-
在自由空间通信领域中,空间激光通信具有小型、传输码率高、保密性强等优点,美国[1−2]、欧空局[3]、日本宇航探索局(JAXA)[4]都对其进行了大量的研究,使得该技术得到了快速发展。2011年和2013年,长春理工大学分别进行了机载激光通信试验。
2016 年,世界首颗量子科学实验卫星“墨子号”发射成功,卫星上搭载了激光相干通信机载荷以实现星地高速通信[5−6],实现了国际首次星地量子密钥分发、千公里级量子纠缠分发以及地星量子隐形传态实验验证。在量子通信(如量子密钥分配、量子纠缠分配和量子隐形传态)中,信息被附加到单光子的偏振态,传输的光子被操纵成特定的偏振方向进行传输和解码[7],需在发射机和接收机之间建立有效、稳定的量子通道链接来提高信道效率和降低量子比特错误率[8]。
在图1所示的量子密钥通信机光学系统[7]中,基于卫星的纠缠分配(810 nm)、高速星地量子密钥分配(850 nm)以及地对星量子隐形传态(780 nm)、闭环精细跟踪(671 nm)和下行链路同步光脉冲(1550 nm)等量子光的入射角分别为10°、35°、22.5°和45°。
量子光在光学系统传输过程中会经过各种不同功能的光学元件,这些光学薄膜元件的极化性能直接影响量子通信终端的总体性能。当量子光倾斜入射时,光学薄膜中P光和S光的有效折射率不一致,从而会引起能量分离,且角度越大,分离越大。该情况下不仅会导致能量损失,而且会因为光学薄膜的偏振分离诱发偏振像差[9−11],还会产生位相差,使得量子通信误码率提高。因此,需对光学系统中涉及到的光学薄膜元件进行位相调控。针对这一应用需求,许多研究人员对位相调控开展了研究[12−13]。
段微波、余德明等人成功研制了金属保偏反射镜[14−15],其在45°入射下,810 nm和850 nm通道处反射率大于98%,消光比达10000∶1,并对其进行了原子氧模拟实验,研究了保偏反射镜的空间适应性。马冲等人成功研制了保偏分色片[16−17],在22.5°入射下,780 nm处透过率大于94%,810 nm处透过率小于3%,消光比达3000∶1。潘永刚等人研制了45°入射时,1500~1600 nm 波段消偏振平均透射/反射比为 8.5∶91.5,在1530、1540、1550、1560 nm进行位相控制的分光膜[18]。新一代中高轨量子通信终端与“墨子号”相比,其偏振保持的角度范围和谱段更宽。在已报道的文献中,位相调控薄膜元件多是在单一入射角度(如10°、22.5°、35°和45°)下进行设计与研制,已不满足新一代中高轨量子通信光机系统的使用要求。目前,关于宽工作角度位相调控反射镜的研究鲜有报道,因此,开展此类薄膜元件的研究,对其在下一代中高轨量子通信系统中的工程应用具有重要意义。
-
高反射率介质反射镜的设计,通常可以采用两种不同折射率的膜层交替实现,从膜系界面上反射的光束因具有相同位相,会发生相长干涉,可以获得很高的反射率[19]。因此,可以采用H和L两种高、低折射率的材料,周期性地叠加作为膜系结构,比如:(H L)^n,n的取值越高则反射率越高。考虑实际镀膜过程中存在膜层的吸收和散射,设计时必须选择合适的膜系层数来实现高反射率。
这样的初始结构较容易实现相应波段的高反射率,但却无法避免P光和S光在宽角度入射下位相差过大的现象。利用等效多层膜理论:对于以中间一层为中心,两边对称安置的多层膜,却具有单层膜特征矩阵的所有特点,推广到任意多层膜组成对称膜系,最终又形成一个等效单层膜[20−21],改变膜系层数和厚度,以获得不同的等效折射率和等效位相,以实现位相调控的目的。
根据以上原理,设计方法如下:选择两种不同折射率材料,H、L分别代表高、低折射率材料,(H L)^n作为基本膜系结构,设计波长以截止带中心位置处于信号通道为准,在基本膜系结构外层加d1L d2H d3L或d1H d2L d3H等效多层位相调控层,考虑初始膜系结构为 G|(H L)^14 |d1H d2L d3H d4L d5H d6L d7H d8L|Air,其中G为基底(石英),Air为空气,d1~d8代表膜层的厚度系数,为非规整位相调控膜层。根据任务指标设定优化目标,采用Global Modified LM或Global Simplex等优化方法进行优化迭代,优化d1~d8,以获得最佳设计结果。
-
反射镜根据系统应用要求,技术指标如表1所示。
Technical index Value Target wavelength/nm 780 Range of incidence angle/(°) 45±7.5 Reflectance ≥99% Phase difference/(°) ≤3 Table 1. Technical index of mirror
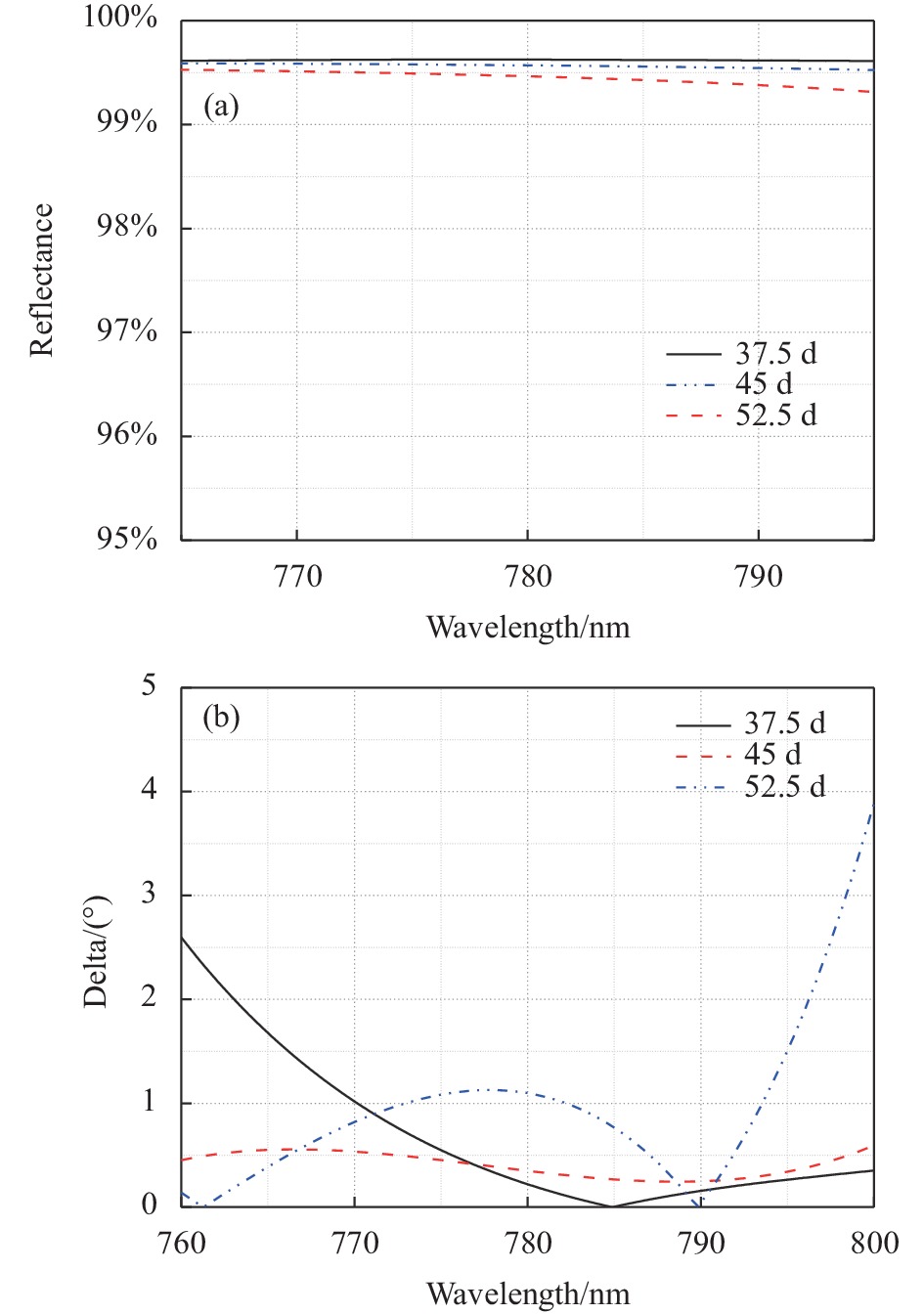
根据上述设计思想,选择薄膜材料时需综合考虑反射镜的工作波段,考察薄膜材料的透明区、折射率、吸收系数及基底和薄膜材料之间的应力匹配、牢固度等因素[22−23]。为此,选择Nb2O5(H)和SiO2(L)作为高、低折射率材料。初始膜系结构为G|(HL)^14 d1H d2L d3H d4L d5H d6L d7H d8L|Air,设计波长890 nm,H的折射率为2.22@890 nm,L的折射率为1.44@890 nm。将初始膜系结构代入光学薄膜设计软件Filmwizard,在优化目标设定时,按照任务要求,分别在37.5°、45°和52.5°三个角度下设置优化目标参数,使得优化结果可以满足入射范围45°±7.5°的任务要求。优化目标设定780 nm处反射率>99%,位相差<3°。通过不断优化每层薄膜的厚度系数,以实现评价函数最小、光谱性能最佳的结果。最终设计结果为:(H L)^14 0.231 H 0.935 L 1 H 1.15 L 1.122 H 1.043 L 1.051 H 0.907 L,设计波长890 nm。设计结果如图2所示。

Figure 2. Reflectance design curve (a) and phase difference design curve (b) of phase control mirror
Incidence angle/(°) Reflectance Phase difference/(°) 37.5 99.62% 0.22 45 99.57% 0.34 52.5 99.46% 1.09 Table 2. Design result of reflectance and phase difference at target wavelength (780 nm)
从表2可以看出,设计能达到预期目标,在目标波长处,45°±7.5°入射范围内实现了99.4%以上的高反射率,且位相差控制在1.1°以内。虽然从图2(b)中可以看出位相差最佳位置在790 nm处,但在大于790 nm时,52.5°入射下位相差急剧变化。考虑研制时不可避免的工艺误差,实际光谱位置会有偏差,结合光谱定位容差考虑,该设计结果是合理可行的。
-
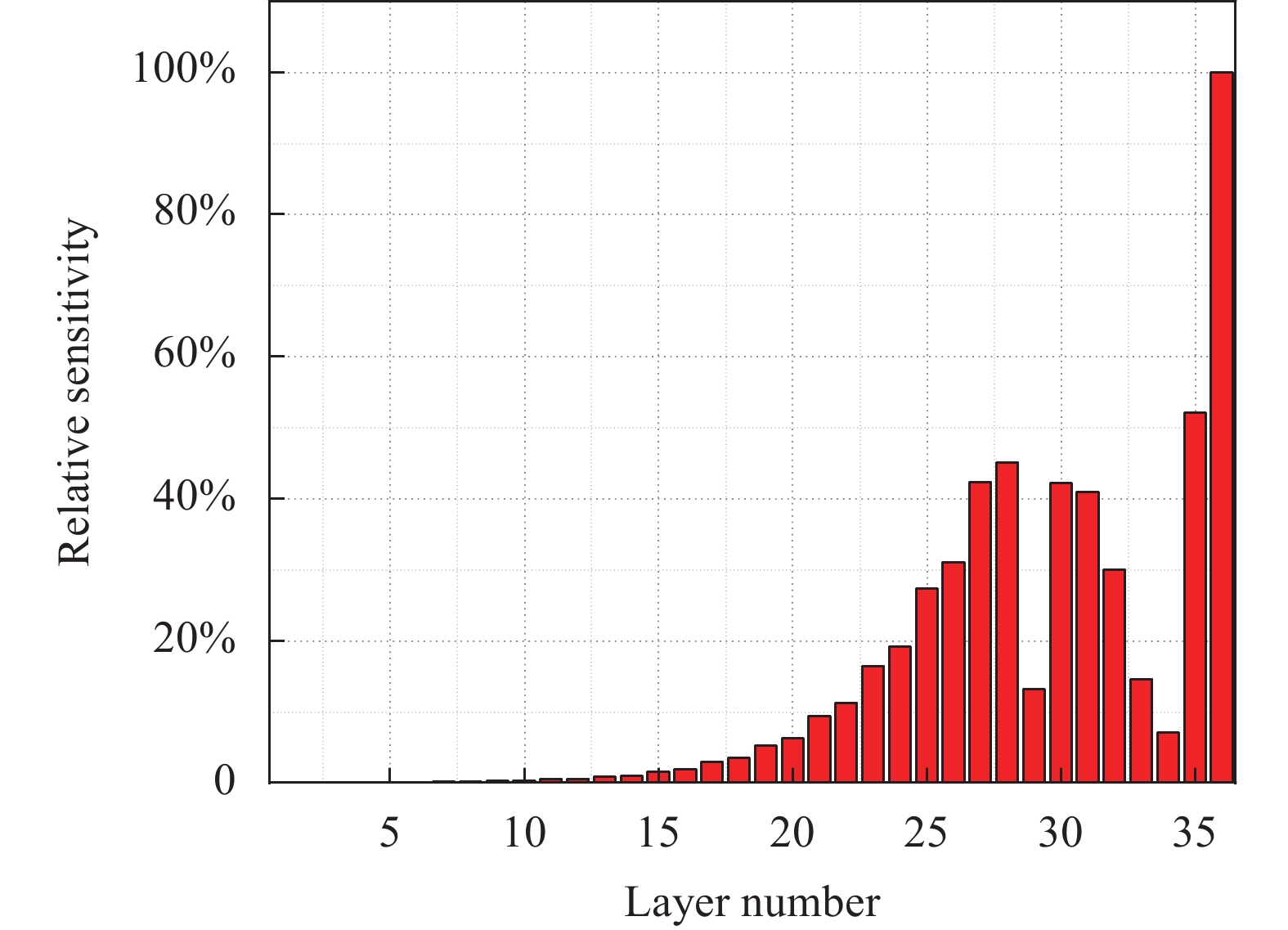
设计膜系的最后八层为非规整膜系,对监控精度要求很高。为此,利用Optilayer对设计膜系进行了膜层误差引起光谱变化的灵敏度分析。
如图3所示,膜系最外层的灵敏度较大,在研制过程中需要进行精确控制。对位相调控膜系引入1%的随机误差,做进一步分析,观察其对位相差的影响,引入误差后的位相差曲线如图4所示。从表3看出,在37.5°、45°和52.5°三个角度下,780 nm处的位相差小于2.5°,可以满足反射镜需将位相差控制在3°以内的任务要求。因此,可以依据上述设计膜系开展实际的研制工作。

Figure 4. Phase difference error analysis curves under 37.5° incidence (a), 45° incidence (b), 52.5° incidence (c)
Incidence angle/(°) Error +1% Error 0% Error −1% 37.5 0.51 0.22 0.017 45 1.326 0.34 0.654 52.5 2.14 1.09 0.291 Table 3. Phase difference error analysis at target wavelength (780 nm)
-
该反射镜的制备是在德国莱宝公司生产的Lab900-plus型真空镀膜机上完成的,设备配有两把e型电子枪,SiO2采用环形坩埚,Nb2O5采用七穴坩埚。同时,配有四探头石英晶振物理厚度控制系统、OMS5100光学自动控制系统和栅网口径为12 cm的Veeco射频(RF)离子源。样品为Φ50×5 mm的石英基片,研制时参考量子卫星保偏金属反射镜研制工艺参数[14−15],具体如下:当真空到达6×10−2 Pa时,打开工件旋转,设定烘烤温度为200 ℃,保温2 h,真空到达2×10−3 Pa时,打开离子源,充入O2 后进行离子辅助薄膜沉积。工艺参数如表4所示。
Parameter Value Nb2O5 SiO2 Rate/nm·s−1 0.15 0.8 EB oxygenation/sccm 40 30 RF bias voltage/V 600 600 RF discharged current/mA 500 500 Background pressure/Pa 2×10−3 2×10−3 Baking temperature/℃ 200 200 Table 4. Deposition process parameters
在研制过程中,首先尝试使用光学极值百分比监控策略 (POEM)进行29~36非规整膜层的监控,但效果并不理想。分析其原因,当采用该监控策略时,监控波长选择时需尽可能使监控停止位置距离下一个极值点保持4%×(Tmax−Tmin) 以上距离[24],以减小监控误差。结合设计膜系,因为29层厚度较薄,导致部分膜层未能找到合适的监控波长,使其判停点处于4%×(Tmax−Tmin)区间,因此产生镀制误差。而与此同时,对坩埚材料蒸发消耗量变化、晶振参数修正等方面进行膜厚分析及改进后,提高了晶振控制的精度,通过实验结果发现,29~36层采用晶振监控方式研制出的位相调控反射镜可满足任务要求。因此,最终选择1~28层光学监控、29~36层晶振监控的监控方式。
-
反射镜的反射率光谱曲线是在美国 PE 公司生产的 Lamda900型分光光度计上完成的,其配有V-W反射率测试附件,可以进行30°~60°入射下的反射率测试;位相差测试是在美国J. A. WOOLLAM 公司生产的 VASE-32可见近红外椭偏仪上完成的,其可以进行15°~90°入射下的位相差测试,测试原理如图5所示。
式中:$\psi $和Δ为椭偏仪能够测量的样品椭偏参数,tan$\psi $为反射光P光与S光的振幅比,Δ为P光与S光的位相差。测试结果如图6所示。
Incidence angle/(°) Reflectance Phase difference/(°) 37.5 99.60% 0.46 45 99.47% 0.36 52.5 99.36% 2.83 Table 5. Test result of reflectance and phase difference at target wavelength (780 nm)
研制结果如表5所示,反射镜在入射角度为37.5°、45°和52.5°时,780 nm处反射率大于99.3%,且位相差小于3°,满足任务要求。
最终研制的反射镜其反射率曲线和位相差虽然都满足任务要求,但与设计结果存在一定的差异。主要是由以下两个原因造成的:1) 非规整膜层监控有误差,导致制备结果出现偏差;2)研制时所用监控参比片和试验件厚度为1 mm,与正式产品厚度的5 mm差异较大,导致薄膜沉积后性能产生偏差。
-
按照航天产品环境模拟实验要求,对反射镜进行了可靠性及牢固度实验,实验结果见表6。实验项目如下[15]。
1) 附着力实验:采样标准聚酯胶带紧贴样品膜层表面,沿膜层表面垂直拉起,观察膜层是否脱落。
2) 浸泡实验:在45±1 ℃ 的水中浸泡8 h,观察膜层是否脱落。
3) 温度交变实验:在50±1 ℃环境中保持 1 h,然后在−25±1 ℃ 环境中保持1 h,循环三次,观察膜层是否脱落。
4) 湿热实验:在相对湿度 95% 、温度45±2 ℃的大气中保持24 h,观察膜层是否脱落。
Experiment Result Adhesion experiment Pass Soaking experiment (45±1 ℃) Pass High (50±1 ℃) and low (−25±1 ℃) temperature experiment Pass Temperature (45±2 ℃) and humidity (95%) experiment Pass Table 6. Reliability and durability results of mirror
-
宽角度位相调控反射镜选用Nb2O5和SiO2分别作为高、低折射率薄膜材料,以石英为基底,采用介质反射膜堆加非规整位相调控膜作为初始膜系,使用Global Modified LM或Global Simplex等优化方法进行优化,设计了一种宽角度范围内具有高反射率且位相差可调控的反射镜。在德国莱宝Lab900-plus设备上,采用电子束蒸发结合RF射频源进行离子辅助的方式,进行薄膜沉积,通过光学监控和晶振监控相结合的监控方法,成功研制了该反射镜。研制结果显示,在780 nm处、入射角范围为45°±7.5°内,其反射率大于99.3%,位相差控制在3°以内,反射镜通过了环境模拟的可靠性及牢固度实验,为该类薄膜元件在下一代中高轨量子通信中的应用打下了坚实的基础,如何保证其空间环境的长寿命是下一阶段研制工作的重点。
Design and fabrication of wide angle phase control mirror
doi: 10.3788/IRLA20230721
- Received Date: 2023-12-27
- Rev Recd Date: 2024-02-06
- Publish Date: 2024-04-25
-
Key words:
- optical thin film /
- phase control /
- mirror /
- polarization /
- wide angle
Abstract:














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: