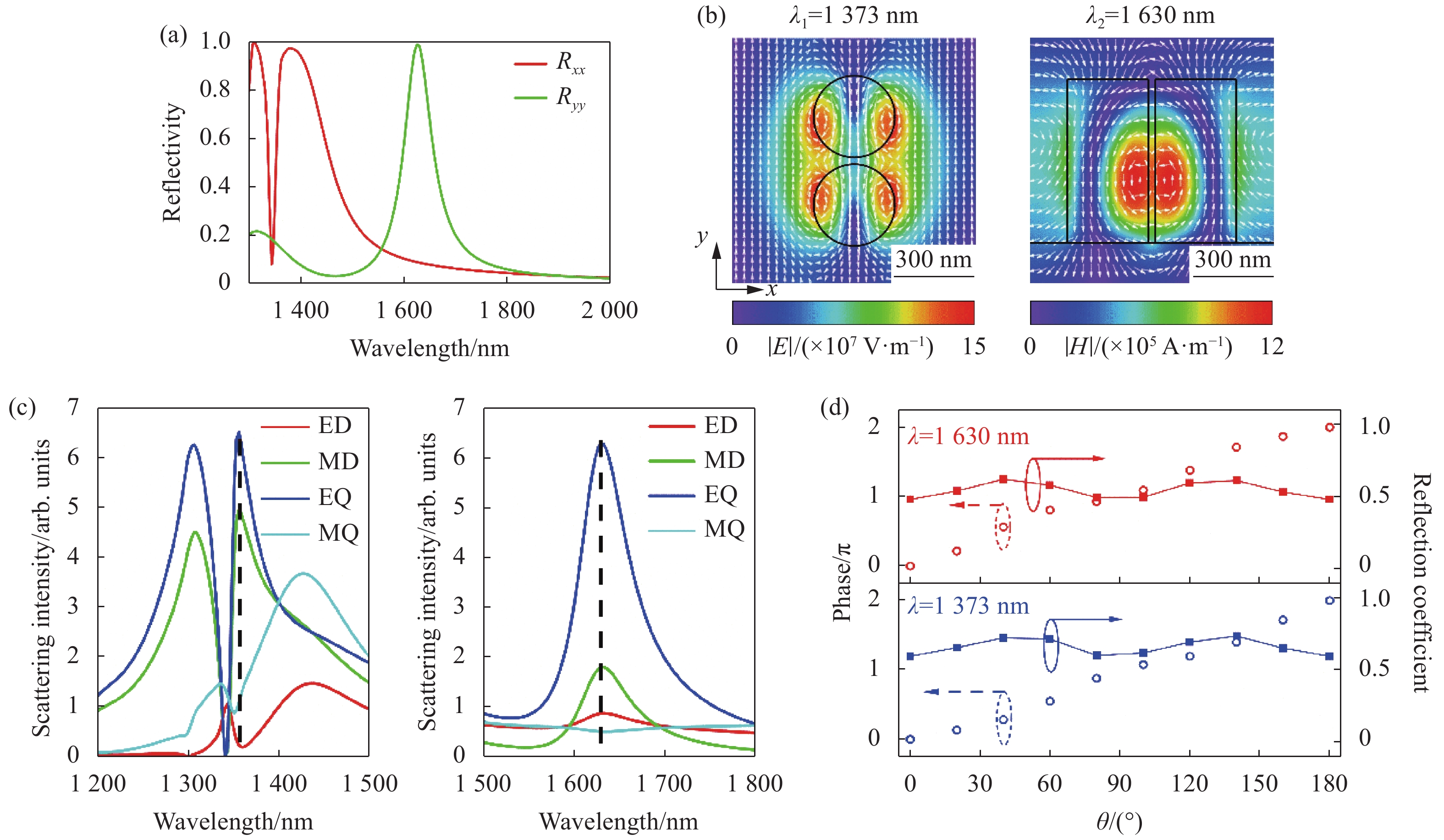
图1为双频带双偏振电介质超表面和单个元胞结构示意图。该超表面以两个非晶硅柱为谐振单元,衬底为二氧化硅(SiO2),元胞周期为Px和Py。每个元胞内有两个高度、直径相同的硅纳米柱,沿两个纳米柱圆心连线的方向作为单个元胞结构的长轴方向,两个硅柱绕元胞中心轴的旋转角计为θ (长轴与y方向的夹角)。所设计的元胞周期为Px = Py = 900 nm,纳米柱直径和高度分别为D = 300 nm,H = 600 nm。文中采用有限时域差分法(FDTD)进行数值计算,得到了所设计超表面的反射率,如图2(a)所示。模拟中纳米柱排列取向角θ = 0,x、y方向采用周期性边界条件,z方向设置为完美匹配层(PML)以吸收散射电磁波。当x偏振入射时,响应波长为1373 nm;而当y偏振入射时,响应波长为1630 nm,即所设计的微结构在不同偏振入射下具有明显的双频带响应特性。为了研究不同偏振下反射谱的差异形成原因,并解释电磁场与微结构作用的机理,对响应波长处入射光与微结构作用的电磁场分布和电磁多极分解进行了模拟,如图2(b)和2(c)所示。图2(c)为两个响应波长附近300 nm的反射场(z轴向上为正方向)中包含的电偶极子(ED)、磁偶极子(MD)、电四极子(EQ)和磁四极子(MQ)的相对强度,在不同偏振入射对应的反射电场中,电四极子(EQ)均具有最高的强度。图2(b)左图为衬底上方300 nm截面处的电场(强度图)和磁场(箭头)分布(x偏振,1373 nm),与图2(c)左图中的以电四极子为主响应峰的结果相对应。类似地,对于y方向偏振入射(见图2(c)右图),电四极子(EQ)同样占据反射场的主要分量;其中xz平面内纳米柱附近的谐振磁场(强度图)和电场(箭头)如图2(b)右图所示。由于单个元胞结构对不同偏振的入射光产生了不同的电磁响应,因而实现了双偏振双频带的反射峰。从图2(b)还可以看出,电磁场与微结构相互作用的电磁能量主要集中在微结构内部,相邻元胞之间的电磁相互作用几乎可以忽略,这也是超表面像素化波前调控的基础。利用琼斯矩阵,单个元胞在电磁波垂直入射时反射系数可以写成:
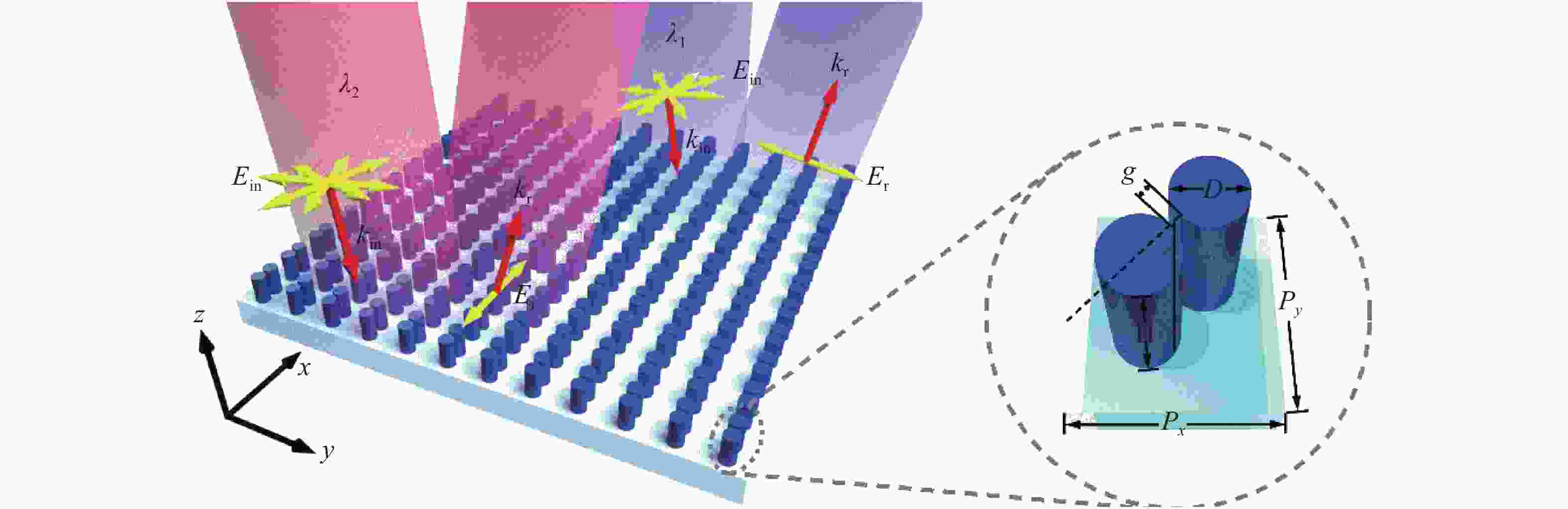
Figure 1. Schematic of the dielectric dual-wavelength dual-polarization metasurface and the unit cell of the structure

Figure 2. Simulated results of the periodic unit cells. (a) Reflectivity for x- and y-polarized incident unit structure (θ=0); (b) Electric and magnetic distributions at two resonant wavelengths for x- and y-polarized incident light (1373 nm and 1630 nm); (c) Electromagnetic multi-pole decomposition for x- and y- polarized incident light; (d) Reflective anomalous intensity and phase for different orientation angles θ at two resonant wavelengths (with left-handed circularly polarized incidence)
式中:u、v表示元胞内纳米柱排列的两个取向主轴;rij表示j偏振入射i偏振出射的反射系数,文中能量反射率表示为R = |r|2。经过圆偏振与线偏振的基矢变换,得到圆偏光反射系数:
上式可以看出反射光的偏振转化分量(即异常分量)相较于入射光分量多了附加相位,其大小为旋转角度θ的2倍(即几何相位)。在左旋光入射条件下,通过改变元胞内的纳米柱取向角θ,在1373 nm和1630 nm两个谐振波长处反射异常圆偏振光的相位和振幅反射率如图2(d)所示。其中反射光的相位随结构取向角度线性变化即
$\varphi = 2\theta $ ,同时保证了45%以上的振幅反射率,这表明所设计的微结构可以用来实现纯相位式的异常反射波前调控。图3(a)和3(b)为利用所设计的具有几何相位特性的微结构阵列实现的异常反射。该阵列的大周期由九个元胞组成,每个元胞中纳米柱排列取向角θ相差20°;这样九个元胞取向角覆盖了0~180°,对应的出射相位覆盖了0~360°。根据广义Snell定律,这样的排列可以实现均匀的相位梯度进而实现异常反射。在理论设计中,1373 nm和1630 nm对应的异常反射角分别为9.75°和11.6°;而通过数值计算测量的异常角分别为9°和11.3°,与理论结果对应,符合广义Snell定律的要求。
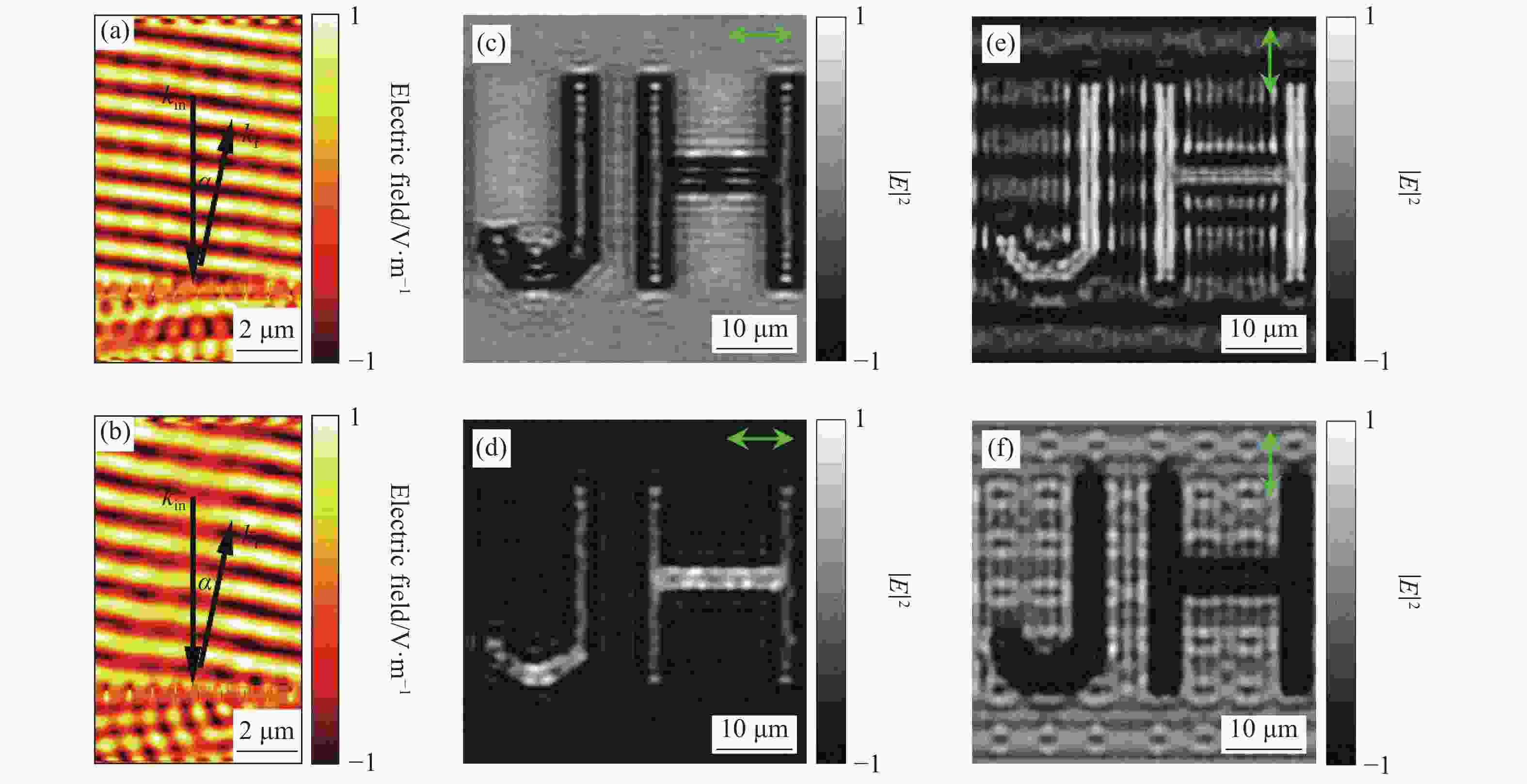
Figure 3. Simulated grayscale imaging and anomalous reflection wavefront manipulation. (a), (b) Anomalous reflection at two resonant wavelengths with a phase gradient array; (c)-(f) Grayscale imaging for dual-wavelength and dual-polarization incidence for the same metasurface sample. The operating wavelength is 1373 nm in (a), (c), (e) and 1630 nm in (b), (d), (f)
所提出超表面设计还可以实现正负的灰度成像技术。由于在进行数值计算时对单个元胞x、y方向采用周期性边界条件,可以视为无限大结构,因此在成像单元的设计中,需要考虑多个元胞实现单一的成像像素元。笔者等在模拟中采用50×50的元胞阵列,通过改变纳米柱的取向,利用偏振光场特性实现明暗分布的像素元,进而使其构成字母“JH”的灰度图像,如图3(c)~3(f)所示。在图像背景处纳米柱取向角θ为0,在字母处纳米柱排列取向角θ为90°。同样采用时域有限差分法(FDTD)进行数值计算,在阵列四周采用完美匹配层(PML)来吸收散射电磁波,使用全场散射光源(TFSF)来保证入射电磁波的平面波特性。当x偏振入射时,由于字母处纳米柱排列取向角为90°,对应的响应波长为1630 nm,所以图3(d)所示的字母位置处反射光的强度大;而字母背景中纳米柱阵列取向角为0,对应图3(c)中背景电场强度大。当y偏振入射时,强度分布刚好相反。由于元胞排列取向对波长和偏振光响应不同,因此产生了双波长双偏振态的正负灰度成像。
文中利用大高宽比的两个亚波长非晶硅柱,通过硅柱间的微小间距产生了较强的电磁多极谐振。进而利用微结构在x、y方向明显的不对称性,实现了双频带、双偏振态的谐振,获得了x偏振入射时1373 nm的强反射和y偏振入射时1630 nm的强反射。通过分析微结构近场的电磁多极谐振展开,对不同谐振的内在机理进行了分析。利用微结构偏振响应的各向异性,通过对微结构进行胞内旋转实现了几何相位,进而实现了反射式双带异常反射,验证了与广义Snell定律的一致性。同时,利用不同取向角的微结构在不同偏振态和不同入射波长下反射强度不同的特性,实现了双频带、双偏振态的多功能正负灰度成像设计。文中所提出的超表面,对于新型多功能超表面的开发以及基于多维度光场联合调控技术的发展具有一定推动作用。
Dual-wavelength and dual-polarization wavefront manipulation based on dielectric metasurfaces
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20211027
- Received Date: 2021-02-01
- Rev Recd Date: 2021-04-02
- Publish Date: 2021-05-21
-
Key words:
- metasurface /
- polarization state /
- dual-wavelength /
- multifunction /
- wavefront manipulation
Abstract: With the development of nano fabrication technology, metasurfaces have shown unprecedented advantages over traditional optical designs in controlling electromagnetic waves at subwavelength scale. A dual-wavelength metasurface operating in two orthogonal polarization states based on the dielectric silicon nanopillars was proposed. The metasurface could realize anomalous reflective wavefront manipulation via the geometric phase gradient resulting from the reflection anisotropy for different incident polarizations. The proposed design also achieved positive and negative grayscale imaging arrays for dual-polarization and dual-wavelength incidence. This approach paves the way for integrated multifunctional photonic technologies based on metasurfaces.











 DownLoad:
DownLoad: