-
自1995年Refrecereer和Javidi提出双随机相位光学图像加密系统以来[1],光学图像加密技术得到了迅速发展[2-5]。许多改进的光学图像加密系统不断被提出,例如基于菲涅耳变换的加密系统[6]、基于数字全息的加密系统[7-8]、基于压缩感知的加密系统[9-10]、基于混沌的加密系统[11-12]和基于偏振的加密系统[13-14]。其中最具代表性的是Nomura和Javidi于2000年提出的基于联合变换相关器(JTC)的光学图像加密系统,由于其结构简单,不需要制作复共轭相位密钥,加密结果是一个振幅型的联合功率谱图像,便于记录和传输,因此成为研究热点[15-18]。然而,JTC图像加密系统也存在严重缺陷,一是解密图像质量差,存在严重的噪声,二是线性JTC图像加密系统安全性差,易被攻击。为了提高解密图像的质量,G-S算法和基于模糊控制理论的迭代算法(IAFC)[19-20]被引入,用于设计随机相位密钥,使傅里叶频谱尽可能均匀来降低噪声。但此类方法需要复杂的数学迭代运算和编程。为了提高JTC加密系统的安全性,像素置乱技术和分数傅里叶变换技术被引入,安全性提高但系统的复杂性也随之增加,且噪声问题仍未解决,解密图像质量较差。近年来,随着大数据技术的飞速发展和信息传输能力的提高,传统的单幅图像加密技术已经不能满足日益增长的信息需求。因此,光学多图像加密技术已成为研究热点之一[21-24]。由于JTC系统在信息加密方面的突出特点,基于JTC系统的多图像加密方法也被提出。例如Tebaldi在JTC结构中利用波长复用技术实现了多图像光学加密[25]。Qin等人提出了一种利用相位密钥旋转复用技术的JTC系统多图像加密方法[26]。然而,JTC系统固有的噪声问题以及多图像之间的串扰问题都没有解决。计算全息技术具有操作灵活、重复性高和大容量等特性,且本身具有一定的加密性质,并能通过二维计算全息图实现三维信息的维度压缩,具有更容易保存、传输和重建三维场景的优势,成为图像信息加密领域研究的热点。例如基于计算全息和随机相位编码的三维信息加密方法[27]、基于计算全息和混沌的彩色图像加密方法等[28]。
针对JTC加密系统的固有噪声问题和安全性低的问题,文中将计算全息技术引入JTC系统,提出一种基于计算全息图(CGH)和频移的JTC系统多图像光学加密方法,将CGH引入JTC光学图像加密系统,在解决其噪声和安全性问题的同时,提高系统加密效率。首先多个不同类型和尺寸的图像被随机相位和和傅里叶变换,然后傅里叶频谱经过频移相位调制后叠加并编码为二元实值计算全息图。之后在JTC图像加密系统中对二进制实值加密CGH进行加密,联合功率谱作为最终的加密图像。在解密过程中,首先在4F解密系统中获得带有噪声的二进制实值CGH,然后通过数字图像处理去噪方法或手动去噪方法进行二元实值CGH的降噪复原,最后经过正确光学密钥调制和傅里叶变换可以获得多幅解密图像。因此,将CGH和频移技术引入JTC图像加密系统中,解决了其固有的噪声问题,极大地提高了其安全性和加密效率,可实现多个不同类型和尺寸图像的并行加密,不存在图像之间的串扰。因此,该研究在网络安全和信息保护方面具有一定的应用前景和实用价值。
-
待加密图像如图1所示,其中图1(a)和(b)为两幅单个汉字的二值图像,尺寸为128×128 pixel;图1(c)为一幅英文单词二值图像,图1(d)为一幅灰度图像,它们的尺寸为128×256 pixel;图1(e)为一幅2 bit量化的灰度图像,尺寸为256×128 pixel;图1(f)为一幅二维码图像,图1(g)为一幅灰度图像,它们的尺寸为256×256 pixel。
文中多个图像加密分为两步完成,第一步为随机相位和频移相位调制及计算全息编码,加密过程如图2所示。
假设待加密图像为
${{o}}_{i}(x,y)$ ,其中$ i $ 的取值为1~7,首先待加密图像经过第一个随机相位${{{p}}_{1 i}}(x,y)$ 调制,${{{p}}_{1 i}}(x,y) = {\text{exp}}[j2\pi \times {\rm{rand}}(x,y)]$ ,其中$ {\rm{rand}}(x,y) $ 表示0~1的随机分布。然后经过傅里叶变换之后的频谱分布为:式中:
${{FT}}[ · ]$ 表示傅里叶变换;$ {{{o}}_i}{\text{(}}\xi ,\eta {\text{)}} $ 为频谱;$ {{{N}}_i}{\text{(}}\xi ,\eta {\text{)}} $ 为相位。利用傅里叶变换的频移特性,各个频谱被频移相位调制后叠加,叠加后的频谱分布可表示为:式中:
$ {{s}}{{{p}}_{1 i}}(\xi ,\eta ) $ 表示每个图像的频移相位。可表示为:该多图像加密方法可以实现多个图像的并行加密和解密,这里以加密七个不同类型和尺寸的图像为例验证该方法的可行性和有效性。根据待加密图像的尺寸和位置,
$ ({a_i},{b_i}) $ 的取值分别为$ ( - 0.375,\; - 0.375) $ ,$ ( - 0.125,\; - 0.375) $ ,$ ( - 0.375,\;0) $ ,$ ( - 0.125,\;0) $ ,$ ( - 0.25,\; 0.375) $ ,$ (0.25,\; - 0.25) $ 和$ (0.25,\;0.25) $ 。经过第二个随机相位调制后的光场为:最后利用罗曼型迂回相位编码方法将公式(4)表示的光场编码为二元实值CGH,编码结果如图3所示[23]。
由图3可见,七幅不同类型和尺寸的待加密图像经过频移和计算全息编码成为单幅二元实值CGH,隐藏了所有原始图像的全部信息。此外,罗曼型迂回相位编码的CGH具有很强的抗噪性能,使其能够应对JTC加密系统的固有噪声问题。下一步是CGH在改进的JTC系统中进行加密,加密系统如图4所示。
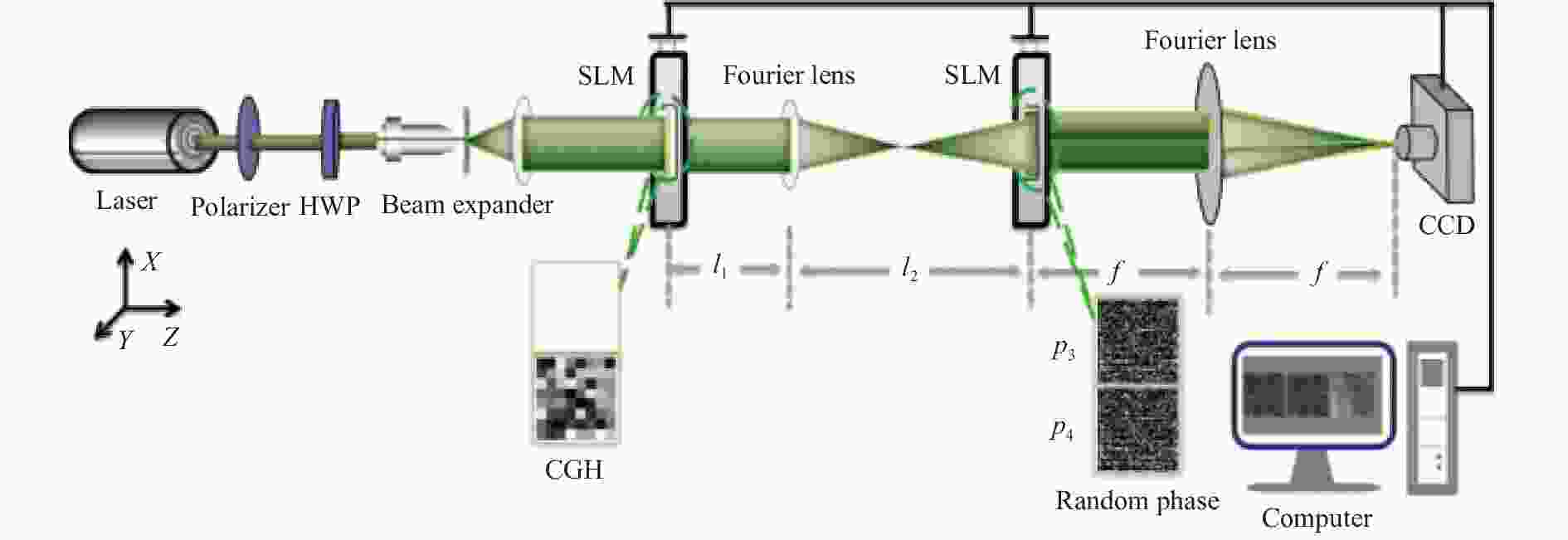
在加密系统中,一个空间光调制器(SLM)经过一个透镜成像于第二个SLM,物像距与两个SLM的像素尺寸匹配。第二个SLM分为两部分,分别加载随机相位
${{{p}}_3}(\xi ,\eta )$ 和${{{p}}_4}(\xi ,\eta )$ ,第一个SLM加载的CGH成像于${{{p}}_3}(\xi ,\eta )$ ,最后经过一次傅里叶变换,联合功率谱被CCD接收为加密结果图像,加密结果可表示为:式中:b为两个随机相位
${{{p}}_3}(\xi ,\eta )$ 和${{{p}}_4}(\xi ,\eta )$ 到光轴(SLM中心)的距离;$( · ) * ( ·)$ 表示卷积运算;${(·)^ * }$ 表示复共轭;$ {{c}}(u,v) $ 、$ {d_3}(u,v) $ 和$ {e_4}(u,v) $ 分别为${{c}}(\xi ,\eta )$ 、${{{p}}_3}(\xi ,\eta )$ 和${{{p}}_4}(\xi ,\eta )$ 的傅里叶变换。 -
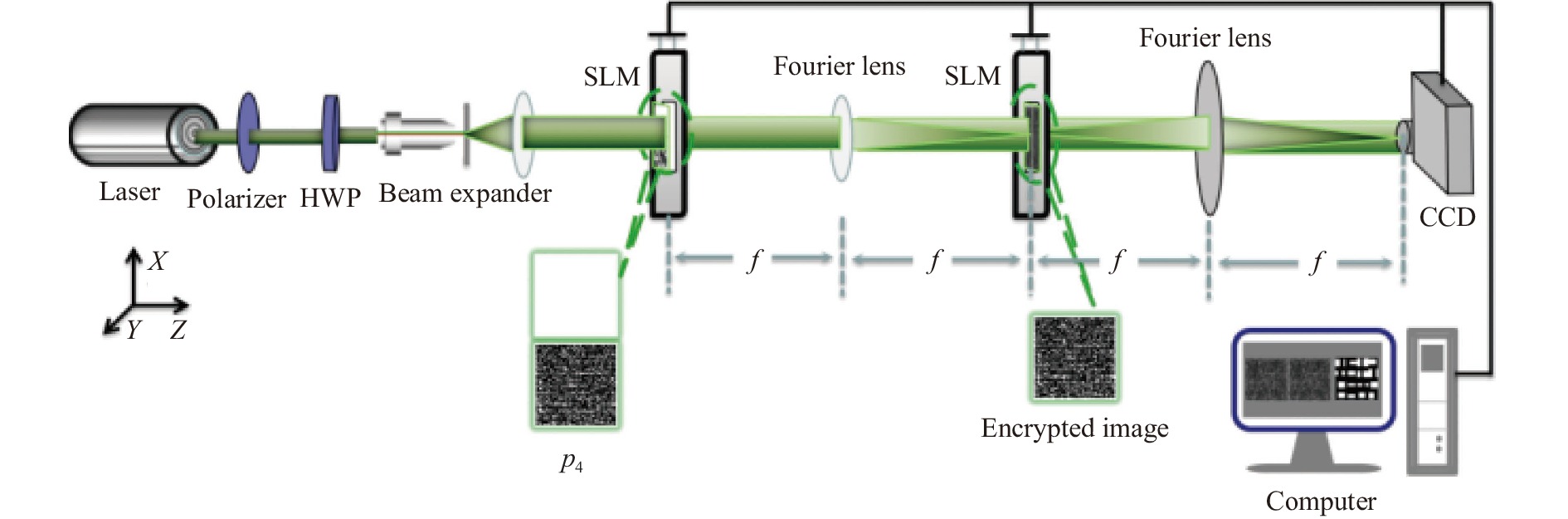
第一步的4F解密系统如图5所示,其中随机相位密钥
$ {{{p}}_4}(\xi ,\eta ) $ 仍然加载到置于输入平面的SLM中$ ( - b,\;0) $ 处,加密图像${{I}}(u,v{\text{)}}$ 则加载到置于频谱面的SLM中$ ({\text{0}},\;0) $ 处。第二个SLM出射的光场分布可表示为:其中,第三项经过傅里叶变换被CCD接收,即为CGH解密图像:
但在实际JTC加密系统中,密钥模板面积有限,为一截断纯相位模板,因此其傅里叶谱不可能是一纯相位函数,即随机相位密钥功率谱
$ {\left| {{{{e}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(}}u,v{\text{)}}} \right|^2} \ne 1 $ ,公式(6)应修改为:所以公式(8)中第三项被CCD接收的解密图像可表示为:
式中:
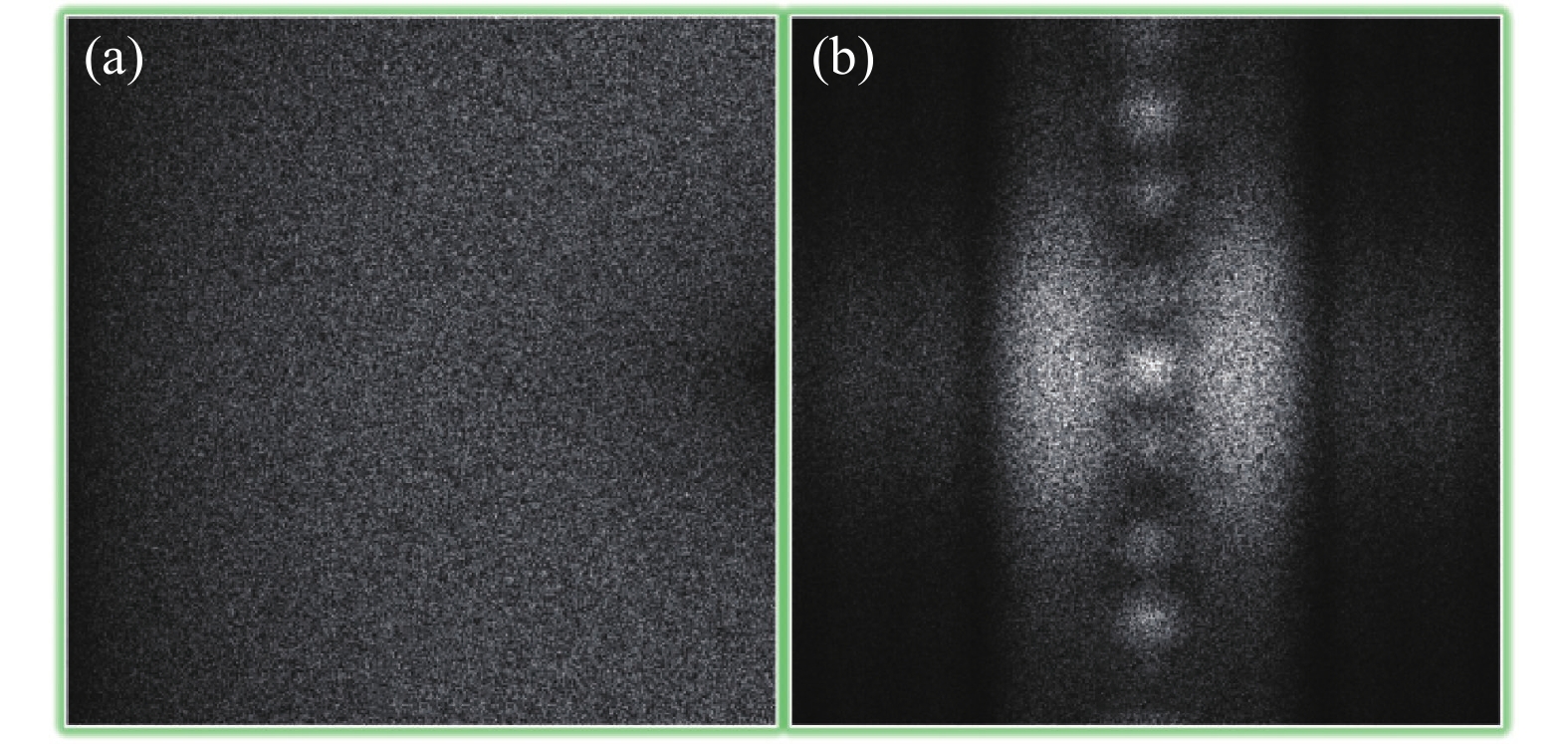
$( · ) \otimes ( · )$ 表示相关。由公式(9)可见,解密图像为CGH和随机相位密钥相关函数的卷积,解密图像中含有严重噪声,不能完全恢复出CGH,解密结果图像如图6(a)所示,这也是JTC加密系统的固有缺陷。在文中的加密方法中,JTC加密系统的图像为二元实值CGH,具有极强的抗噪性能,通过数字图像处理(按编码单元寻矩形开孔)去噪方法或手动去噪方法,以及深度学习去噪方法都可恢复CGH,准确率皆超过98%。去噪CGH如图6(b)所示,可见CGH的引入能够克服JTC图像加密系统的固有噪声问题。解密过程第二步为CGH调制再现,解密光学系统如图7所示,SLM分为两个区域,分别加载CGH和随机相位密钥
${{p}}_{2}(\xi ,\eta )$ ,两个区域通过一个4F成像系统连接,相当于密钥${{p}}_{2}(\xi ,\eta )$ 紧贴CGH放置。在该过程中,随机相位密钥${{p}}_{2}(\xi ,\eta )$ 需要编码为与CGH加密图像同尺寸的相位图,单个编码单元的尺寸也相同。因为同一个SLM的像素完全相同,编码单元与编码单元的对准方式降低了像素对准的难度[23],然后${{p}}_{2}(\xi ,\eta )$ 调制的CGH经过一次傅里叶变换完成再现,最后解密图像被CCD接收。CGH经过随机相位密钥
${{p}}_{2}(\xi ,\eta )$ 调制后的频谱表示为:+1级频谱的强度:
被CCD接收,可见七幅原始图像可被解密获得,解密结果如图8所示。
由图8可见,当密钥正确时,七幅不同类型和尺寸的原始图像能够被并行解密获得,且七幅图像之间不存在串扰问题。文中的罗曼型迂回相位编码单元为7×7 pixel,导致CGH再现的解密结果也是7×7重复单元分布,每个单元包含七幅解密图像。每一幅解密图像的位置由频移相位中的
$ ({a_i},{b_i}) $ 控制,如果$ ({a_i},{b_i}) $ 太大,解密结果图像会与其他单元重叠,因此该方法的加密容量和编码单元与CGH加密结果的尺寸有关。由公式(10)和(11)所示,+1级、+2级和+3级衍射图像为正确解密结果,但解密图像受到CGH采样和量化编码误差影响,存在一定噪声,且CGH衍射级次越大,噪声越大,因此,+1级解密图像质量最佳。该噪声可通过增加CGH编码单元的尺寸来降低。因此,文中提出的多图像加密方法实现了多个不同类型和尺寸的图像的并行加密和解密。 -
为了验证文中提出多图像加密方法的安全性和有效性,引入相关系数(cc)来评估原始图像和解密图像之间的相似性。相关系数的计算公式如下:
式中:
$ {{\bar {{o}}}} $ 和$ {{\bar {{o}}'}} $ 分别表示$ {{\bar {{o}}(x,y)}} $ 和$ {{\bar {{o}}'}}(x,y{{)}} $ 的平均值。当所有密钥正确时(如图8所示),原始图像和解密结果的cc值分别为0.9484、0.9471、0.9398、0.9481、0.8682、0.9247和0.8519,可见解密效果良好,获得了高质量的解密图像。同时,在解密过程中,当随机相位密钥${{p}}_{2}(\xi ,\eta )$ 和${{{p}}_4}(u,v)$ 错误时的解密结果如图9(a)和(b)所示。显然,当随机相位密钥错误时,七幅原始图像的任何信息无法获得,在这种情况下,七幅解密图像的cc值都小于0.02。由图9可见,将CGH引入JTC加密系统后,双重密钥极大地提高了多图像加密系统的安全性,解决了JTC系统的安全性问题。
-
文中提出了一种基于计算全息和频移的JTC系统多图像光学加密方法,实现了多幅不同类型、不同尺寸图像的并行加密和解密,解决了JTC图像加密系统的固有噪声和安全性问题,同时提高了系统加密效率。因此,文中提出的多图像光学加密方法在信息安全领域具有广阔的应用前景。
Multi-image optical encryption method of JTC system combining CGH and frequency shift
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220175
- Received Date: 2022-03-13
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-04-05
- Publish Date: 2022-06-08
-
Key words:
- optical image encryption /
- information security /
- computer generated hologram (CGH) /
- JTC system
Abstract: In order to improve the practicability of JTC optical image encryption system, solve its noise problem, improve its encryption efficiency and security, a multi-image optical encryption method based on computer generated hologram (CGH) and the frequency shift of Fourier transform was proposed. Firstly, each image with different size and type was modulated by random phase and Fourier transform, then the frequency spectrum of multiple images was modulated by frequency-shift phase and superimposed to be encoded into binary real-value CGH, finally the CGH was encrypted into joint power spectrum by JTC optical image encryption system. In the decryption process, the encrypted image was decrypted by 4F system to obtain the CGH. The binary real-value CGH has strong noise resistance to eliminate the effects of noise. Then, multiple decrypted images can be obtained after Fourier transform. Simulation results show that the proposed method can encrypt and decrypt multiple images of different sizes and types in parallel, and has high encryption efficiency. Meanwhile, multiple images with mutual keys and double optical keys ensure the security of the encryption system.



































































 DownLoad:
DownLoad: